Abstract
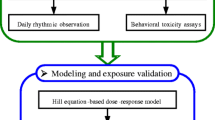
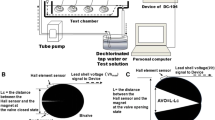
Arsenic (As) is the element of greatest ecotoxicological concern in aquatic environments. Effective monitoring and diagnosis of As pollution via a biological early warning system is a great challenge for As-affected regions. The purpose of this study was to synthesize water chemistry-based bioavailability and valve daily rhythm in Corbicula fluminea to design a biomonitoring system for detecting waterborne As. We integrated valve daily rhythm dynamic patterns and water chemistry-based Hill dose–response model to build into a programmatic mechanism of inductance-based valvometry technique for providing a rapid and cost-effective dynamic detection system. A LabVIEW graphic control program in a personal computer was employed to demonstrate completely the functional presentation of the present dynamic system. We verified the simulated dissolved As concentrations based on the valve daily rhythm behavior with published experimental data. Generally, the performance of this proposed biomonitoring system demonstrates fairly good applicability to detect waterborne As concentrations when the field As concentrations are less than 1 mg L−1. We also revealed that the detection times were dependent on As exposure concentrations. This biomonitoring system could particularly provide real-time transmitted information on the waterborne As activity under various aquatic environments. This parsimonious C. fluminea valve rhythm behavior-based real-time biomonitoring system presents a valuable effort to promote the automated biomonitoring and offers early warnings on potential ecotoxicological risks in regions with elevated As exposure concentrations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock S, Barcelo D, Hansen PD (2003) Monitoring freshwater sediments. Biosens Bioelectron 18:1077–1083
Anestis A, Lazou A, Pörtner HO, Michaelidis B (2007) Behavioral, metabolic, and molecular stress responses of marine bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis during long-term acclimation at increasing ambient temperature. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R911–R921
Bacci JP, Showers WJ, Levine JF, Usry B (2008) Valve gape response to turbidity in two freshwater bivalves (Corbicula fluminea and Lampsilis radiate). J Freshw Ecol 23:479–483
Bakhmet IN, Khalaman VV (2006) Heart rate variation patterns in some representatives of bivalvia. Biol Bull 33:276–280
Bonnard M, Romeo M, Amiard-Triquet C (2009) Effects of copper on the burrowing behavior of estuarine and coastal invertebrates, the Polychaete Nereis diversicolor and the bivalve Scrobicularia plana. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 15:11–26
Chambon C, Legeay A, Durrieu G, Gonzalez P, Ciret P, Massabuau JC (2007) Influence of the parasite worm Polydora sp. on the behavior of the oyster Crassostrea gigas: a study of the respiratory impact and associated oxidative stress. Mar Biol 152:329–338
Chen WY, Liao CM, Jou LJ, Jau SF (2010) Predicting bioavailability and bioaccumulation of arsenic by freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea using valve daily activity. Environ Monit Assess 169:647–659
Cherry DS, Soucek DJ (2006) Case study: comparison of Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea) in situ testing to several nontarget test organism responses to biocidal dosing at a nuclear power plant. In: Farris JL, van Hassel JH (eds) Freshwater bivalve ecotoxicology. CRC Press, New York, pp 285–310
Fdil MA, Mouabad A, Outzourhit A, Benhra A, Maarouf A, Pihan JC (2006) Valve movement response of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to metals (Cu, Hg, Cd and Zn) and phosphate industry effluents from Moroccan Atlantic coast. Ecotoxicology 15:447–486
Fergusion JF, Gavis J (1972) A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res 6:1259–1274
Gerhardt A, de Bisthoven LJ, Soares AMV (2005) Evidence for the stepwise stress model: Gambusia holbrooki and Daphnia magna under acid mine drainage and acidified reference water stress. Environ Sci Technol 39:4150–4158
Gerhardt A, Ingram MK, Kang IJ, Ulitzur S (2006) In situ on-line toxicity biomonitoring in water: recent developments. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2263–2271
Gnyubbkin VF (2010) The circadian rhythms of valve movements in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Russ J Mar Biol 36:419–428
Hansen PD (2008) Biosensors and ecotoxicology. Eng Life Sci 8:26–31
Huang YK, Lin KH, Chen HW, Chang CC, Liu CW, Yang MH, Hsueh YM (2003) Arsenic species contents that aquaculture farm and in farmed mouthbreeder (Oreochromis mossambicus) in blackfoot disease hyperendemic areas. Food Chem Toxicol 41:1491–1500
Jou LJ, Chen WY, Liao CM (2009) Online detection of waterborne bioavailable copper by valve daily rhythms in freshwater clam Corbicula flumines. Environ Monit Assess 155:257–272
Kadar E, Salanki J, Jugdaohsingh R, Powell JJ, McCrohan CR, White KN (2001) Avoidance responses to aluminium in the freshwater bivalve Anodonta cygnea. Aquat Toxicol 55:137–148
Liao CM, Chen BC, Singh S, Lin MC, Han BC (2003) Acute toxicity and bioaccumulation of arsenic in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus from blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Environ Toxicol 18:252–259
Liao CM, Jau SF, Chen WY, Lin CM, Jou LJ, Liu CW, Liao VHC, Chang FJ (2008) Acute toxicity and bioaccumulation of arsenic in freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea. Environ Toxicol 23:702–711
Liao CM, Jau SF, Lin CM, Jou LJ, Liu CW, Liao VHC, Chang FJ (2009) Valve movement response of freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea following exposure to waterborne arsenic. Ecotoxicology 18:567–576
Lin MC, Liao CM, Liu CW, Singh S (2001) Bioaccumulation of arsenic in aquaculture large-scale mullet Liza macrolepis from blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 67:91–97
Lin MC, Lin HY, Cheng HH, Chen YC, Liao CM, Shao KT (2005) Risk assessment of arsenic exposure from consumption of cultured milkfish, Chanos chanos (Forsskål), from the arsenic-contaminated area in southwestern Taiwan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:637–644
Liu CW, Huang FH, Hsueh YM (2005) Revised cancer risk assessment of inorganic arsenic upon consumption of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) from blackfoot disease hyperendemic areas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 74:1037–1044
Liu CW, Liang CP, Huang FM, Hsueh YM (2006) Assessing the human health risks from exposure of inorganic arsenic through oyster (Crassostrea gigas) consumption in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 361:57–66
Liu CW, Liang CP, Lin KH, Jang CS, Wang SW, Huang YK, Hsueh YM (2007) Bioaccumulation of arsenic compounds in aquacultural clams (Meretrix lusoria) and assessment of potential carcinogenic risks to human health by ingestion. Chemosphere 69:128–134
Newton TJ, Cope WG (2007) Biomarker response of unionid mussels to environmental contaminants. In: Farris JL, van Hassel JH (eds) Freshwater bivalve ecotoxicology. CRC Press, New York, pp 257–284
Ortmann C, Grieshaber MK (2003) Energy metabolism and valve closure behaviour in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. J Exp Biol 206:4167–4178
Reich ES (2011) Conflicting studies fuel arsenic debate. Nature 478:437–438
Rodland DL, Schöne BR, Helama S, Nielsen JK, Baier S (2006) A clockwork mollusk: ultradian rhythms in bivalve activity revealed by digital photography. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 334:316–323
Shaw JR, Glaholt SP, Greenberg NS, Sierra-Alvarez R, Folt CL (2007) Acute toxicity of arsenic to Daphnia pulex: influence of organic functional group and oxidation state. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:1532–1537
Soucek DJ (2007) Sodium sulfate impact feeding, specific dynamic action, and growth rate in the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Aquat Toxicol 83:315–322
Tran D, Fournier E, Durrieu G, Massabuau JC (2004) Copper detection in the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea: optimum valve closure response. Aquat Toxicol 66:333–343
van der Schalie WH, Shedd TR, Knechtages PL, Widder MW (2001) Using higher organism in biological early warning systems for real-time toxicity detection. Biosens Bioelectron 16:457–465
Williams L, Schoof RA, Yager JW, Goodrich-Mahoney JW (2006) Arsenic bioaccumulation in freshwater fishes. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 12:904–923
Zhou QF, Zhang JB, Fu JJ, Shi JB, Jiang GB (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606:135–150
Acknowledgments
The Authors acknowledge the National Science Council of Republic of China for financial support under the Grant NSC 95-2313-B-002-052-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WY., Jou, LJ., Chen, SH. et al. A real-time biomonitoring system to detect arsenic toxicity by valve movement in freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea . Ecotoxicology 21, 1177–1187 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0872-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0872-9