Abstract
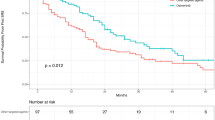
The prognosis and prognostic factors of patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) from lung adenocarcinoma have not been established. Particularly, the impact of EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements on survival remains unclear. This retrospective study evaluated the prognosis and prognostic factors of patients receiving WBRT for LM. We evaluated overall survival (OS) from WBRT initiation and clinical variables in 80 consecutive patients receiving WBRT for LM from lung adenocarcinoma at our institution between June 2013 and June 2021. After a median follow-up of 5.2 (range 0.5–56.5) months, the median OS was 6.2 months (95% CI 4.4–12.4). Of the 80 patients, 51 were classified as EGFR/ALK mutant (EGFR: 44; ALK: 6; both: 1) and 29 as wild-type. The median OS was 10.4 (95% CI 5.9–20.9) versus 3.8 (95% CI 2.5–7.7) months in the EGFR/ALK-mutant versus wild-type patients (HR = 0.49, P = 0.0063). Multivariate analysis indicated that EGFR/ALK alterations (HR = 0.54, P = 0.021) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) of 0–1 (HR = 0.25, P < 0.001) were independent factors associated with favorable OS. Among the patients who underwent brain MRI before and after WBRT, intracranial progression-free survival was longer in the 26 EGFR/ALK-mutant than 13 wild-type patients (HR = 0.31, P = 0.0039). Although the prognosis of patients receiving WBRT for LM remains poor, EGFR/ALK alterations and good ECOG PS may positively impact OS in those eligible for WBRT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed for this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ALK:
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- ECOG PS:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- LANO:
-
Leptomeningeal Assessment in Neuro-Oncology
- LM:
-
Leptomeningeal metastasis
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- WBRT:
-
Whole-brain radiotherapy
References
Remon J, Le Rhun E, Besse B (2017) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a continuing challenge in the personalized treatment era. Cancer Treat Rev 53:128–137
Alexander M, Lin E, Cheng H (2020) Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: optimal systemic management in NSCLC with and without driver mutations. Curr Treat Options Oncol 21(9):1–15
Cheng H, Perez-Soler R (2018) Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 19(1):e43–e55
Network NCC (n.d.) Central nervous system cancers (version 2.2021). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cns.pdf. Accessed 9 Aug 2022
Yan W, Liu Y, Li J, Han A, Kong L, Yu J et al (2019) Whole brain radiation therapy does not improve the overall survival of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with leptomeningeal metastasis. Radiat Oncol 14(1):1–10
Morris PG, Reiner AS, Szenberg OR, Clarke JL, Panageas KS, Perez HR et al (2012) Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer: survival and the impact of whole brain radiotherapy. J Thorac Oncol 7(2):382–385
Le Rhun E, Weller M, Brandsma D, Van den Bent M, de Azambuja E, Henriksson R et al (2017) EANO-ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours. Ann Oncol 28(4):iv84–iv99
Le Rhun E, Devos P, Boulanger T, Smits M, Brandsma D, Ruda R et al (2019) The RANO Leptomeningeal Metastasis Group proposal to assess response to treatment: lack of feasibility and clinical utility and a revised proposal. Neuro Oncol 21(5):648–658
Ozdemir Y, Yildirim BA, Topkan E (2016) Whole brain radiotherapy in management of non-small-cell lung carcinoma associated leptomeningeal carcinomatosis: evaluation of prognostic factors. J Neuro-oncol 129(2):329–335
Liao B-C, Lee J-H, Lin C-C, Chen Y-F, Chang C-H, Ho C-C et al (2015) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Thorac Oncol 10(12):1754–1761
Ozcan G, Singh M, Vredenburgh JJ (2022) Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer and current landscape of treatments. Clin Cancer Res 29(1):11–29
Yin K, Li Y-S, Zheng M-M, Jiang B-Y, Li W-F, Yang J-J et al (2019) A molecular graded prognostic assessment (molGPA) model specific for estimating survival in lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Lung Cancer 131:134–138
Amornwichet N, Oike T, Shibata A, Nirodi CS, Ogiwara H, Makino H et al (2015) The EGFR mutation status affects the relative biological effectiveness of carbon-ion beams in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Sci Rep 5(1):1–7
Das AK, Chen BP, Story MD, Sato M, Minna JD, Chen DJ et al (2007) Somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) abrogate EGFR-mediated radioprotection in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 67(11):5267–5274
Nakamura M, Kageyama S-I, Udagawa H, Zenke Y, Yoh K, Niho S et al (2020) Differences in failure patterns according to the EGFR mutation status after proton beam therapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 149:14–17
Gow C-H, Chien C-R, Chang Y-L, Chiu Y-H, Kuo S-H, Shih J-Y et al (2008) Radiotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastases: effects of activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations on clinical response. Clin Cancer Res 14(1):162–168
Sit D, Bale M, Lapointe V, Olson R, Hsu F (2022) Association between EGFR and ALK mutation status on patient-reported symptoms after palliative radiation for bone pain in NSCLC. JTO Clin Res Rep 3(8):100371
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund (2021-A-8) and The Yasuda Medical Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: HO, H. Hirata, YH. Formal analysis: HO, H. Hirata. Data curation: HO, YH. Resources: Y. Zhou, KT, TF, MN, H. Hojo, AM, SIK. Writing original-draft: HO, H. Hirata. Writing-review and editing: SZ, Y. Zenke, KG, SI, SN, TA. Project administration: H. Hirata, TA. Supervision: TA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was approved by the National Cancer Center Hospital East Institutional Review Board (Protocol Number 2017-440).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10585_2023_10225_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1 (PDF 409 kb) Supplementary Fig. 1 Kaplan–Meier survival curves showing differences in the overall survival of patients with EGFR-mutant (n = 44) versus ALK-rearranged (n = 6) leptomeningeal metastasis treated with WBRT. One patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring both EGFR and ALK alterations was excluded from the analysis. OS overall survival, WBRT whole-brain radiotherapy
10585_2023_10225_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file2 (PDF 426 kb) Supplementary Fig. 2 Overall survival of patients with EGFR/ALK-mutant leptomeningeal metastasis who received WBRT with versus without concurrent TKI therapy. TKI tyrosine kinase inhibitor, OS overall survival, WBRT whole-brain radiotherapy
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oyoshi, H., Hirata, H., Hirano, Y. et al. Prognostic impact of EGFR/ALK alterations in leptomeningeal metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma treated with whole-brain radiotherapy. Clin Exp Metastasis 40, 407–413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-023-10225-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-023-10225-7