Abstract
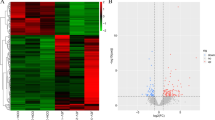
Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most frequently diagnosed dementia, is a senile neurodegenerative disorder characterized by amnesia and cognitive dysfunction. Unfortunately, there are still no successful strategies to prevent AD progression. Thus, the vast majority of research focuses on recognizing risk factors for develo** and progressing this disease. Human spirochetes, fungi, Borrelia burgdorferi, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, and human herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) have all been implicated in the development and progression of AD. Identifying microRNAs (miRs) encoded by DNA viruses has indicated that viruses can be evolved to exploit RNA silencing to regulate host and viral genes. Similar to host miR, v-miR can interact with the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the target mRNA to regulate gene expression. Although HSV-1 can also encode various miRs, their significance in the development and progression of AD is still unclear. In the present study, utilizing the bioinformatics approach (R software and related packages), we analyzed the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in AD samples (grey matter) of GSE37263 dataset obtained from the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Then, the sequences of HSV-1-encoded-miRs were retrieved from miRbase, and their targets were predicted by miRDB. Afterward, the common genes between downregulated DEGs in AD and targets of HSV-1-encoded miRs were identified to shed new light on the relationship between HSV-1 infection and AD development. Our results have indicated that HSV-1-encoded-miRs can target the downregulated DEGs in AD, and these aberrant interactions can offer valuable diagnostic/prognostic biomarkers for affected patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
Consent for Publication and Data Availability
All the authors accept the publication of this manuscript. The data is completely available from Nima Hemmat and Haniyeh Asadzadeh, as the first authors, as well as Dr. Behzad Baradaran, as the corresponding author.
References
Agostini S, Mancuso R, Baglio F, Clerici M (2017) A protective role for herpes simplex virus type-1-specific humoral immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 15:89–91
Apostolova LG (2016) Alzheimer disease. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 22:419–434. https://doi.org/10.1212/CON.0000000000000307
Arias B et al (2014) DISC1-TSNAX and DAOA genes in major depression and citalopram efficacy. J Affect Disord 168:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.06.048
Ball MJ (1982) Limbic predilection in Alzheimer dementia: is reactivated herpes virus involved? Can J Neurol Sci 9:303–306
Barbu MG et al (2020) MicroRNA involvement in signaling pathways during viral infection. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:143. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00143
Bello-Morales R, Andreu S, Lopez-Guerrero JA (2020) The role of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in demyelination of the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci 21:5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145026
Bradshaw MJ, Venkatesan A (2016) Herpes simplex virus-1 encephalitis in adults: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Neurotherapeutics 13:493–508
Bruscella P, Bottini S, Baudesson C, Pawlotsky J-M, Feray C, Trabucchi M (2017) Viruses and miRNAs: more friends than foes. Front Microbiol 8:824
Bylund J, Zhang C, Harder DR (2002) Identification of a novel cytochrome P450, CYP4X1, with unique localization specific to the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:677–684
Chen Y, Wang X (2020) miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D127–D131. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz757
Chen Y, Zheng J, Li X, Zhu L, Shao Z, Yan X, Zhu X (2020) Wdr47 controls neuronal polarization through the Camsap family microtubule minus-end-binding proteins. Cell Rep 31:107526
Cui C et al (2006) Prediction and identification of herpes simplex virus 1-encoded microRNAs. J Virol 80:5499–5508. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00200-06
Cullen BR (2011) Viruses and microRNAs: RISCy interactions with serious consequences. Genes Dev 25:1881–1894. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.17352611
Davis S, Meltzer PS (2007) GEOquery: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 23:1846–1847
De Chiara G et al (2019) Recurrent herpes simplex virus-1 infection induces hallmarks of neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits in mice. PLoS Pathog 15:e1007617
Dehhaghi M, Kazemi Shariat Panahi H, Guillemin GJ (2018) Microorganisms’ footprint in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 12:466
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy—analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315
Götz J, Bodea L-G, Goedert M (2018) Rodent models for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:583–598
Hajjari SN, Mehdizadeh M, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Shanehbandi D, Teimourian S, Baradaran B (2017) Secretases-related miRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease: new approach for biomarker discovery. Neurol Sci 38:1921–1926
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97:1634–1658
Harris SA, Harris EA (2018) Molecular mechanisms for herpes simplex virus type 1 pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10:48
Hennah W et al (2009) DISC1 association, heterogeneity and interplay in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 14:865–873. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.22
Hsu M-H, Savas Ü, Griffin KJ, Johnson EF (2007) Human cytochrome p450 family 4 enzymes: function, genetic variation and regulation. Drug Metab Rev 39:515–538
Huang Y, Mucke L (2012) Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 148:1204–1222
Huber W et al (2015) Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat Methods 12:115
Itzhaki RF (2018) Corroboration of a major role for herpes simplex virus type 1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10:324
Kannan M et al (2017) WD40-repeat 47, a microtubule-associated protein, is essential for brain development and autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:E9308–E9317
Karim S et al (2014) The role of viruses in neurodegenerative and neurobehavioral diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets Former Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 13:1213–1223
Katic J, Loers G, Tosic J, Schachner M, Kleene R (2017) The cell adhesion molecule CHL1 interacts with patched-1 to regulate apoptosis during postnatal cerebellar development. J Cell Sci 130:2606–2619
Kearns CA, Ravanelli AM, Cooper K, Appel B (2015) Fbxw7 limits myelination by inhibiting mTOR signaling. J Neurosci 35:14861–14871
Khalilzadeh B, Rashidi M, Soleimanian A, Tajalli H, Kanberoglu GS, Baradaran B, Rashidi M-R (2019) Development of a reliable microRNA based electrochemical genosensor for monitoring of miR-146a, as key regulatory agent of neurodegenerative disease. Int J Biol Macromol 134:695–703
Köroğlu Ç, Baysal L, Cetinkaya M, Karasoy H, Tolun A (2013) DNAJC6 is responsible for juvenile Parkinsonism with phenotypic variability. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:320–324
La Rosa F et al (2019) Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) infection induces a potent but ineffective IFN-λ production in immune cells of AD and PD patients. J Transl Med 17:1–10
Li J et al (2017) Molecular dissection of neuroligin 2 and Slitrk3 reveals an essential framework for GABAergic synapse development. Neuron 96:808-826.e808
López-Romero P (2011) Pre-processing and differential expression analysis of Agilent microRNA arrays using the AgiMicroRna Bioconductor library. BMC Genomics 12:1–8
Mancuso R, Sicurella M, Agostini S, Marconi P, Clerici M (2019) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: link and potential impact on treatment. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 17:715–731
Martin C, Solís L, Concha MI, Otth C (2011) Herpes simplex virus type 1 as risk factor associated to Alzheimer disease. Rev Med Chile 139:779–786
Mattson MP (2004) Infectious agents and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Ageing Res Rev 3:105–120
Mishra R, Kumar A, Ingle H, Kumar H (2020) The interplay between viral-derived miRNAs and host immunity during infection. Front Immunol 10:3079
Montojo J et al (2010) GeneMANIA Cytoscape plugin: fast gene function predictions on the desktop. Bioinformatics 26:2927–2928
Naqvi AR, Shango J, Seal A, Shukla D, Nares S (2018) Herpesviruses and MicroRNAs: new pathogenesis factors in oral infection and disease? Front Immunol 9:2099
Palo OM et al (2007) Association of distinct allelic haplotypes of DISC1 with psychotic and bipolar spectrum disorders and with underlying cognitive impairments. Hum Mol Genet 16:2517–2528
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47–e47
Shannon P et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Sharifi F, Fakhrzadeh H, Varmaghani M, Arzaghi SM, Khoei MA, Farzadfar F, Tanjani PT (2016) Prevalence of dementia and associated factors among older adults in Iran: National Elderly Health Survey (NEHS). Arch Iran Med 19(12):838–844
Smith TF (2008) Diversity of WD-repeat proteins. In: The coronin family of proteins. Springer, Berlin, pp 20–30
Snyder JL, Kearns CA, Appel B (2012) Fbxw7 regulates Notch to control specification of neural precursors for oligodendrocyte fate. Neural Dev 7:1–12
Takahashi H et al (2012) Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction. Nat Neurosci 15:389–398
Tan MG, Chua WT, Esiri MM, Smith AD, Vinters HV, Lai MK (2010) Genome wide profiling of altered gene expression in the neocortex of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 88:1157–1169
Uchoa MF, Moser VA, Pike CJ (2016) Interactions between inflammation, sex steroids, and Alzheimer’s disease risk factors. Front Neuroendocrinol 43:60–82
Umbach JL, Kramer MF, Jurak I, Karnowski HW, Coen DM, Cullen BR (2008) MicroRNAs expressed by herpes simplex virus 1 during latent infection regulate viral mRNAs. Nature 454:780–783
Wang F, **ang H, Fischer G, Liu Z, Dupont MJ, Hogan QH, Yu H (2016) HMG-CoA synthase isoenzymes 1 and 2 localize to satellite glial cells in dorsal root ganglia and are differentially regulated by peripheral nerve injury. Brain Res 1652:62–70
Wozniak MA, Itzhaki RF, Shipley SJ, Dobson CB (2007) Herpes simplex virus infection causes cellular β-amyloid accumulation and secretase upregulation. Neurosci Lett 429:95–100
Wulansari N et al (2021) Neurodevelopmental defects and neurodegenerative phenotypes in human brain organoids carrying Parkinson’s disease-linked DNAJC6 mutations. Sci Adv 7:eabb1540
Zheng K, Liu Q, Wang S, Ren Z, Kitazato K, Yang D, Wang Y (2018) HSV-1-encoded microRNA miR-H1 targets Ubr1 to promote accumulation of neurodegeneration-associated protein. Virus Genes 54:343–350
Zhou L, Miranda-Saksena M, Saksena NK (2013) Viruses and neurodegeneration. Virol J 10:1–17
Acknowledgements
All the authors would like to thank the Neurosciences Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences for their kind supports during this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Immunology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NH and HA: first authors of the manuscript, analyzing raw microarray data with R software and other bioinformatics analysis, writing the draft. ZA and MAS: Structural and grammatical editing of the manuscript, figures arrangement, and statistical analysis. BB: the corresponding author of the manuscript, creating the primary concept of the manuscript, final editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors also declared that no personal or financial relationship with other people or organizations exists in this study.
Ethical Approval
In the current study, the data of the GSE37263 dataset, which has ethical approval, was analyzed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmat, N., Asadzadeh, H., Asadzadeh, Z. et al. The Analysis of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1)-Encoded MicroRNAs Targets: A Likely Relationship of Alzheimer's Disease and HSV-1 Infection. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 2849–2861 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01154-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01154-8