Abstract
Micro- and Nano-Fibrillated Cellulose (MNFC) have gained increasing attention due to their remarkable properties, but their production usually requires an intensive multi-step process. This study proposes to find a novel approach involving steam explosion for the production of lignin-containing micro- and nano-fibrillated cellulose (L-MNFC) using Eucalyptus globulus bark as a new lignocellulosic feedstock. Eucalyptus globulus bark was first pre-treated by steam explosion in alkaline conditions (200 °C, 8 min) or by soda cooking in a rotating autoclave (170 °C, 60 min), refined and then ground until gels formed. The chemical composition of the pulps was studied with ion chromatography and FTIR-ATR. The morphology of the products was studied with measurements of suspension turbidity and Morfi Neo, optical and atomic force microscopies. Nanopapers were produced from L-MNFC to investigate mechanical properties. Results obtained showed that steam explosion produced pulps with slightly higher lignin content (≈ 9%), containing shorter fibers (≈ 400 µm) and higher amounts of fines (≈ 86%) compared to soda cooking (≈ 5%, ≈ 560 µm and 66%, respectively). AFM images of SteamEx L-MNFC gels showed a web-like structure containing lignin nanoparticles.
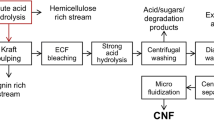
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA, Jacob M, Thomas S, Cvelbar U, Anandjiwala R (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: a novel approach. Carbohyd Polym 86(4):1468–1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.034
Ahola S (2008) Cellulose nanofibrils—adsorption with poly(amideamine) epichlorohydrin studied by QCM-D and application as a paper strength additive. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9167-3
Albornoz-Palma G, Ching D, Valerio O, Mendonça RT, Pereira M (2020) Effect of lignin and hemicellulose on the properties of lignocellulose nanofibril suspensions. Cellulose 27(18):10631–10647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03304-5
Avellar BK, Glasser WG (1998) Steam-assisted biomass fractionation. I. Process considerations and economic evaluation. Biomass and Bioenergy 14(3):205–218
Bäckström M, Bolivar S, Paltakari J (2012) Effect of ionic form on fibrillation and the development of the fibre network strength during the refining of the kraft pulps. O Papel 7:57–65
Becerra CF, Montory JS, Vega-Lara J, Norambuena-Contreras J (2016) New Biobased composite material using bark fibres Eucalyptus. In: Proceedings of the 13th Pacific Rim Bio-Based Composite Symposium Bio-Based Composites for a Sustainable Future, Concepción, Chile, pp 13–15
Bian H, Gao Y, Wang R, Liu Z, Wu W, Dai H (2018) Contribution of lignin to the surface structure and physical performance of cellulose nanofibrils film. Cellulose 25(2):1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1658-x
Carrillo I, Mendonça RT, Ago M, Rojas OJ (2018) Comparative study of cellulosic components isolated from different eucalyptus species. Cellulose 25(2):1011–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1653-2
Chadni M, Grimi N, Bals O, Ziegler-Devin I, Brosse N (2019) Steam explosion process for the selective extraction of hemicelluloses polymers from spruce sawdust. Ind Crops Prod 141(décembre):111757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111757
Chandra RP, Chu QL, **guang H, Zhong N, Lin M, Lee J-S, Saddler J (2016) The influence of lignin on steam pretreatment and mechanical pul** of poplar to achieve high sugar recovery and ease of enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresource Technol 199(janvier):135–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.019
Cherian BM, Pothan LA, Nguyen-Chung T, Günter M, Kottaisamy M, Thomas S (2008) A novel method for the synthesis of cellulose nanofibril whiskers from banana fibers and characterization. J Agric Food Chem 56(14):5617–5627. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8003674
Cherian BM, Leão AL, de Ferreira Souza S, Thomas S, Pothan LA, Kottaisamy M (2010) Isolation of nanocellulose from pineapple leaf fibres by steam explosion. Carbohyd Polym 81(3):720–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.03.046
Desmaisons J, Boutonnet E, Rueff M, Dufresne A, Bras J (2017) A new quality index for benchmarking of different cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohyd Polym 174(octobre):318–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.032
Dufresne A (2012) Nanocellulose: from nature to high performance tailored materials. De Gruyter. https://lib.hpu.edu.vn/handle/123456789/30932. Accessed Mar and Apr 2020
Ehman NV, Lourenço AF, McDonagh BH, Vallejos ME, Felissia FE, Ferreira PJT, Chinga-Carrasco G, Area MC (2020) Influence of initial chemical composition and characteristics of pulps on the production and properties of lignocellulosic nanofibers. Int J Biol Macromol 143(janvier):453–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.165
Eriksen Ø, Syverud K, Gregersen Ø (2008) The use of microfibrillated cellulose produced from kraft pulp as strength enhancer in TMP paper. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 23(3):299–304. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2008-23-03-p299-304
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA, Lindström T (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43(8):3434–3441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.05.038
Herrick FW, Casebier RL, Hamilton JK, Sandberg KR (1983) Microfibrillated cellulose: morphology and accessibility. J Appl Polym Sci: Appl Polym Symp., (United States) 37 (janvier). https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5039044. Accessed Mar and Apr 2020
Ho TT, Thu KA, Zimmermann T, Yano H (2015) Nanofibrillation of pulp fibers by twin-screw extrusion. Cellulose 22(1):421–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0518-6
Jacquet N, Vanderghem C, Blecker C, Paquot M (2010) La steam explosion: application en tant que prétraitement de la matière lignocellulosique, BASE [En ligne], numéro spécial 2, Volume 14, 561–566. https://popups.uliege.be/1780-4507/index.php?id=6226
Kaushik A, Singh M (2011) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibrils from wheat straw using steam explosion coupled with high shear homogenization. Carbohyd Res 346(1):76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2010.10.020
Kessler RW, Becker U, Kohler R, Goth B (1998) Steam explosion of flax—a superior technique for upgrading fibre value. Biomass Bioenergy 14(3):237–249
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(24):5438–5466. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201001273
Kumar V, Bollström R, Yang A, Chen Q, Chen G, Salminen P, Bousfield D, Toivakka M (2014) Comparison of nano- and microfibrillated cellulose films. Cellulose (london) 21(5):3443–3456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0357-5
Lavoie J-M, Capek-Menard E, Gauvin H, Chornet E (2010) Production of pulp from salix viminalis energy crops using the FIRSST process. Biores Technol 101(13):4940–4946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.021
Lavoine N, Desloges I, Dufresne A, Bras J (2012) Microfibrillated cellulose–Its barrier properties and applications in cellulosic materials: a review. Carbohydr Polym 90(2):735–764
Lin N, Dufresne A (2014) Surface chemistry, morphological analysis and properties of cellulose nanocrystals with gradiented sulfation degrees. Nanoscale 6(10):5384–5393. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR06761K
Lindström T, M. Ankerfors, C. Aulin (2011) Nanocellulose research and developments at innventia. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:ri:diva-9473. Accessed Mar and Apr 2020
Luo H, Zhang H, Yue L, Pizzi A, **aoning Lu (2018) Effects of steam explosion on the characteristics of windmill palm fiber and its application to fiberboard. Eur J Wood and Wood Prod 76(2):601–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-017-1259-7
Miranda I, Gominho J, Pereira H (2012) Incorporation of bark and tops in Eucalyptus globulus wood pul**. Bioresources 7(3):4350–4361
Missoum K, Belgacem M, Bras J (2013) Nanofibrillated cellulose surface modification: a review. Materials 6(5):1745–1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6051745
Nechyporchuk O, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2016) Production of cellulose nanofibrils: a review of recent advances. Ind Crops Prod 93:2–25
Nuopponen M, Päiväläinen T, Laukkanen A, Paltakari J (2013) Method for manufacturing nanofibrillated cellulose pulp and use of the pulp in paper manufacturing or in nanofibrillated cellulose composites. United States US20130000855A1, filed 5 novembre 2010, et issued 3 janvier 2013. https://patents.google.com/patent/US20130000855A1/en. Accessed Mar and Apr 2020
Obame SN, Ziegler-Devin I, Safou-Tchima R, Brosse N (2019) Homolytic and heterolytic cleavage of β-ether linkages in hardwood lignin by steam explosion. J Agric Food Chem 67(21):5989–5996. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01744
Park C-W, Han S-Y, Namgung H-W, Seo P-N, Lee S-Y, Lee S-H (2017) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanofibrils with varying chemical compositions. BioResources 12(3):5031–44. https://doi.org/10.1576/biores.12.3.5031-5044
Richard B, Quilès F, Carteret C, Brendel O (2014) Infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to appraise α-cellulose extracted from wood for stable carbon isotope measurements. Chem Geol 381(août):168–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.010
Rojo E, Peresin MS, Sampson WW, Hoeger IC, Vartiainen J, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2015) Comprehensive elucidation of the effect of residual lignin on the physical, barrier, mechanical and surface properties of nanocellulose films. Green Chem 17(3):1853–1866. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4GC02398F
Romaní A, Larramendi A, Yáñez R, Cancela Á, Sánchez Ángel, Teixeira JA, Domingues L (2019) Valorization of eucalyptus nitens bark by organosolv pretreatment for the production of advanced biofuels. Ind Crops Prod 132(juin):327–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.02.040
Sartori C, da Silva G, Mota JF, Miranda I, Mori FA, Pereira H (2016) Chemical characterization of the bark of eucalyptus urophylla hybrids in view of their valorization in biorefineries. Holzforschung 70(9):819–828. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2015-0258
Sauvageon T, Lavoie J-M, Segovia C, Brosse N (2018) Toward the cottonization of hemp fibers by steam explosion—part 1: defibration and morphological characterization. Text Res J 88(9):1047–1055. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517517697644
Sehaqui H (2011) High-porosity aerogels of high specific surface area prepared from nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC). Compos Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.07.003
Siro I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17(3):459–494
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2011) A comparative study of energy consumption and physical properties of microfibrillated cellulose produced by different processing methods. Cellulose 18(4):1097–1111
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83(1):1–11
Sutka A, Kukle S, Gravitis J, Berzins A (2013) Chemical and physical modification of hemp fibres by steam explosion technology. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering, Vol. 49, No. 1. IOP Publishing, p 012053
Taha M, Hassan M, Dewidare M, Kamel MA, Ali WY, Dufresne A (2021) Evaluation of eco-friendly cellulose and lignocellulose nanofibers from rice straw using multiple quality index. Egypt J Chem 64(8):4707–4717
Takada M, Chandra RP, Saddler JN (2019) The Influence of lignin migration and relocation during steam pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of softwood and corn stover biomass substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 116(11):2864–2873. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27137
Tuzzin G, Godinho M, Dettmer A, Zattera AJ (2016) Nanofibrillated cellulose from tobacco industry wastes. Carbohydr Polym 148(septembre):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.045
Ullah H, Santos HA, Khan T (2016) Applications of bacterial cellulose in food, cosmetics and drug delivery. Cellulose 23(4):2291–2314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0986-y
Vignon MR, Garcia-Jaldon C, Dupeyre D (1995) Steam explosion of woody hemp chenevotte. Int J Biol Macromol 17(6):395–404
Wang X, Cui X, Zhang L (2012) Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing nanofibrillar cellulose. Procedia Environ Sci 16:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.017
Yuan T, Zeng J, Wang B, Cheng Z, Chen K (2021) Lignin containing cellulose nanofibers (LCNFs): lignin content-morphology-rheology relationships. Carbohydr Polym 254(février):117441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117441
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Labex Tec21 and LAbex Arbre for the thesis funding. This work was also supported by the Franco-Chilean EcosSud Collaborative Program C18E05, ANID PIA/Apoyo CCTE AFB170007 of Universidad de Concepción. We thank the Spectroscopy and Microscopy of interfaces Service Facility (SMI) of LCPME where the IR-ATR and AFM measurements were performed (Université de Lorraine-CNRS–(www.lcpme.cnrs-nancy.fr); LCPME, UMR7564, 405 rue de Vandoeuvre 54600, France).
Funding
This study was funded by the LabEx Tec 21 (Investissements d ’Avenir - grant agreement n°ANR-11-LABX-0030) and the French National Research Agency (ANR) as part of the “Investissements d’Avenir” program (ANR-11-LABX-0002-01, Lab of Excellence ARBRE). This work was also funded by the Franco-Chilean EcoSud Collaborative Program C18E05, ANID PIA/Apoyo CCTE AFB170007 of Universidad de Concepción.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: NB, EM and SN; Methodology and investigation: SN, MK, IZ-D, FQ and SElKC; Original draft preparation: SN; Review and editing: NB, EM and S; Supervision: NB and EM; Funding acquisition: NB, EM and CF. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nader, S., Brosse, N., Khadraoui, M. et al. A low-cost environmentally friendly approach to isolate lignin containing micro and nanofibrillated cellulose from Eucalyptus globulus bark by steam explosion. Cellulose 29, 5593–5607 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04632-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04632-4