Abstract
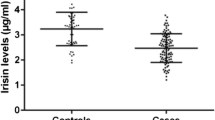
We examined the relationship of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and its primary growth factor, IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) with malignant melanoma using interview data and sera from cases (n = 286) and controls (n = 289) in a population-based case–control study conducted in 1986–1992 on Oahu, Hawaii. Serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 concentrations were measured by ELISA. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated by unconditional logistic regression and adjusting for age, sex, education, number of blistering sunburns, ability to tan, hair color, energy intake, BMI, height, smoking status, and drinking status. An inverse relationship was found between IGF-I concentration and melanoma (OR for upper vs. lower tertile: 0.44, 95% CI: 0.25–0.79), but clear associations were not observed between malignant melanoma and upper tertiles of IGFBP-3 and the IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio. The inverse association with IGF-I was strongest among subjects who did not report a history of non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) (OR for ≥ vs. < median: 0.39, 95% CI: 0.24–0.65), and a positive association was found among those with such a history (OR: 3.6, 95% CI: 1.0–13; p interaction = 0.0035). Our findings observed here between serum IGF-I and malignant melanoma warrants replication in studies with a larger sample size and a prospective design.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IGF-I:
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I
- IGFBP-3:
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- NMSC:
-
Non-melanoma skin cancer
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
References
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A, Friend KE (2000) The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev 21:215–244
Chen W, Wang S, Tian T et al (2009) Phenotypes and genotypes of insulin-like growth factor 1, IGF-binding protein-3 and cancer risk: evidence from 96 studies. Eur J Hum Genet 17:1668–1675
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M (2004) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 363:1346–1353. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16044-3
Ferry RJ Jr, Cerri RW, Cohen P (1999) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: new proteins, new functions. Horm Res 51:53–67
Rodeck U, Herlyn M, Menssen HD, Furlanetto RW, Koprowsk H (1987) Metastatic but not primary melanoma cell lines grow in vitro independently of exogenous growth factors. Int J Cancer 40:687–690
Satyamoorthy K, Li G, Vaidya B, Patel D, Herlyn M (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces survival and growth of biologically early melanoma cells through both the mitogen-activated protein kinase and beta-catenin pathways. Cancer Res 61:7318–7324
Furlanetto RW, Harwell SE, Baggs RB (1993) Effects of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibition on human melanomas in culture and in athymic mice. Cancer Res 53:2522–2526
Rodeck U, Melber K, Kath R et al (1991) Constitutive expression of multiple growth factor genes by melanoma cells but not normal melanocytes. J Investig Dermatol 97:20–26
Stracke ML, Engel JD, Wilson LW, Rechler MM, Liotta LA, Schiffmann E (1989) The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor is a motility receptor in human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 264:21544–21549
Karasic TB, Hei TK, Ivanov VN (2010) Disruption of IGF-1R signaling increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis: A new potential therapy for the treatment of melanoma. Exp Cell Res 316:1994–2007. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.014]
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Santonocito C, Paradisi A, Capizzi R et al (2008) Insulin-like growth factor I (CA) repeats are associated with higher melanoma’s Breslow index but not associated with the presence of the melanoma. A pilot study. Clinica Chimica Acta 390:104–109
Øy GF, Slipicevic A, Davidson B, Faye RS, Mælandsmo GM, Flørenes VA (2010) Biological effects induced by insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) in malignant melanoma. Int J Cancer 126:350–361
** Y, Nakajima G, Hamil T, Fodstad O, Riker A, Ju J (2006) Association of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 expression with melanoma progression. Mol Cancer Ther 5:3078–3084
Yu J, Warycha M, Christos P et al (2008) Assessing the clinical utility of measuring insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in tissues and sera of melanoma patients. J Transl Med 6:70
Gruber SB, Armstrong BK (2006) Cutaneous and ocular melanoma. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF (eds) Cancer epidemiology and prevention. Oxford Press, New York, pp 1196–1217
Rivers JK (2004) Is there more than one road to melanoma? Lancet 363:728–730. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15649-3
Le Marchand L, Saltzman BS, Hankin JH et al (2006) Sun exposure, diet, and melanoma in Hawaii Caucasians. Am J Epidemiol 164:232–245
US Department of Agriculture (1992) Nutrient database for standard reference, release 10. Human Nutrion Information Service, USDA, Bethesda, MD
Hilmi C, Larribere L, Giuliano S, et al. (2007) IGF1 promotes resistance to apoptosis in melanoma cells through an increased expression of BCL2, BCL-X(L), and survivin. J Invest Dermatol 128:1499–1505
Satyamoorthy K, Li G, Vaidya B, Kalabis J, Herlyn M (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-I-induced migration of melanoma cells is mediated by interleukin-8 induction. Cell Growth Differ 13:87–93
Rosen CJ (1999) Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins: clinical implications. Clin Chem 45:1384–1390
Fleming MG, Howe SF, Graf LH Jr (1994) Expression of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in nevi and melanomas. Am J Dermatopathol 16:383–391
Lacey JV, Potischman N, Madigan MP et al (2004) Insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women: results from a U.S. case–control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 13:607–612
Gunter MJ, Hoover DR, Yu H et al (2008) A prospective evaluation of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I as risk factors for endometrial cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17:921–929
Jacobs ET, Martínez ME, Alberts DS et al (2008) Plasma insulin-like growth factor I is inversely associated with colorectal adenoma recurrence: a novel hypothesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17:300–305
Yue J, Mulder KM (2001) Transforming growth factor-[beta] signal transduction in epithelial cells. Pharmacol Ther 91:1–34
Baxter RC (1994) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the human circulation: a review. Horm Res 42:140–144
Kanter-Lewensohn L, Dricu A, Girnita L, Wejde J, Larsson O (2000) Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and p27Kip1 in melanocytic tumors: a potential regulatory role of IGF-1 pathway in distribution of p27Kip1 between different cyclins. Growth Factors 17:193–202
Fürstenberger G, Senn H-J (2002) Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Lancet Oncol 3:298–302
Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Lukanova A, Akhmedkhanov A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Toniolo P (2001) Correspondence re: Giovannucci et al., a prospective study of plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 9:345–349, 2000. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 10:1103–1104
Parekh N, Roberts CB, Vadiveloo M, Puvananayagam T, Albu JB, Lu-Yao GL (2010) Lifestyle, anthropometric, and obesity-related physiologic determinants of insulin-like growth factor-1 in the third national health and nutrition examination survey (1988–1994). Ann Epidemiol 20:182–193. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2009.11.008
Ito Y, Nakachi K, Imai K, et al. (2005) Stability of frozen serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-II, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, transforming growth factor beta, soluble Fas, and superoxide dismutase activity for the JACC study. J Epidemiol 15(Suppl 1):S67–S73
Ming ME, Levy RM, Hoffstad OJ, Filip J, Gimotty PA, Margolis DJ (2004) Validity of patient self-reported history of skin cancer. Arch Dermatol 140:730–735
Colditz GA, Martin P, Stampfer MJ et al (1986) Validation of questionnaire information on risk factors and disease outcomes in a prospective cohort study of women. Am J Epidemiol 123:894–900
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NCI grant P01 CA33619 and US department of Heath and Human Services contract N01-PC67010. S.L.P and the lab assays were supported by NCI T32 CA09142. We would like to thank Dr. Gang Zeng and his research group at UCLA for use of their laboratory space and equipment. In addition, we are in debt to the study participants for contributing their time and specimens.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.L., Setiawan, V.W., Kanetsky, P.A. et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 levels with risk of malignant melanoma. Cancer Causes Control 22, 1267–1275 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9800-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-011-9800-1