Abstract
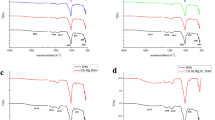
This study investigates the correlation between the biomedical and structural properties of Zn/Sr-modified Calcium Phosphates (ZnSr–CaPs) synthesized via the sol–gel combustion method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed the presence of Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 (HAp), CaCO3, and Ca(OH)2 phases in the undoped sample, while the additional phase, Ca3(PO4)2 (β-TCP) was formed in modified samples. X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) analysis demonstrated the incorporation of Sr into the lattice, with a preference for occupying the Ca1 sites in the HAp matrix. The introduction of Zn, furthermore, led to the formation of ZnO and CaZnO2 species. The ZnSr–CaPs exhibited significant antibacterial activity attributed to the generation of reactive oxygen species by ZnO, the oxidation reaction of CaZnO2, and the presence of Sr ions. Cytotoxicity tests revealed a correlation between the variation in ZnO content and cellular viability, with lower ZnO concentrations corresponding to higher cell viability. Additionally, the cooperative effects of Zn and Sr ions were found to enhance the bioactivity of CaPs, despite ZnO hindering the apatite formation process. These findings contribute to the deep understanding of the diverse role in modulating the antibacterial, cytotoxic, and bioactive properties of ZnSr–CaPs, offering potential applications in the field of biomaterials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaravathy P, Kumar TSS (2019) Bioactivity enhancement by Sr doped Zn–Ca–P coatings on biomedical magnesium alloy. J Magnes Alloys 7:584–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2019.05.014
Applerot G, Lipovsky A, Dror R, Perkas N, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A (2009) Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS-mediated cell injury. Adv Func Mater 19:842–852. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200801081
Bazin D, Reguer S, Vantelon D, Haymann J-P, Letavernier E, Frochot V, Daudon M, Esteve E, Colboc H (2022) XANES spectroscopy for the clinician. C R Chim 25:189–208. https://doi.org/10.5802/crchim.129
Black J (2005) Biological performance of materials: fundamentals of biocompatibility, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bootchanont A, Sailuam W, Sutikulsombat S, Temprom L, Chanlek N, Kidkhunthod P, Suwanna P, Yimnirun R (2017) Synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of local structure in strontium-doped hydroxyapatite. Ceram Int 43:11023–11027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.144
Bootchanont A, Wechprasit T, Isran N, Theangsunthorn J, Chaosuan N, Chanlek N, Kidkhunthod P, Yimnirun R, Jiamprasertboon A, Eknapakul T, Siritanon T, Sailuam W, Saisopa T (2022) Correlation of the antibacterial activity and local structure in Zn- and Mn-doped hydroxyapatites by Rietveld refinement and the first-principles method. Materialia 26:101586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101586
Chen K, Ustriyana P, Moore F, Sahai N (2019) Biological response of and blood plasma protein adsorption on silver-doped hydroxyapatite. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00996
Costescu A, Ciobanu CS, Iconaru SL, Ghita RV, Chifiriuc CM, Marutescu LG, Predoi D (2013) Fabrication, characterization, and antimicrobial activity, evaluation of low silver concentrations in silver-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2013:194854. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/194854
Eglin D, Maalheem S, Livage J, Coradin T (2006) In vitro apatite forming ability of type I collagen hydrogels containing bioactive glass and silica sol–gel particles. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-006-6820-6
Fiume E, Magnaterra G, Rahdar A, Verné E, Baino F (2021) Hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications: a short overview. Ceramics 4:542–563
Goto T, Sasaki K (2014) Effects of trace elements in fish bones on crystal characteristics of hydroxyapatite obtained by calcination. Ceram Int 40:10777–10785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.03.067
Gultom NS, Abdullah H, Kuo D-H (2020) Phase transformation of bimetal zinc nickel oxide to oxysulfide photocatalyst with its exceptional performance to evolve hydrogen. Appl Catal B 272:118985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118985
Guo X, Yan H, Zhao S, Li Z, Li Y, Liang X (2013) Effect of calcining temperature on particle size of hydroxyapatite synthesized by solid-state reaction at room temperature. Adv Powder Technol 24:1034–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2013.03.002
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Akbar Ashkarran A, Jimenez de Aberasturi D, Larramendi IRd, Rojo T, Serpooshan V, Parak WJ, Mahmoudi M (2012a) Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 30:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.06.004
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, Jimenez de Aberasturi D, de Larramendi IR, Rojo T, Serpooshan V, Parak WJ, Mahmoudi M (2012b) Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 30:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.06.004
Hedin L, Lundqvist BI (1971) Explicit local exchange-correlation potentials. J Phys C: Solid State Phys 4:2064. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3719/4/14/022
Hu Q, Tan Z, Liu Y, Tao J, Cai Y, Zhang M, Pan H, Xu X, Tang R (2007) Effect of crystallinity of calcium phosphate nanoparticles on adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Chem 17:4690–4698. https://doi.org/10.1039/B710936A
Jaakkola T, Rich J, Tirri T, Närhi T, Jokinen M, Seppälä J, Yli-Urpo A (2004) In vitro Ca–P precipitation on biodegradable thermoplastic composite of poly(ε-caprolactone-co-dl-lactide) and bioactive glass (S53P4). Biomaterials 25:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00558-1
Kędziora A, Speruda M, Krzyżewska E, Rybka J, Łukowiak A, Bugla-Płoskońska G (2018) Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020444
Khamkongkaeo A, Boonchuduang T, Klysubun W, Amonpattaratkit P, Ht C, Tuchinda N, Pimsawat A, Daengsakul S, Suksangrat P, Sailuam W, Vongpramate D, Bootchanont A, Lohwongwatana B (2021) Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite ceramics prepared from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) bone and commercial powder for biomedical applications. Ceram Int 47:34575–34584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.372
Kokubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27:2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.017
Kolmas J, Groszyk E, Kwiatkowska-Różycka D (2014) Substituted hydroxyapatites with antibacterial properties. Biomed Res Int 2014:178123. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/178123
Lebre F, Sridharan R, Sawkins MJ, Kelly DJ, O’Brien FJ, Lavelle EC (2017) The shape and size of hydroxyapatite particles dictate inflammatory responses following implantation. Sci Rep 7:2922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03086-0
Likit Temprom SLS, Tippayawat P, Suwanna P (2017) Bioactivity, cytotoxicity and antibacterial evaluation of undoped, Zn-doped, Sr-doped, and Zn/Sr-codoped hydroxyapatites synthesized by a sol–gel method. Chiang Mai J Sci 44:630–639
Liu Y-C, Lee Y-T, Huang T-C, Lin G-S, Chen Y-W, Lee B-S, Tung K-L (2021) In vitro bioactivity and antibacterial activity of strontium-, magnesium-, and zinc-multidoped hydroxyapatite porous coatings applied via atmospheric plasma spraying. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4:2523–2533. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c01535
Olejnik M, Kersting M, Rosenkranz N, Loza K, Breisch M, Rostek A, Prymak O, Schürmeyer L, Westphal G, Köller M, Bünger J, Epple M, Sengstock C (2021) Cell-biological effects of zinc oxide spheres and rods from the nano- to the microscale at sub-toxic levels. Cell Biol Toxicol 37:573–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09571-z
Park MV, Neigh AM, Vermeulen JP, de la Fonteyne LJ, Verharen HW, Briedé JJ, van Loveren H, de Jong WH (2011) The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 32:9810–9817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.085
Paul S, Pal A, Choudhury AR, Bodhak S, Balla VK, Sinha A, Das M (2017) Effect of trace elements on the sintering effect of fish scale derived hydroxyapatite and its bioactivity. Ceram Int 43:15678–15684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.127
Ramselaar MMA, Driessens FCM, Kalk W, De Wijn JR, Van Mullem PJ (1991) Biodegradation of four calcium phosphate ceramics;in vivo rates and tissue interactions. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00703460
Ran J, Jiang P, Sun G, Ma Z, Hu J, Shen X, Tong H (2017) Comparisons among Mg, Zn, Sr, and Si doped nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan composites for load-bearing bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Chem Front 1:900–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6QM00192K
Reller LB, Weinstein M, Jorgensen JH, Ferraro MJ (2009) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a review of general principles and contemporary practices. Clin Infect Dis 49:1749–1755. https://doi.org/10.1086/647952
Ruban Kumar A, Kalainathan S (2010) Sol–gel synthesis of nanostructured hydroxyapatite powder in presence of polyethylene glycol. Physica B 405:2799–2802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.03.067
Shannon RD, Prewitt CT (1969) Effective ionic radii in oxides and fluorides. Acta Crystallogr B 25:925–946. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740869003220
Sinulingga K, Sirait M, Siregar N, Doloksaribu ME (2021) Investigation of antibacterial activity and cell viability of Ag/Mg and Ag/Zn Co-doped hydroxyapatite derived from natural limestone. ACS Omega 6:34185–34191. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c05921
Suh SW, Won SJ, Hamby AM, Yoo BH, Fan Y, Sheline CT, Tamano H, Takeda A, Liu J (2009) Decreased brain zinc availability reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in mice and rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:1579–1588. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2009.80
Tiwari V, Mishra N, Gadani K, Solanki PS, Shah NA, Tiwari M (2018) Mechanism of anti-bacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticle against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01218
Wang J-Y, Liu Y-C, Lin G-S, Chang H-H, Li Y-T, Yang Y-C, Matsuyama H, Lee B-S, Chen Y-W, Tung K-L (2020) Flame-sprayed strontium- and magnesium-doped hydroxyapatite on titanium implants for osseointegration enhancement. Surf Coat Technol 386:125452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125452
Xu J, Ding G, Li J, Yang S, Fang B, Sun H, Zhou Y (2010) Zinc-ion implanted and deposited titanium surfaces reduce adhesion of Streptococccus mutans. Appl Surf Sci 256:7540–7544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.06.002
Zeleke MA, Kuo D-H, Ahmed KE, Gultom NS (2018) Facile synthesis of bimetallic (In, Ga)2(O, S)3 oxy-sulfide nanoflower and its enhanced photocatalytic activity for reduction of Cr(VI). J Colloid Interface Sci 530:567–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.06.092
Zheng Y, Li R, Wang Y (2009) In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility studies of ZnO nanoparticles. Int J Mod Phys B 23:1566–1571. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979209061275
Acknowledgements
This research work has received funding supports from the NRFS via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research, and Innovation (PMU-B) (Grant No. B05F640090). The authors would like to thank the computing resources provided by the Computational Materials Physics Project, SLRI, Thailand, Rajamangala University of Technology ISAN, and Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Atipong Bootchanont: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing—review & editing. Natthaphon Chaosuan: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. Sasina Promdee: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. Jantima Teeka: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. Pinit Kidkhunthod: Supervision. Rattikorn Yimnirun: Supervision. Wutthigrai Sailuam: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. Nutthaporn Isran: Supervision. Arreerat Jiamprasertboon: Formal analysis, Writing—review & editing. Theeranun Siritanon: Supervision. Tanachat Eknapakul: Visualization, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Thanit Saisopa: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bootchanont, A., Chaosuan, N., Promdee, S. et al. Correlation between biomedical and structural properties of Zn/Sr modified calcium phosphates. Biometals (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-024-00599-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-024-00599-w