Abstract
Objective
To construct recombinant Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis) expressing viral protein 1 (VP1) of enterovirus 71 (EV71) and evaluate its immunogenicity to be used as an oral vaccine in BALB/c mice.
Results
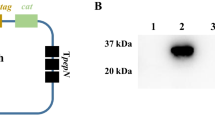
Recombinant L. lactis competent in secreting VP1 (~ 30 kDa) into the extracellular environment with the aid of the signal peptide Usp45 was produced. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed that significant VP1-specific antibody response including the production of both serum IgG and fecal IgA (p < 0.05) was elicited in BALB/c mice upon oral immunization with recombinant L. lactis. Moreover, in contrast to negative control, recombinant L. lactis induced adequate neutralizing antibodies in mouse sera (p < 0.05) as demonstrated in virus neutralization assay, whereas the presence of neutralizing antibodies in fecal samples was obvious but not significant (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Recombinant L. lactis expressing VP1 of EV71 has the potential to be used as an oral vaccine candidate. The findings may provide some preliminary evidences for further development of effective and needle-free EV71 vaccines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Kassaa I, Hober D, Hamze M, Chihib NE, Drider D (2014) Antiviral potential of lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 6:177–185
Cano-Garrido O, Seras-Franzoso J, Garcia-Fruitos E (2015) Lactic acid bacteria: reviewing the potential of a promising delivery live vector for biomedical purposes. Microb Cell Fact 14:137
Gao F, Wang Y, Mao Q, Yao X, Liu S, Li F, Zhu F, Yang J et al (2012) Enterovirus 71 viral capsid protein linear epitopes: identification and characterization. Virol J 9:26
Ku Z, Ye X, Shi J, Wang X, Liu Q, Huang Z (2015) Single neutralizing monoclonal antibodies targeting the VP1 GH loop of enterovirus 71 inhibit both virus attachment and internalization during viral entry. J Virol 89:12084–12095
Lee MS, Chang LY (2010) Development of enterovirus 71 vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines 9:149–156
Li L, Qiao X, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zheng Q, Hou J (2018) Surface-displayed porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus from cell culture onto gram-positive enhancer matrix particles. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45:889–898
Mao QY, Wang Y, Bian L, Xu M, Liang Z (2016) EV71 vaccine, a new tool to control outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). Expert Rev Vaccines 15:599–606
Peng X, Fang X, Li J, Kong L, Li B, Ding X (2016) Enhancing immune responses of EV71 VP1 DNA vaccine by co-inoculating plasmid IL-12 or GM-CSF expressing vector in mice. Cell Mol Biol 62:35–41
Ventarola D, Bordone L, Silverberg N (2015) Update on hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Clin Dermatol 33:340–346
Wang X, Peng W, Ren J, Hu Z, Xu J, Lou Z, Li X, Yin W et al (2012) A sensor-adaptor mechanism for enterovirus uncoating from structures of EV71. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:424–429
Wyszynska A, Kobierecka P, Bardowski J, Jagusztyn-Krynicka EK (2015) Lactic acid bacteria–20 years exploring their potential as live vectors for mucosal vaccination. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2967–2977
Yi EJ, Shin YJ, Kim JH, Kim TG, Chang SY (2017) Enterovirus 71 infection and vaccines. Clin Exp Vaccine Res 6:4–14
Yuan J, Tang X, Yin K, Tian J, Rui K, Ma J, Mao C, Chen J et al (2015) GITRL as a genetic adjuvant enhances enterovirus 71 VP1 DNA vaccine immunogenicity. Immunol Res 62:81–88
Zhou BY, Sun JC, Li X, Zhang Y, Luo B, Jiang N, Liu MC (2018) Analysis of immune responses in mice orally immunized with recombinant pMG36e-SP-TSOL18/Lactococcus lactis and pMG36e-TSOL18/Lactococcus lactis vaccines of taenia solium. J Immunol Res 2018:9262631
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Scientific Research Project of Universities of Henan Province, China (Grant Nos. 19A330004 and 18B360012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, P., Wang, Y., Tao, L. et al. Recombinant lactococcus lactis secreting viral protein 1 of enterovirus 71 and its immunogenicity in mice. Biotechnol Lett 41, 867–872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02695-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02695-1