Abstract
Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC), a prevalent kind of cancerous tumor in female reproductive system that has a dismal prognosis in women worldwide. Given the very limited studies of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs (CRLs) in UCEC. Our purpose was to construct a prognostic profile based on CRLs and explore its assess prognostic value in UCEC victims and its correlation with the immunological microenvironment.Methods: 554 UCEC tumor samples and 23 normal samples’ RNA-seq statistics and clinical details were compiled from data in the TCGA database. CRLs were obtained using Pearson correlation analysis. Using LASSO Cox regression, multivariate Cox regression, and univariate Cox regression analysis, six CRLs are confirmed to develop a risk prediction model at last.We identified two main molecular subtypes and observed that multilayer CRLs modifications were related to patient clinicopathological features, prognosis, and tumor microenvironment (TME) cell infiltration characteristics, and then we verified the prognostic hallmark of UCEC and examined its immunological landscape.Finally, using qRT-PCR, model hub genes’ expression patterns were confirmed. Results: A unique CRL signature was established by the combination of six differently expressed CRLs that were highly linked with the prognosis of UCEC patients. According to their CRLs signatures, the patients were divided into two groups: the low-risk and the high-risk groups. Compared to individuals at high risk, patients at low risk had higher survival rates (p < 0.001). Additionally, Cox regression reveals that the profiles of lncRNAs linked to cuproptosis may independently predict prognosis in UCEC patients. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year risks’ respective receiver operating characteristics (ROC) exhibited AUC values of 0.778, 0.810, and 0.854. Likewise, the signature could predict survival in different groups based on factors like stage, age, and grade, among others. Further investigation revealed differences between the different risk score groups in terms of drug sensitivity,immune cell infiltration,tumor mutation burden (TMB) score and microsatellite instability (MSI) score. Compared to the group of high risk, the low-risk group had greater rates of TMB and MSI. Results from qRT-PCR revealed that in UCEC vs normal tissues, AC026202.2, NRAV, AC079466.2, and AC090617.5 were upregulated,while LINC01545 and AL450384.1 were downregulated. Conclusions: Our research clarified the relationship between CRLs signature and the immunological profile and prognosis of UCEC.This signature will establish the framework for future investigations into the endometrial cancer CRLs mechanism as well as the exploitation of new diagnostic tools and new therapeutic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
UCEC occurs as the second common female reproductive system tumors globally. According to the GLOBOCAN database, 417,367 new UCEC cases and 97,370 deaths have occurred worldwide by 2020 (Bray et al. 2018). Postmenopausal women constitute the predominant demographic affected by endometrial cancer. Presently, the incidence of this condition exhibits a yearly rise, which can be attributed to the aging population and the escalating prevalence of obesity among women (Gu et al. 2021). It is thought that as many as 25% of cases were also found before menopause, and even if UCEC patients with early stage accepted surgical therapy got good prognosis, however, for patients with advanced stages or recurrent endometrial cancer, 5-year survival rates were only approximately 17% (Siegel et al. 2021).A lower five-year survival rate is indicated that these present approaches to risk and prognosis prediction based on the clinicopathologic characteristics of patients may be insufficient. As a result, it is of the utmost importance to locate new biomarkers to construct a risk prediction model for UCEC.
Copper is an important trace element because it participates in many metabolic reactions that take place within the human body. However,copper has dual effects on metabolic pathways in all species,excess intracellular copper is poisonous and can kill cells. Cuproptosis, which is thought to be a copper-triggered mechanism of mitochondrial cell death, has recently come into focus.Related studies suggest that compared to healthy populations, cancer patients had greater serum and tumor tissue copper levels (Blockhuys et al. 2017; Ge et al. 2022; Ishida et al. 2013). Intracellular copper levels could impact on the initiation and progression of cancer, and copper overload could cause cytotoxicity (Tchounwou et al. 2008).Copper dysregulation plays a role in the beginning and development of diseases like cancer. Several types of cancer have been found to have increased levels of copper in malignant tissues, including breast, lung, stomach, ovarian, cervical, and leukemia (Denoyer et al. 2015; Saleh et al. 2020).Cuproptosis is a mechanism of neuronal death that differs from previous recognized procedures (such as pyroptosis, apoptosis, and iron death). Cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis, the three main aspects of cancer progression are all influenced by copper (Hanahan and Weinberg 2011).Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that copper is capable of adhering directly to the lipoacylated elements of the TCA cycle, eventually leading to toxic protein dilatation and death of cells (Shimada et al. 2018; Tsvetkov et al. 2022). Consequently, it is thought that one new therapeutic strategy for killing cancer cells is to increase the buildup of intracellular cancer (Ge et al. 2022).There is convincing evidence linking copper levels to endometrial cancer (Chen 2022). The mechanism states that in UCEC patients, identifying the regulators of the unique type of cell death is essential.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) is a term used to describe non-coding RNAs that exceed 200 nucleotides in length (** techniques. The results indicated that six CRLs features, rather than the entire CRLs, cuproptosis-associated mRNAs, or the whole genome could more accurately identify between patients at low and high risk (Fig. 6A–D). To gain insight into the discrepancies in biochemical functions and signaling molecules between the different risk organizations, we identified differential genes with log2|FC |> 1 and FDR < 0.05 for the sake of GO and KEGG enrichment analysis and visualized the leading 15 outcomes.In GO analysis, the main biological process (Supplementary Table 3) in differential gene enrichment is microtubule − based movement, cilium organization, cilium assembly andcilium movement. The molecular function enrichment was mainly focused on the tubulin binding, microtubule motor activity and cytoskeletal motor activity, while the cellular components were mainly plasma membrane bounded cell projection cytoplasm, motile cilium,and cytoplasmic region (Fig. 6E).Furthermore, depending on KEGG analysis, the molecular pathways of neurodegeneration-multiple diseases, muscular atrophy-lateral sclerosis, and neuroactive ligand receptor interaction were considerably enriched (Fig. 6F).
PCA analysis and enrichment analysis. A–D PCA plots for all risk genes, risk score, CRLs, and cuproptosis-related coding genes. E The circle graph demonstrated that the top GO signaling pathways involved biological processes in BP, MF, and CC. F KEGG analysis of differential genes in the prognostic model’s high- and low-risk groups (circle plot)
We subsequently analyzed the different risk score groups in biological function and pathways by GSEA analysis to further elucidate the variations in biological function between different risk groups.Findings indicated that the calcium signaling pathway, ECM-receptor interaction pathway,neuroactive ligand receptor interaction, heart muscle contraction and dilated cardiomyopathy were more prevalent in the high-risk subgroup (Fig. 7A). Parkinson’s disease, glycerolipid metabolism,oxidative phosphorylation, olfactory transduction, and the ribosome pathway were more prevalent in the low-risk subgroup(Fig. 7B).
Different Risk Groups Have Distinct Immune Profiles
We quantified the enrichment scores of the 23 immune cell subsets and their associated immune functions or immune pathways using ssGSEA aim to better explore the differences in immunological status among the various risk score groups. The findings demonstrated that many immune cell types showed substantial differences with low and high risk scores (P < 0.05, Fig. 8A), including activated CD8+ T cells, eosinophils, immature dendritic cells, MDSC, and monocytes. Additionally, the low-risk score group was more prevalent in Type II IFN Response, Cytolytic activity, T cell co-stimulation, and HLA (P < 0.05, Fig. 8B). To further assess the immune infiltration differences between the high and low risk groups,we validated our data correlated with immune cells by using the “TIMER” (http://timer.cistrome.org) analysis tool.Furthermore, we also used the CIBERSORT algorithm to predict immune cell infiltration in tumor samples(Thorsson et al. 2018), with a high overlap between the results of the different algorithms (Fig. S8A, B).For example, those for ssGSEA,CIBERSORT and TIMER multiple immune infiltrations indicated a link between CD8 + T cell enrichment and low risk scores. Previous studies have also showed that the CD8 + T cells are crucial for protective immunity against intracellular infections and malignancies (Kurachi 2019), indicating that knowing the molecular mechanism of T cell depletion is essential for develo** effective immunotherapeutic approaches.However, due to the diversity of algorithms and the difference of immune cell types, the results of each algorithm also are slightly difference.
Immune cell infiltration features in the risk subgroups. A ssGSEA for the relationship between TIICs and related functions in various risk groups. B Heatmap using the ssGSEA approach to show the variations in immune-related functions between the two risk groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
It is generally recognized that TIICs can influence the immunological microenvironment, which in turn can influence tumor formation. To further comprehend the connection between immune cell invasion and lncRNAs associated to cuproptosis.We created a heatmap to illustrate the connection between immune cells and lncRNAs relevant to cuprotosis (Fig. 9A), then demonstrate how the relationship between the risk index and immune infiltrating cells is statistically significant.Co-expression pattern among immune cells and the risk score based on cuproptosis-related lncRNAs prognosis characteristics were significantly correlated with the infiltration levels of resting DCs (R = − 0.26 P = 8.6e-05), activated DCs (R = 0.3, P = 5.3e-06), macrophages M1 (R = 0.15, P = 0.024), and CD8+T cells (R =− 0.15, P = 0.028), regulatory T cells (treg) (R = − 0.15, P = 0.024) (Fig. 9B-F). In conclusion, the immune cell invasion is linked to the cuproptosis-related lncRNAs of UCEC.
The relationships between the risk scores calculated by the 6-lncRNA signature and immune infiltration cells were evaluated. A A corrplot was employed to demonstrate the association between the 19 immune cells, risk ratings, and the six lncRNAs. B–F Risk assessments and the relationship between various tumor immune cells *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
Alteration Landscapes Among High- and Low-Risk Score Categories
To learn more about the variations in tumor mutation status among the various risk categories, we assessed the tumor mutation burden within these groups. A significant variation in TMB status between the two groups was shown by the TMB analysis (Fig. 10A, B).When compared to the high-risk subset, the low-risk subset exhibited a larger percentage of mutations (Fig. 9G). We separated the UCEC samples into subsets with different mutations by the median TMB score. Patients with low mutation rates significantly outlived those with high mutation rates, the level of TBM load and patients’ overall survival rates were found to be correlated by a Kaplan–Meier analysis (Fig. 9E, F). In the examination of tumor mutations, the low-risk group’s tumor mutation rate reached 99.27%, which was higher than 96.85% in the high-risk group. Among those at low risk score group, the PTEN gene mutation was the most common (81%); Among those at high risk, the TP 53 gene mutation was more common (48%). In addition, missense mutations and single-nucleotide polymorphism mutations were most widespread in the two risk groups (C > T), followed by (C > A). (Fig. 10C, D) illustrates somatic mutation details. The MSI status of the tumor might be categorized into three categories: high (MSI-H), low (MSI-L), and stable (MSS). Our data demonstrate lower risk scores in individuals with MSI-H (high microsatellite instability), compared with two other low microsatellite instability phenotypes, such as MSI-L and MSS, in solid tumors, including endometrial cancer, CRC, and gastric cancer (Fig. 9H, I). These findings imply that endometrial cancer patients’ risk scores due to the six cuproptosis-related lncRNAs could present genomic stability.Considering the findings above, we concluded that risk score model has the ability to predict immunotherapy response.
The mutational patterns and MSI of different populations at risk. A, B Somatic mutations between groups of people with different risk score. C, D The somatic mutation profiles of the high-risk group and low-risk group in UCEC patients. E H-TMB and L-TMB patient subsets’ Kaplan–Meier curves for OS. F The OS Kaplan–Meier curve for TMB plus risk. G The bar plot is used to show the relative frequency of the various risk groups among the low and high mutation groups. H TMB discrepancy between high-risk and low-risk individuals on a violin plot. I Boxplot displaying the risk scores for the MSI-H, MSI-L,and MSS
Sensitivity Testing for Drugs
Given the importance of chemotherapeutic drugs for UCEC, we further performed a sensitivity analysis of chemotherapeutic drugs in different groups and compared the IC50 values of sensitive drugs in patients with the two subtypes. Our findings indicated that low-risk score group had greater MG-132, MS-275 (Entinostat), and Bortezomib IC50 values, while the IC50 values of (5-FU) and PHA-665752 were higher in high-risk score group, which further demonstrated that the statistical significance of differences in commonly used chemotherapy medications divided into risk score categories, which is beneficial to provide a reference for screening sensitive chemotherapeutic drugs in people with diverse risk scores (Fig. 11A, B).
Verification of lncRNA Expression Associated with Cuproptosis
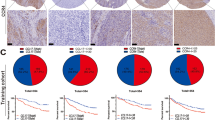
To further validate the results of the bioinformatics analysis described above, qRT-PCR tests were conducted on various endometrial cancer cell lines. Our findings revealed that the expression of AC079466.2, AC090617.5, AC026202.2, and NRAV was markedly increased in the three common endometrial cancer cell lines (HEC-1A, KLE,and Ishikawa cell lines) compared to the human normal endometrial epithelial (HEEC) and endometrial stromal cell line (HESC) (Fig. 12a–d).In addition, our experimental results further showed that the expression level of LINC01545 and AL450384.1 was up-regulated in non-endometrial cancer cell lines, and between the HEEC and HESC cell lines, there was no statistically significant change in the expression of these two genes (Fig. 12e, f). The sequencing process of the target lncRNA was performed at the multicellular line level, so we have every reason to believe in the reliability of the results of this experiment. Overall, the results of this experiment matched our bioinformatics analysis, and further verified validated the accuracy of our risk measurement based on the six lncRNA associated with cuproptosis. For additional assurance that the target gene is expressed at the same level across most cell lines,we further used the cell line database CCLE (Since The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia), the results showed that six lncRNAs were expressed in 28 cervical cancer cell lines and the expression trend was similar to the biocredit analysis (Fig. S12A, B),but there were also differences in expression between the different cell lines.We examined possible causes. Tissues consist of various cells, and lncRNA expression varies among cell lines. The expression in tissues follows the same pattern as in all cells. The cell line we chose may have different lncRNA expression. But what is more noteworthy, we found that only included endometrial cancer cell lines and distant metastatic cell lines lacked non-tumor lines in the CCLE database,it is therefore impossible to contrast the differences between the tumor and non-tumor cell lines.
Verification of the expression level of the six CRLs in UCEC cell lines. a–f Relative expression of six CRLs in tumor cell lines (HEC-1A, KLE, Ishikawa) and normal cell lines (HEEC, HESC).The results of this study were all compared with the expression levels of the HEC-1A cell lines. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
Discussion
UCEC is best commonly diagnosed cancer of the female reproductive system, with the aging population in recent years and the decreasing fertility rate (Tsilidis et al. 2015; Wang et al. 2022a, b), the increasing incidence of endometrial cancer. The research found that the distant metastasis of endometrial cancer patients 5-year survival rate is only 16% (Chen et al. 2021). Although treatment may continue, due to tumor heterogeneity, even if UCEC patients have similar clinical characteristics and treatment, their prognoses can vary greatly. This shows that clinical stage and pathological classification alone are not enough to determine a patient’s prognosis. Early identification of endometrial cancer is difficult without unambiguous signs. Create accurate prognostic indicators to revive the UCEC prognostic forecast, stratify patients by risk profile, and predict drug susceptibility to give patients customized treatment options is essential.
The acknowledgment of RNA regulation as a pivotal aspect in the process of gene expression and the emergence of phenotypic intricacy originated from novel techniques and biological understandings that were established during the period of the 1970s–1980s (Sharp 2009).Extensive investigations into the transcriptome of mammals have revealed that the quantity and diversity of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) surpass those of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that encode proteins. Views on eukaryotic gene expression have changed recently due to the discovery that RNA can produce a great deal of variation (Licatalosi and Darnell 2010).When whole genome sequencing became possible, it was discovered that 99.7% of the coding regions in the human and chimpanzee genomes are the same (Calarco et al. 2022). Several lines of evidence indicate that lncRNA NRAV is involved in the immunological reaction against viruses and is a negative regulator of the antiviral response (Li et al. 2020; Zhang et al. 2018). According to research by Wang et al.,NRAV influences the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to cells of hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion (Peng et al. 2018).Moreover, it has been shown thatNRAV is also a biomarker for clinical prognosis in HCC and low-grade gliomas (Feng et al. 2021; Maimaiti et al. 2021; Xu et al. 2021) LINC01545 is a long interstromal non-coding RNA that has been studied as a biomarker for predicting the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (Qin et al. 2012).Moreover, recent studies have identified AC090617.5 as a predictive indicator for lung adenocarcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer (Yao et al. 2023), the conclusions concur with our findings, in which AC090617.5 also plays a protective role.So far, the functions and detailed molecular interaction mechanisms of the remaining three lncRNAs have not been further explained.To completely understand the roles performed through these lncRNAs, further research is therefore required.
We adopted GO and KEGG enriched analysis investigated the differences in gene expression between the low and high categories to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying endometrial cancer-related genes. The findings indicate that the molecular function enrichment of DEGs is primarily concentrated on extracellular structural organization and external encapsulated structural organization.The main manifestations of molecular function enrichment are signaling receptor activator, receptor ligand activity, and sulfur compound binding, the main cellular component is the type I collagen containing extracellular matrix KEGG analysis showed that DEGs in neurodegeneration-a variety of disease pathways, muscle atrophy-lateral sclerosis, neuroactive ligand receptor interaction and other molecular pathways. Tumor cells, stromal cells, and extracellular matrix make up the majority of the TME (ECM). Tumor cells are involved in tumor progression, which is strongly related to other TME components (Pitt et al. 2016), especially the immune cells. And tumor patients for immunotherapy responsiveness, can be evaluated by TMB, TMB reflects the variation of tumor cell genome, high TMB (TMB-H) tumor patients have the potential to get more new antigen, and is related to tumor heterogeneity, theoretically high TMB can enhance tumor immunogenicity and reaction with ICI. Numerous studies have established that a high TMB is linked to a significant benefit from immunotherapy. According to our results, TMB was more prevalent in low-risk score group, and the survival study using TMB data and risk stratification demonstrated that people with high mutation load and low risk score had the best prognosis. When DNA mismatch repair (mismatch repair, MMR) function abnormal, microsatellite replication errors are not corrected and accumulated, makes the microsatellite sequence length or base composition changes, called microsatellite instability (microsatellite instability, MSI), at the same time can lead to genome present high mutation phenotype, and the study found that MSI is a predictor of immunotherapy efficacy in advanced solid tumors. The proportion of microsatellite height instability (MSI-high, MSI-H) was significantly higher in the low-risk category (41% VS 23%) than in the high-risk category, however according our research results. This research backs up our hypothesis that people with the disease with low risk will respond positively to immunotherapy and benefit more from it.
Additionally, we performed a susceptibility analysis on individuals with various risk scores (Zhang et al. 2022), and in the end, we discovered a connection between five chemotherapy medications and the risk score, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and PHA-665752 were connected with the lower risk score.Compared to the lower risk category, the greater risk category had higher IC50 values, and the other three drugs’ IC50-value, MG-132, MS-275 (Entinostat), Bortezomib was linked to a lower risk score, and in the low-risk group, the IC50 value was lower than it was in the high-risk group.5-FU is the first antimetabolizing drug synthesized according to certain assumptions, and it is the most widely used anti-pyrimidine drug clinically. It has good efficacy on digestive tract cancer and other solid tumors, and is crucial in the management of medical oncology. A new target for many solid cancers is the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase (including lung cancer). PHA665752 in mouse xenografts from small cell (NCI-H441 and A549) and non-small cell (NCI-H441 and A549) lung cancer cell lines(NCI-H69), angiogenic conversion was caused by in of c-Met phosphorylation and angiogenesis at the c-Cbl binding site, due to this, thrombsinin-1 synthesis increased whereas vascular endothelial growth factor production dropped (Crosswell et al. 2009).These investigations indicate the effectiveness of competitive small-molecule ATP inhibitors in selective c-Met targeting, and they propose that PHA665752 could offer a potential tumor therapeutic approach. Bortezomib and MG-132 both belong to the proteasome inhibitor class of drugs, which are currently used in the treatment of various tumor diseases, and have achieved outstanding clinical effects. According to numerous studies, bortezomib inhibits the expansion of tumor cells by influencing the proteins associated to apoptosis, such as nuclear transcription factors, intra-cell apoptosis signals, and cell-cycle-related proteins. While Entinostat is a well-tolerated HDAC inhibitor and has shown its therapeutic potential in both solid and hematological tumors. Despite the fact that the effect of some medicines in UCEC has not been studied, our findings might offer fresh suggestions for their treatment.
There have been several previous reports on the establishment of cuproptosis-related lncRNA models for predicting the prognosis of UCEC (Hu et al., 2023; Qi et al. 2023). Compared to a study by Qi et al., our model incorporated new lncRNAs (LINC01545, NRAV, AL450384.1, AC079466.2 and AC090617.5), and we further explored differential expression of lncRNAs in the model as well as CCLE database. Overall, the actual survival and predicted survival of the nomogram in our signature showed good consistency, as indicated by calibration curves. When evaluating survival predictions, AUCs at 1, 3 and 5 year were 0.778, 0.810 and 0.854 for the training group, respectively, which were significantly higher than those of previous studies.Our signature was also valuable for predicting PFS in UCEC patients. In summary, our prognostic model has good and stable prognostic prediction ability.
Finally, the identification of regulatory linkages between mRNA, lncRNA, and miRNA in UCEC holds potential for advancing our understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in UCEC formation. This knowledge can contribute to the improvement of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for UCEC, as well as the creation of tailored pharmaceutical interventions (Zhou et al. 2023). The first step in exploring ceRNA is finding miRNA that may bind lncRNA.Therefore, we predicted the downstream target genes of CRLs and visualized the results using the Cytoscape program (Fig.S?).The results showed that AL450384.1 and AC079466.2 may be regulatory hubs, AL450384.1 may exert a biological function by regulating downstream microRNA-181.Previous studies have shown that the miR-181 family is dysregulated in multiple tumor tissues,and plays a key role in carcinogenesis, Rezaei et al. believe that microRNA-181 plays a dual role in the development of human cancer (Rezaei et al. 2020).In addition,our data also reveal a substantial correlation of CRLs with miR-3140, Feng, et al. found Hypoxia-induced circCCDC66 promotes the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer via the miR-3140/autophagy pathway (Feng et al. 2020) which may open up new UCEC research avenues.However, the impact of these pathways on tumor formation requires further validation through foundational tests.
Furthermore,some limitations of our study remain. For example, more clinical groups may be needed to cross-verify the prognostic accuracy and predictability of the characteristic. Furthermore, additional research is required to understand the mechanisms underlying the association as between cuproptosis-related lncRNAs and the prognosis of the UCEC.
Conclusions
In conclusion,our research establishes a novel predictive model with six genes and speculate that cuproptosis may play a role in the development of UCEC. And we find that CRLs are significantly associated with abnormal immune infiltration expression and may be important genes for immune regulation of UCEC. Moreover, CRLs gene has a high predictive value for the prognostic risk of UCEC patients and can provide a reference for guiding immunotherapy in UCEC patients.
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- UCEC:
-
Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
- CRLs:
-
Cuproptosis-related lncRNAs
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- GDSC:
-
Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer
- TME:
-
Tumor Microenvironment
- IC50:
-
Half-maximal inhibitory concentration
References
Blockhuys S, Celauro E, Hildesjö C, Feizi A, Stål O, Fierro-González JC, Wittung-Stafshede P (2017) Defining the human copper proteome and analysis of its expression variation in cancers. Metallomics 9(2):112–123. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mt00202a
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Calarco JA, **ng Y, Cáceres M, Calarco JP, **ao X, Pan Q, Blencowe BJ (2007) Global analysis of alternative splicing differences between humans and chimpanzees. Genes Dev 21(22):2963–2975. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1606907
Chen Y (2022) Identification and validation of cuproptosis-related prognostic signature and associated regulatory axis in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. Front Genet 13:912037. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.912037
Chen S, Gu J, Zhang Q, Hu Y, Ge Y (2021) Development of biomarker signatures associated with anoikis to predict prognosis in endometrial carcinoma patients. J Oncol 2021:3375297. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3375297
Choudhari R, Sedano MJ, Harrison AL, Subramani R, Lin KY, Ramos EI, Gadad SS (2020) Chapter three - long noncoding RNAs in cancer: from discovery to therapeutic targets. In: Makowski GS (ed) Advances in clinical chemistry, vol 95. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 105–147
Crosswell HE, Dasgupta A, Alvarado CS, Watt T, Christensen JG, De P, Findley HW (2009) PHA665752, a small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met, inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated migration and proliferation of c-Met-positive neuroblastoma cells. BMC Cancer 9:411. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-4112
Denoyer D, Masaldan S, La Fontaine S, Cater MA (2015) Targeting copper in cancer therapy: ‘Copper That Cancer.’ Metallomics 7(11):1459–1476. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mt00149h
Du XH, Wei H, Qu GX, Tian ZC, Yao WT, Cai QQ (2020) Gene expression regulations by long noncoding RNAs and their roles in cancer. Pathol Res Pract 216(6):152983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.152983
Feng J, Li Z, Li L, **e H, Lu Q, He X (2020) Hypoxia-induced circCCDC66 promotes the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer via the miR-3140/autophagy pathway. Int J Mol Med 46(6):1973–1982. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4747
Feng Y, Hu X, Ma K, Zhang B, Sun C (2021) Genome-wide screening identifies prognostic long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int 2021:6640652. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6640652
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 33(1):1–22
Ge EJ, Bush AI, Casini A, Cobine PA, Cross JR, DeNicola GM, Chang CJ (2022) Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 22(2):102–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2
Geeleher P, Cox N, Huang RS (2014) pRRophetic: an R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107468
Gu B, Shang X, Yan M, Li X, Wang W, Wang Q, Zhang C (2021) Variations in incidence and mortality rates of endometrial cancer at the global, regional, and national levels, 1990–2019. Gynecol Oncol 161(2):573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2021.01.036
Guo T, Jiang L, Wang T, Zhang J, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang X (2023) Screening and identification of prognostic genes associated with eosinophilic features of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Heliyon 9(6):e16479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16479
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Hu P, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhao L, Qi C, Jiang G (2023) Development and verification of a newly established cuproptosis-associated lncRNA model for predicting overall survival in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res 12(8):1963–1979. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-23-61
Ishida S, Andreux P, Poitry-Yamate C, Auwerx J, Hanahan D (2013) Bioavailable copper modulates oxidative phosphorylation and growth of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(48):19507–19512. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318431110
Kamarudin AN, Cox T, Kolamunnage-Dona R (2017) Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: current methods and applications. BMC Med Res Methodol 17(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-017-0332-6
Kurachi M (2019) CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Semin Immunopathol 41(3):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-019-00744-5
Li J, Li M, Wang X, Sun M, Ma C, Liang W, Wei L (2020) Long noncoding RNA NRAV promotes respiratory syncytial virus replication by targeting the MicroRNA miR-509–3p/Rab5c axis to regulate vesicle transportation. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00113-20
Licatalosi DD, Darnell RB (2010) RNA processing and its regulation: global insights into biological networks. Nat Rev Genet 11(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2673
Liu X, Zhou L, Gao M, Dong S, Hu Y, Hu C (2022) Signature of seven cuproptosis-related lncRNAs as a novel biomarker to predict prognosis and therapeutic response in cervical cancer. Front Genet 13:989646. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.989646
Maimaiti A, Jiang L, Wang X, Shi X, Pei Y, Hao Y, Kasimu M (2021) Identification and validation of an individualized prognostic signature of lower-grade glioma based on nine immune related long non-coding RNA. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 201:106464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106464
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C, Koeffler HP (2018) Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res 28(11):1747–1756. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.239244.118
Peng X, Chen Z, Farshidfar F, Xu X, Lorenzi PL, Wang Y, Liang H (2018) Molecular characterization and clinical relevance of metabolic expression subtypes in human cancers. Cell Rep 23(1):255-269.e254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.077
Pitt JM, Marabelle A, Eggermont A, Soria JC, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L (2016) Targeting the tumor microenvironment: removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann Oncol 27(8):1482–1492. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw168
Qi S, Feng H, Li X (2023) LncRNAs signatures associated with cuproptosis predict the prognosis of endometrial cancer. Front Genet 14:1120089. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1120089
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11450
Rezaei T, Amini M, Hashemi ZS, Mansoori B, Rezaei S, Karami H, Baradaran B (2020) MicroRNA-181 serves as a dual-role regulator in the development of human cancers. Free Radic Biol Med 152:432–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.043
Saleh SAK, Adly HM, Abdelkhaliq AA, Nassir AM (2020) Serum levels of selenium, zinc, copper, manganese, and iron in prostate cancer patients. Curr Urol 14(1):44–49. https://doi.org/10.1159/000499261
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA (2018) Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg 126(5):1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.0000000000002864
Sharp PA (2009) The centrality of RNA. Cell 136(4):577–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.007
Shen S, Wang G, Zhang R, Zhao Y, Yu H, Wei Y, Chen F (2019) Development and validation of an immune gene-set based Prognostic signature in ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine 40:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.054
Shen Y, Peng X, Shen C (2020) Identification and validation of immune-related lncRNA prognostic signature for breast cancer. Genomics 112(3):2640–2646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.02.015
Shi H, Jiang Y, Yang Y, Peng Y, Li C (2021) Copper metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: an update. Biometals 34(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00264-y
Shimada K, Reznik E, Stokes ME, Krishnamoorthy L, Bos PH, Song Y, Stockwell BR (2018) Copper-binding small molecule induces oxidative stress and cell-cycle arrest in glioblastoma-patient-derived cells. Cell Chem Biol 25(5):585-594.e587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.02.010
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Tchounwou PB, Newsome C, Williams J, Glass K (2008) Copper-induced cytotoxicity and transcriptional activation of stress genes in human liver carcinoma (HepG(2)) cells. Met Ions Biol Med 10:285–290
Thorsson V, Gibbs DL, Brown SD, Wolf D, Bortone DS, Ou Yang TH, Shmulevich I (2018) The immune landscape of cancer. Immunity 48(4):812-830.e814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.023
Tsilidis KK, Kasimis JC, Lopez DS, Ntzani EE, Ioannidis JP (2015) Type 2 diabetes and cancer: umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. BMJ 350:g7607. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7607
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Golub TR (2022) Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 375(6586):1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf0529
Wang Y, Zeng X, Tan J, Xu Y, Yi C (2022a) Diabetes mellitus and endometrial carcinoma: Risk factors and etiological links. Medicine (baltimore) 101(34):e30299. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000030299
Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhou F (2022b) Cuproptosis: a new form of programmed cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 19(8):867–868. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-022-00866-1
**ao X, Zhu W, Liao B, Xu J, Gu C, Ji B, Yang J (2018) BPLLDA: predicting lncrna-disease associations based on simple paths with limited lengths in a heterogeneous network. Front Genet 9:411. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00411
Xu Q, Wang Y, Huang W (2021) Identification of immune-related lncRNA signature for predicting immune checkpoint blockade and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol 92:107333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107333
Yao H, Jiang X, Fu H, Yang Y, ** Q, Zhang W, Zhou S (2022) Exploration of the immune-related long noncoding rna prognostic signature and inflammatory microenvironment for cervical cancer. Front Pharmacol 13:870221. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.870221
Yao Y, Yang F, Chen A, Hua Q, Gao W (2023) Costimulatory molecule-related lncRNA model as a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med 12(5):6419–6436. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.5391
Zhang L, Wei TT, Li Y, Li J, Fan Y, Huang FQ, Qi LW (2018) Functional metabolomics characterizes a key role for N-acetylneuraminic acid in coronary artery diseases. Circulation 137(13):1374–1390. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.117.031139
Zhang W, Cao W, Tong Z, ** Q, Jiang X, Yang Y, Zhou S (2022) Identification and validation of a novel necroptosis-related prognostic signature in cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 12:1011000. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1011000
Zhou X, Zhang H, Duan Y, Zhu J, Dai H (2023) m6A-related long noncoding RNAs predict prognosis and indicate therapeutic response in endometrial carcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal 37(1):e24813. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24813
Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge the contributions from TCGA project.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province (Grant Number KJ2021A0352), the Research Fund Project of Anhui Medical University (Grant Number 2020xkj236), and the Applied Medicine Research Project of Hefei Health Commission (Grant Number HWKJ2019-172-14), the Postgraduate Innovation Research and Practice Program of Anhui Medical University (YJS20230095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, XYJ and JJH; data curation, WYZ and HY; formal analysis, WYZ and XYJ; funding acquisition, SGZ; investigation, YTY; GC and QQJ; methodology, LH and JM; project administration, RW and JJL; software, FT and JJH; validation, YL, LZ and SXC; visualization, YH and YS; writing–original draft, XYJ; writing—review and editing, SGZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
As the sequencing data for the datasets used in the text are publicly available, there is no need for additional ethics committee approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2023_10574_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 2395 KB)— Supplementary Table 1.19 cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) were acquired from TCGA and previous publications. Supplementary Table 2.Clinicopathologic characteristics in entire, testing, and training groups.Supplementary Table3.The sequences of primers used in our study.FIG.S3 Train,test and all cohort clinical characteristics and risk score ROC curves.Fig.S8-A Results of immune cell infiltration under the TIMER algorithm.Fig.S8-B The relationship between immune cell infiltration analysis using the CIBERSORT algorithm and CRLs score.Fig.S12 CCLE database validation.Fig.S13 Network interaction regulation of CRLs and miRNA composition.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, XY., Hu, JJ., Wang, R. et al. Cuproptosis-Associated lncRNA Gene Signature Establishes New Prognostic Profile and Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Endometrial Carcinoma. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10574-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10574-8