Abstract
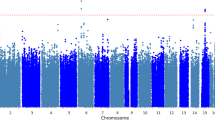
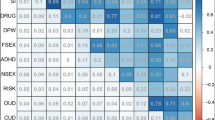
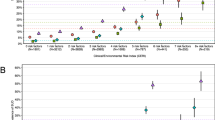
This study presents results from a collaboration across five longitudinal studies seeking to test and replicate models of gene–environment interplay in the development of substance use and externalizing disorders (SUDs, EXT). We describe an overview of our conceptual models, plan for gene–environment interplay analyses, and present main effects results evaluating six candidate genes potentially relevant to SUDs and EXT (MAOA, 5-HTTLPR, COMT, DRD2, DAT1, and DRD4). All samples included rich longitudinal and phenotypic measurements from childhood/adolescence (ages 5–13) through early adulthood (ages 25–33); sample sizes ranged from 3487 in the test sample, to ~600–1000 in the replication samples. Phenotypes included lifetime symptom counts of SUDs (nicotine, alcohol and cannabis), adult antisocial behavior, and an aggregate externalizing disorder composite. Covariates included the first 10 ancestral principal components computed using all autosomal markers in subjects across the data sets, and age at the most recent assessment. Sex, ancestry, and exposure effects were thoroughly evaluated. After correcting for multiple testing, only one significant main effect was found in the test sample, but it was not replicated. Implications for subsequent gene–environment interplay analyses are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We checked to see whether normalizing the genetic risk score (calculated by dividing by the number of assessed risk alleles in each person) impacted results in the test sample (MCTFR). The correlation between the original genetic risk score and the normalized genetic risk score was nearly perfect (r = .98, p < .001), suggesting limited impact. We also checked whether the pattern of results changed as a result of using the normalized variable in the test sample and found essentially identical results.
References
APA (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC
August GJ, Realmuto GM, Crosby RD, MacDonald AW 3rd (1995) Community-based multiple-gate screening of children at risk for conduct disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 23(4):521–544
Bailey JA, Hill KG, Meacham MC, Young SE, Hawkins JD (2011) Strategies for characterizing complex phenotypes and environments: general and specific family environmental predictors of young adult tobacco dependence, alcohol use disorder, and co-occurring problems. Drug Alcohol Depend 118(2–3):444–451
Bailey JA, Samek DR, Keyes MA, Hill KG, Hicks BM, McGue M, Iacono WG, Epstein M, Catalano RF, Haggerty KP, Hawkins JD (2014) General and substance-specific predictors of young adult nicotine dependence, alcohol use disorder, and problem behavior: replication in two samples. Drug Alcohol Depend 138:161–168
Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van Ijzendoorn MH (2011) Differential susceptibility to rearing environment depending on dopamine-related genes: new evidence and a meta-analysis. Dev Psychopathol 23(1):39–52
Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van IJzendoorn MH (2015) The hidden efficacy of interventions: gene × environment experiments from a differential susceptibility perspective. Annu Rev Psychol 66:66381–66409
Bierut LJ, Agrawal A, Bucholz KK, Doheny KF, Laurie C, Pugh E et al (2010) A Genome-Wide Association study of alcohol depdence. PNAS 107(11):5082–5087
Borenstein M, Hedges L, Higgins J, Rothstein H (2005) Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 2. Biostat, Englewood
Bronfenbrenner U, Ceci SJ (1994) Nature-nurture reconceptualized in developmental perspective: a bioecological model. Psychol Rev 101(4):568–586
Brookes K, Xu X, Chen W, Zhou K, Neale B, Lowe N, Anney R, Franke B, Gill M, Ebstein R, Buitelaar J, Sham P, Campbell D, Knight J, Andreou P, Altink M, Arnold R, Boer F, Buschgens C, Butler L, Christiansen H, Feldman L, Fleischman K, Fliers E, Howe-Forbes R, Goldfarb A, Heise A, Gabriels I, Korn-Lubetzki I, Johansson L, Marco R, Medad S, Minderaa R, Mulas F, Muller U, Mulligan A, Rabin K, Rommelse N, Sethna V, Sorohan J, Uebel H, Psychogiou L, Weeks A, Barrett R, Craig I, Banaschewski T, Sonuga-Barke EJS, Eisenberg J, Kuntsi J, Manor I, McGuffin P, Miranda A, D Oades R, Plomin R, Roeyers H, Rothenberger A, Sergeant J, Steinhausen HC, Taylor E, Thompson M, Faraone SV, Asherson P (2006) The analysis of 51 genes in DSM-IV combined type Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: association signals in DRD4, DAT1 and 16 other genes (vol 11, pg 934, 2006). Mol Psychiatry 11(12):1139
Brown EC, Catalano RF, Fleming CB, Haggerty KP, Abbott RD (2005) Adolescent substance use outcomes in the Raising Healthy Children project: a two-part latent growth curve analysis. J Consult Clin Psychol 73(4):699–710
Byrd AL, Manuck SB (2014) MAOA, childhood maltreatment, and antisocial behavior: meta-analysis of a gene–environment interaction. Biol Psychiatry 75(1):9–17
Caspi A, McClay J, Moffitt TE, Mill J, Martin J, Craig IW, Taylor A, Poulton R (2002) Role of genotype in the cycle of violence in maltreated children. Science 297(5582):851–854
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301(5631):386–389
Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Cannon M, McClay J, Murray R, Harrington H, Taylor A, Arseneault L, Williams B, Braithwaite A, Poulton R, Craig IW (2005) Moderation of the effect of adolescent-onset cannabis use on adult psychosis by a functional polymorphism in the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene: longitudinal evidence of a gene × environment interaction. Biol Psychiatry 57(10):1117–1127
Catalano RF, Mazza JJ, Harachi TW, Abbott RD, Haggerty KP, Fleming CB (2003) Raising healthy children through enhancing social development in elementary school: results after 1.5 years. J Sch Psychol 41:143–164
Chabris CF, Hebert BM, Benjamin DJ, Beauchamp J, Cesarini D, van der Loos M, Johannesson M, Magnusson PK, Lichtenstein P, Atwood CS, Freese J, Hauser TS, Hauser RM, Christakis N, Laibson D (2012) Most reported genetic associations with general intelligence are probably false positives. Psychol Sci 23(11):1314–1323
Chassin L, Fora DB, King KM (2004) Trajectories of alcohol and drug use and dependence from adolescence to adulthood: the effects of familial alcoholism and personality. J Abnorm Psychol 113(4):483–498
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analyses for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawurence Earlbaum Associates, Hillside, NJ
Dick DM, Aliev F, Krueger RF, Edwards A, Agrawal A, Lynskey M et al (2011) Genome-Wide Association study of conduct disorder symptomatology. Mol Psychiatry 16:800–808
Dick DM, Agrawal A, Keller MC, Adkins A, Aliev F, Monroe S, Hewitt JK, Kendler KS, Sher KJ (2015) Candidate gene–environment interaction research: reflections and recommendations. Perspect Psychol Sci 10(1):37–59
Duncan LE, Keller MC (2011) A critical review of the first 10 years of candidate gene-by-environment interaction research in psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry 168(10):1041–1049
Duncan LE, Pollastri AR, Smoller JW (2014) Mind the gap: why many geneticists and psychological scientists have discrepant views about gene–environment interaction (G × E) research. Am Psychol 69(3):249–268
Durbin CE, Hicks BM (2014) Personality and psychopathology: a stagnant field in need of development. Eur J Personal 28(4):362–386
Epstein M, Hill KG, Bailey JA, Hawkins JD (2013) The effect of general and drug-specific family environments on comorbid and drug-specific problem behavior: a longitudinal examination. Dev Psychol 49(6):1151–1164
Estrada G, Fatjo-Vilas M, Munoz MJ, Pulido G, Minano MJ, Toledo E, Illa JM, Martin M, Miralles ML, Miret S, Campanera S, Bernabeu C, Navarro ME, Fananas L (2011) Cannabis use and age at onset of psychosis: further evidence of interaction with COMT Val158Met polymorphism. Acta Psychiatr Scand 123(6):485–492
Faraone SV, Doyle AE, Mick E, Biederman J (2001) Meta-analysis of the association between the 7-repeat allele of the dopamine D-4 receptor gene and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Am J Psychiatry 158(7):1052–1057
Feinn R, Nellissery M, Kranzler HR (2005) Meta-analysis of the association of a functional serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism with alcohol dependence. Am J Med Genet Part B 133b(1):79–84
Ficks CA, Waldman ID (2014) Candidate genes for aggression and antisocial behavior: a meta-analysis of association studies of the 5HTTLPR and MAOA-uVNTR. Behav Genet 44(5):427–444
Forero DA, Lopez-Leon S, Shin HD, Park BL, Kim DJ (2015) Meta-analysis of six genes (BDNF, DRD1, DRD3, DRD4, GRIN2B and MAOA) involved in neuroplasticity and the risk for alcohol dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 149:259–263
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Koesterer R, Smith AH et al (2014) Genome-Wide Association study of alcohol dependence: significant findings in African and European-Americans including novel risk loci. Mol Psychiatry 19:41–49
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Herman AI, Koesterer R, Zhao H, Farrer LA (2015) Genome-Wide Association study of nicotine dependence in American populations: identification of novel risk loci in both African-Americans and European-Americans. Biol Psychiatry 77(5):493–503
Haberstick BC, Smolen A (2004) Genoty** of three single nucleotide polymorphisms following whole genome preamplification of DNA collected from buccal cells. Behav Genet 34(5):541–547
Haberstick BC, Smolen A, Stetler GL, Tabor JW, Roy T, Casey R et al (2014) Simple sequence repeats in the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health: an ethnically diverse resource for genetic analysis of health and behavior. Behav Genet 44:487–497
Haggerty KP, Fleming CB, Catalano RF, Harachi TW, Abbott RD (2006) Raising healthy children: examining the impact of promoting healthy driving behavior within a social development intervention. Prev Sci 7(3):257–267
Hawkins JD, Catalano RF, Miller JY (1992) Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychol Bull 112(1):64–105
Hawkins JD, Catalano RF, Kosterman R, Abbott R, Hill KG (1999) Preventing adolescent health-risk behaviors by strengthening protection during childhood. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 153(3):226–234
Hawkins JD, Smith BH, Hill KG, Kosterman R, Catalano RF, Abbott RD (2003) Understanding and preventing crime and violence: findings from the Seattle SOcial Development Project. In: Thornberry TP, Krohn MD (eds) Taking stock of juvenile delinquency: an overview of findings from contemporary longitudinal studies. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 255–312
Hawkins JD, Kosterman R, Catalano RF, Hill KG, Abbott RD (2005) Promoting positive adult functioning through social development intervention in childhood—long-term effects from the Seattle Social Development Project. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 159(1):25–31
Hewitt JK (2012) Editorial policy on candidate gene association and candidate gene-by-environment interaction studies of complex traits. Behav Genet 42(1):1–2
Hicks BM, Durbin CE, Blonigen DM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2012) Relationship between personality change and the onset and course of alcohol dependence in young adulthood. Addiction 107(3):540–548
Hill KG, Hawkins JD, Bailey JA, Catalano RF, Abbott RD, Shapiro VB (2010) Person-environment interaction in the prediction of alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence in adulthood. Drug Alcohol Depend 110(1–2):62–69
Hung CF, Lung FW, Hung TH, Chong MY, Wu CK, Wen JK, Lin PY (2012) Monoamine oxidase A gene polymorphism and suicide: an association study and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 136(3):643–649
Iacono WG, Carlson SR, Taylor J, Elkins IJ, McGue M (1999) Behavioral disinhibition and the development of substance-use disorders: findings from the Minnesota Twin Family Study. Dev Psychopathol 11(4):869–900
Johnson W, McGue M, Iacono WG (2009) School performance and genetic and environmental variance in antisocial behavior at the transition from adolescence to adulthood. Dev Psychol 45(4):973–987
Johnston C, Lahey BB, Matthys W (2013) Editorial policy for candidate gene studies. J Abnorm Child Psychol 41(4):511–514
Jonas KG, Markon KE (2014) A meta-analytic evaluation of the endophenotype hypothesis: effects of measurement paradigm in the psychiatric genetics of impulsivity. J Abnorm Psychol 123(3):660–675
Karg K, Burmeister M, Shedden K, Sen S (2011) The serotonin transporter promoter variant (5-HTTLPR), stress, and depression meta-analysis revisited: evidence of genetic moderation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68(5):444–454
Keller MC (2014) Gene × environment interaction studies have not properly controlled for potential confounders: the problem and the (simple) solution. Biol Psychiatry 75(1):18–24
Kendler KS, Gardner C, Dick DM (2011) Predicting alcohol consumption in adolescence from alcohol-specific and general externalizing genetic risk factors, key environmental exposures and their interaction. Psychol Med 41(7):1507–1516
Kim-Cohen J, Caspi A, Taylor A, Williams B, Newcombe R, Craig IW, Moffitt TE (2006) MAOA, maltreatment, and gene–environment interaction predicting children’s mental health: new evidence and a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 11(10):903–913
Kluger AN, Siegfried Z, Ebstein RP (2002) A meta-analysis of the association between DRD4 polymorphism and novelty seeking. Mol Psychiatry 7(7):712–717
Lee YH, Song GG (2014) COMT Val158Met and PPAR gamma Pro12Ala polymorphisms and susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 35(5):643–651
Lesch KP (2014) Editorial: Illuminating the dark matter of developmental neuropsychiatric genetics—strategic focus for future research in child psychology and psychiatry. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 55(3):201–203
Li DW, Sham PC, Owen MJ, He L (2006) Meta-analysis shows significant association between dopamine system genes and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Hum Mol Genet 15(14):2276–2284
Lopez LS, Croes EA, Sayed-Tabatabaei FA, Claes S, Van Broeckhoven C, van Duijn CM (2005) The dopamine D4 receptor gene 48-base-pair-repeat polymorphism and mood disorders: a meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 57(9):999–1003
Loukola A, Buchwald J, Gupta R, Palviainen T, Hallfors J, Tikkanen E et al (2015) A Genome-Wide Association study of a biomarker of nicotine metabolism. PLoS Genet 11(9):e1005498
Maher BS, Marazita ML, Ferrell RE, Vanyukov MM (2002) Dopamine system genes and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: a meta-analysis. Psychiatr Genet 12(4):207–215
McGue M, Slutske W, Taylor J, Iacono WG (1997) Personality and substance use disorders: I. Effects of gender and alcoholism subtype. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21(3):513–520
McGue M, Slutske W, Iacono WG (1999) Personality and substance use disorders: II. Alcoholism versus drug use disorders. J Consult Clin Psychol 67(3):394–404
McGue M, Keyes M, Sharma A, Elkins I, Legrand L, Johnson W, Iacono WG (2007) The environments of adopted and non-adopted youth: evidence on range restriction from the Sibling Interaction and Behavior Study (SIBS). Behav Genet 37(3):449–462
McGue M, Zhang Y, Miller MB, Basu S, Vrieze S, Hicks B, Malone S, Oetting WS, Iacono WG (2013) A Genome-Wide Association Study of behavioral disinhibition. Behav Genet 43(5):363–373
Miller MB, Basu S, Cunningham J, Eskin E, Malone SM, Oetting WS, Schork N, Sul JH, Iacono WG, McGue M (2012) The Minnesota Center for Twin and Family Research Genome-Wide Association study. Twin Res Hum Genet 15(6):767–774
Miller R, Wankerl M, Stalder T, Kirschbaum C, Alexander N (2013) The serotonin transporter gene-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) and cortisol stress reactivity: a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 18(9):1018–1024
Monroe SM, Simons AD (1991) Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychol Bull 110(3):406–425
Munafo MR, Gage SH (2013) Improving the reliability and reporting of genetic association studies. Drug Alcohol Depend 132(3):411–413
Munafo MR, Bowes L, Clark TG, Flint J (2005) Lack of association of the COMT (Val(158/108) Met) gene and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Mol Psychiatry 10(8):765–770
Munafo MR, Yalcin B, Willis-Owen SA, Flint J (2008) Association of the dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene and approach-related personality traits: meta-analysis and new data. Biol Psychiatry 63(2):197–206
Munafo MR, Durrant C, Lewis G, Flint J (2009a) Gene × environment interactions at the serotonin transporter locus. Biol Psychiatry 65(3):211–219
Munafo MR, Timpson NJ, David SP, Ebrahim S, Lawlor DA (2009b) Association of the DRD2 gene Taq1A polymorphism and smoking behavior: a meta-analysis and new data. Nicotine Tob Res 11(1):64–76
Murphy SE, Norbury R, Godlewska BR, Cowen PJ, Mannie ZM, Harmer CJ, Munafo MR (2013) The effect of the serotonin transporter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) on amygdala function: a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 18(4):512–520
Muthén LK, Muthén BO (1998–2012) Mplus User’s Guide, 7th edition. Muthén and Muthén Los Angeles, CA
Neville MJ, Johnstone EC, Walton RT (2004) Identification and characterization of ANKK1: a novel kinase gene closely linked to DRD2 on chromosome band 11q23.1. Hum Mutat 23:540–545
Nikolaidis A, Gray JR (2010) ADHD and the DRD4 exon III 7-repeat polymorphism: an international meta-analysis. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 5(2–3):188–193
Ohmoto M, Sakaishi K, Hama A, Morita A, Nomura M, Mitsumoto Y (2013) Association between dopamine receptor 2 TaqIA polymorphisms and smoking behavior with an influence of ethnicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis update. Nicotine Tob Res 15(3):633–642
Peterson PA, Brown SP (2005) On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol 90(1):175–181
Quinn PD, Fromme K (2011) The role of person–environment interactions in increased alcohol use in the transition to college. Addiction 106(6):1104–1113
Quinn PD, Harden KP (2013) Differential changes in impulsivity and sensation seeking and the escalation of substance use from adolescence to early adulthood. Dev Psychopathol 25(1):223–239
Reif A, Weber H, Domschke K, Klauke B, Baumann C, Jacob CP, Strohle A, Gerlach AL, Alpers GW, Pauli P, Hamm A, Kircher T, Arolt V, Wittchen HU, Binder EB, Erhardt A, Deckert J (2012) Meta-analysis argues for a female-specific role of MAOA-uVNTR in panic disorder in four European populations. Am J Med Genet Part B 159(7):786–793
Reif A, Richter J, Straube B, Hofler M, Lueken U, Gloster AT, Weber H, Domschke K, Fehm L, Strohle A, Jansen A, Gerlach A, Pyka M, Reinhardt I, Konrad C, Wittmann A, Pfleiderer B, Alpers GW, Pauli P, Lang T, Arolt V, Wittchen HU, Hamm A, Kircher T, Deckert J (2014) MAOA and mechanisms of panic disorder revisited: from bench to molecular psychotherapy. Mol Psychiatry 19(1):122–128
Risch N, Herrell R, Lehner T, Liang KY, Eaves L, Hoh J, Griem A, Kovacs M, Ott J, Merikangas KR (2009) Interaction between the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR), stressful life events, and risk of depression: a meta-analysis. JAMA 301(23):2462–2471
Robins LN, Helzer JE, Croughan J, Williams JBW, Spitzer RL (1981) NIMH diagnostic interview schedule: version III. National Institute of Mental Health, Rockville
Robins LN, Wing J, Wittchen HU, Helzer JE, Babor TF, Burke J, Farmer A, Jablenski A, Pickens R, Regier DA et al (1988) The Composite International Diagnostic Interview. An epidemiologic Instrument suitable for use in conjunction with different diagnostic systems and in different cultures. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45(12):1069–1077
Rutter M (2012) Response to commentaries on discussion paper gene–environment interdependence. Eur J Dev Psychol 9(4):426–431
Samek DR, Keyes MA, Hicks BM, Bailey J, McGue M, Iacono WG (2014) General and specific predictors of nicotine and alcohol dependence in early adulthood: genetic and environmental influences. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 75(4):623–634
Samek DR, Hicks BM, Keyes MA, Bailey J, McGue M, Iacono WG (2015) Gene–environment interplay between parent–child relationship problems and externalizing disorders in adolescence and young adulthood. Psychol Med 45(2):333–344
Samek DR, Hicks BM, Keyes MA, McGue M, Iacono WG (2016) Antisocial peer affiliation and externalizing disorders: evidence for gene × environment × development interaction. Dev Psychopathol. doi:10.1017/S0954579416000109
Sameroff AJ, Mackenzie MJ (2003) Research strategies for capturing transactional models of development: the limits of the possible. Dev Psychopathol 15(3):613–640
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Gibbon M (1987) Structured clinical interview for DSM-III-R (SCID). New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research, New York
Stapleton JA, Sutherland G, O’Gara C (2007) Association between dopamine transporter genotypes and smoking cessation: a meta-analysis. Addict Biol 12(2):221–226
Taylor S (2013) Molecular genetics of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a comprehensive meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Mol Psychiatry 18(7):799–805
Taylor A, Kim-Cohen J (2007) Meta-analysis of gene–environment interactions in developmental psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 19(4):1029–1037
Vink JM, Smit AB, de Geus EJC, Sullivan P, Wilemsen G, Hottenga J et al (2009) Genome-Wide Association study of smoking initiation and current smoking. Am J Hum Genet 84(3):367–379
Vrieze SI, Vaidyanathan U, Hicks BM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2014) The role of constraint in the development of nicotine, marijuana, and alcohol dependence in young adulthood. Behav Genet 44(1):14–24
WHO (1990) Composite International Diagnostic Interview, Version 1.0. World Health Organization, Geneva
Winters KC (1999) A new multiscale measure of adult substance abuse. J Subst Abuse Treat 16(3):237–246
Winters KC (2015) Minnesota drug abuse and ADHD study. Department of Psychiatry, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
Winters KC, Henly GA (1993) Adolescent diagnostic interview schedule and manual. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
Winters KC, Stinchfield RD, Fulkerson J, Henly GA (1993) Measuring alcohol and cannabis use disorders in an adolescent clinical sample. Psychol Addict Behav 7(3):185–196
Winters KC, Latimer W, Stinchfield RD (1999) The DSM-IV criteria for adolescent alcohol and cannabis use disorders. J Stud Alcohol 60(3):337–344
Wu J, **ao H, Sun H, Zou L, Zhu LQ (2012) Role of dopamine receptors in ADHD: a systematic meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol 45(3):605–620
Yang B, Chan RC, **g J, Li T, Sham P, Chen RY (2007) A meta-analysis of association studies between the 10-repeat allele of a VNTR polymorphism in the 3’-UTR of dopamine transporter gene and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B(4):541–550
Zhang L, Hu L, Li X, Zhang J, Chen B (2014) The DRD2 rs1800497 polymorphism increase the risk of mood disorder: evidence from an update meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 15:871–877
Zou YF, Wang F, Feng XL, Li WF, Tian YH, Tao JH, Pan FM, Huang F (2012) Association of DRD2 gene polymorphisms with mood disorders: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 136(3):229–237
Acknowledgments
Authors Ken C. Winters and Susanne Lee would like to thank Dr.’s George Realmuto and Irv Gottesman for their help consulting with the genetic portion of their study.
Funding
This research was supported by Grants DA024417, DA05147, DA13240, DA012995, DA024411-01-06, DA009679, DA036216, DA008093-15-18, and DA037280 (to S. W.) from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and Grant AA09367, and Grant AA11886 from the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The first author (D. R. S.) was also supported by the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Hatch project 1006129. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the aforementioned funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Diana R. Samek, Jennifer Bailey, Karl G. Hill, Sylia Wilson, Susanne Lee, Margaret A. Keyes, Marina Epstein, Andrew Smolen, Michael Miller, Ken C. Winters, J. David Hawkins, Richard F. Catalano, William G. Iacono, and Matt McGue declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Edited by Valerie Knopik.
Ken C. Winters is now affiliated with the Winters Consulting Group, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samek, D.R., Bailey, J., Hill, K.G. et al. A Test-Replicate Approach to Candidate Gene Research on Addiction and Externalizing Disorders: A Collaboration Across Five Longitudinal Studies. Behav Genet 46, 608–626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-016-9800-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-016-9800-8