Abstract
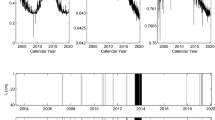
Significant association between flux emergence and the complexity of the involved processes in the solar corona could be substantial in estimating magnetic field activities and related driving mechanisms. In this study, we analysed solar magnetic activity in the time period between 1939 and 2022, covering solar cycles 17 to the present cycle 25. Our study was principally based on green coronal intensity, which was calculated using observations collected from a global network of coronal stations. Specifically, we utilized the homogenized Fe XIV 530.3 nm coronal emission line provided by the Astronomical Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences, as well as of the International Sunspot number index. The analyses were carried out using the Cross-Correlation and Empirical Mode Decomposition techniques. Firstly, the study found that there are strong and positive correlations between the two indices, with high coefficients specifically during the examined solar cycles. Secondly, the empirical mode decomposition technique reveals unique properties of the intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), highlighting distinctions between the emergence of sunspots and green coronal emissions based on their various modulations. Indeed, these IMFs are most likely closely linked to the magnetic flux rope structure and indirectly connected with the emergence of sunspot events. The observed lag between MCI and the SSN could potentially be linked to the dynamics between coronal response time and the evolutions of active regions. Furthermore, there is a steady decrease observed in the green coronal index from solar cycle 17 to the current cycle 25 that could be attributed to waning behaviour of solar magnetic field strength. This decline can also be regarded as evidence of the Centennial Gleissberg solar activity cycle during the descending phase. Interestingly, the green coronal index exhibits a significant degree of phase synchronization with sunspot numbers, suggesting that the intricate relationship between green coronal intensity and sunspot numbers can be potentially driven by processes such as heating, the formation of active coronal regions, and the emergence of magnetic flux.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfvén, H.: Existence of electromagnetic-hydrodynamic waves. Nature 150(3805), 405–406 (1942)
Altrock, R.: Solar and stellar coronal structure and dynamics; Proceedings of the ninth Sacramento peak summer symposium, Sunspot, NM, Aug. 17–21, 1987. Tech. rep., National Solar Observatory, Sunspot, NM (1988)
Ataç, T., Özgüç, A.: Flare index during the rising phase of solar cycle 23. Sol. Phys. 198, 399–407 (2001)
Badalyan, O.: Relationship between the brightness in the coronal green line and magnetic fields on various scales. Astron. Rep. 57, 222–232 (2013)
Badalyan, O., Bludova, N.: Relation of the green coronal line intensity to sunspot areas and magnetic fields of different scales. Sol. Syst. Res. 48, 305–315 (2014)
Bludova, N.: On the correspondence between the coronal green-line brightness, magnetic field strength and some sunspot activity indices. Astron. Astrophys. Trans. 24(1), 39–44 (2005)
Bludova, N., Badalyan, O.: Relation of the coronal green line intensity to magnetic fields and sunspot areas in the solar cycle. Astron. Lett. 32, 698–706 (2006)
Bludova, N., Obridko, V., Badalyan, O.: The relative umbral area in spot groups as an index of cyclic variation of solar activity. Sol. Phys. 289, 1013–1028 (2014)
Cameron, R.H., Schuessler, M.: Solar activity: periodicities beyond 11 years are consistent with random forcing. Astron. Astrophys. 625, A28 (2019)
Ellison, M.: Die sonnenkorona-struktur und variationen der korona: M. waldmeier: Band ll. birkhäuser verlag, basel und stuttgart, 1957. 353 pp., 299 diagrams, 68.50 sfr. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 12(1), 87–88 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9169(58)90015-1. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0021916958900151
Elmhamdi, A., Roman, M.T., Penãloza-Murillo, M.A., et al.: Impact of the eclipsed sun on terrestrial atmospheric parameters in desert locations: a comprehensive overview and two events case study in Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere 15(1), 62 (2024)
Feynman, J., Ruzmaikin, A.: The centennial Gleissberg cycle and its association with extended minima. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119(8), 6027–6041 (2014)
Habbal, S.R., Druckmüller, M., Morgan, H., et al.: Thermodynamics of the solar corona and evolution of the solar magnetic field as inferred from the total solar eclipse observations of 2010 July 11. Astrophys. J. 734(2), 120 (2011)
Hagino, M., Sakurai, T., Miyazawa, A.: Phase relationship between the activity cycles of sunspots and polar faculae. In: The Solar-B Mission and the Forefront of Solar Physics, p. 157 (2004)
Huang, N.E., Wu, Z.: A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: method and its applications to geophysical studies. Rev. Geophys. 46(2), RG2006 (2008)
Huang, N.E., Long, S.R., Shen, Z.: The mechanism for frequency downshift in nonlinear wave evolution. Adv. Appl. Mech. 32, 59–117 (1996)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., et al.: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. R. Soc. Lond. Proc., Ser. A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1971), 903–995 (1998)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R.: A new view of nonlinear water waves: the Hilbert spectrum. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 31(1), 417–457 (1999)
Le, G.M., Wang, J.L.: Wavelet analysis of several important periodic properties in the relative sunspot numbers. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 3(5), 391 (2003)
Liu, X., Zeng, S., Deng, L., et al.: Predicting the 25th and 26th solar cycles using the long short-term memory method. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 75(3), 691–699 (2023)
Mancuso, S., Lee, T., Taricco, C., et al.: Multivariate analysis of intermediate periodicities of the green corona. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 13(S340), 57–58 (2018)
Minarovjech, M., Rybanskỳ, M., Rušin, V.: Periodic variations in the coronal green line intensity and their connection with the white-light coronal structures. J. Astrophys. Astron. 21, 197–200 (2000)
Minarovjech, M., Rušin, V., Saniga, M.: The green corona database and the coronal index of solar activity. Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skaln. Pleso 41, 137–141 (2011)
Oloketuyi, J., Liu, Y., Zhao, M.: The periodic and temporal behaviors of solar X-ray flares in solar cycles 23 and 24. Astrophys. J. 874(1), 20 (2019)
Oloketuyi, J., Liu, Y., Amanambu, A.C., et al.: Responses and periodic variations of cosmic ray intensity and solar wind speed to sunspot numbers. Adv. Astron. 2020, Article ID 3527570 (2020)
Oloketuyi, J., Liu, Y., Elmhamdi, A.: Investigating the associations between solar flares and magnetic complexity of active regions. New Astron. 100, 101972 (2023)
Raju, K., Chandrasekhar, T., Ashok, N.: Analysis of coronal green line profiles: evidence of excess blueshifts. Astrophys. J. 736(2), 164 (2011)
Ramesh, K., Nagabhushana, B., Varghese, B.: Green coronal intensity enhancements and their relation to the underlying photospheric/chromospheric activity. Sol. Phys. 188, 99–113 (1999)
Ramesh, K., Nagabhushana, B., Varghese, B.: The enhanced coronal green line intensity and the magnetic field gradients. J. Astrophys. Astron. 21, 419–420 (2000)
Rusin, V.: The N-S asymmetry of the solar emission corona in the years 1965–1978. Bull. Astron. Inst. Czechoslov. 31(1), 9–13 (1980)
Rušin, V., Rybansky, M.: The green corona and magnetic fields. Sol. Phys. 207, 47–61 (2002)
Rybansky, M., Rusin, V.: The total brightness of the corona during the solar eclipse of February 16, 1980. Bull. Astron. Inst. Czechoslov. 36(2), 73–77 (1985)
Rybansky, M., Rusin, V.: Homogeneous data set of coronal green line intensities over the period 1964–1990. Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skaln. Pleso 22, 229–230 (1992)
Rybansky, M., Tyagun, N.: The projection effect when solar activity phenomena are mapped in galactic coordinates. Pism’a Astron. Zh. 6, 179–181 (1980)
Rybansky, M., Rusin, V., Dzifcáková, E.: Solar 530.3 nm corona irradiance variations in the cycle 21. Publ. Astron. Inst. Czechoslov. Acad. Sci. 1, 85–87 (1987)
Rybanskỳ, M., Rušin, V., Minarovjech, M., et al.: Reexamination of the coronal index of solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110(A8), A08106 (2005)
Sha, F., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., et al.: Characterization and correction of the scattering background produced by dust on the objective lens of the Lijiang 10-cm coronagraph. Sol. Phys. 298(11), 139 (2023)
Stenflo, J.: Evolution of solar magnetic fields over an 11-year period. Sol. Phys. 23, 307–339 (1972)
Sỳkora, J.: The coronal responses to the large-scale and long-term phenomena of the lower layers of the sun. In: Symposium-International Astronomical Union, pp. 87–104. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1980)
Sykora, J.: The large-scale behaviour of the green emission corona Fe XIV 530.3 nm over the last 4.5 solar activity cycles. Adv. Space Res. 14(4), 73–76 (1994)
Tang, R., Fei, Y., Li, C., et al.: Periodic variations of solar corona index during 1939–2020. Universe 8(7), 375 (2022)
Temmer, M., Veronig, A., Hanslmeier, A.: Does solar flare activity lag behind sunspot activity? Sol. Phys. 215, 111–126 (2003)
To, A.S., James, A.W., Bastian, T., et al.: Understanding the relationship between solar coronal abundances and F10.7 cm radio emission. Astrophys. J. 948(2), 121 (2023)
Waldmeier, M.: Die koronale kondensation bei der sonnenfinsternis vom 5. februar 1962. mit 5 textabbildungen. Z. Astrophys. 56, 291 (1963)
Waldmeier, M.: Die Sonnenkorona: Beobachtungen der Korona 1939–1949, vol. 4. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Wang, Y.M.: The radial interplanetary field strength at sunspot minimum as polar field proxy and solar cycle predictor. Astrophys. J. Lett. 961(2), L27 (2024)
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N. Jr, Hawley, S., et al.: The green line corona and its relation to the photospheric magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 485(1), 419 (1997)
Wang, Y., Guo, J., Li, G., et al.: Variation in cosmic-ray intensity lags sunspot number: implications of late opening of solar magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 928(2), 157 (2022)
Wheatland, M., Litvinenko, Y.E.: Energy balance in the flaring solar corona. Astrophys. J. 557(1), 332 (2001)
Zhang, X.F., Liu, Y., Zhao, M.Y., et al.: Comparison of the coronal green-line intensities with the EUV measurements from SDO/AIA. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 22(7), 075012 (2022)
Zhao, M., Chen, J., Liu, Y.: Statistical analysis of sunspot groups and flares for solar maximum and minimum. Sci. Sin. Phys., Mech. Astron. 44, 109–120 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the providers of data used; Astronomical Institute, Slovak Academy of Sciences for the Modified Coronal Index and the Sunspot Index and Long-term Solar Observations for the Sunspot data.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 12373063,11533009) and the 25-cm Coronagraph Development Project. The research work of A. Elmhamdi in this project was supported by King Saud University, Deanship of Scientific Research, College of Science Research Center. This work also received support from “Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program” Innovation Team Project (202405AS350012), and the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (grant No. 202301AV070007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
There is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oloketuyi, J., Liu, Y., Elmhamdi, A. et al. Understanding the long-term evolution of green line coronal emission and its relation to the sunspots. Astrophys Space Sci 369, 35 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-024-04300-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-024-04300-y