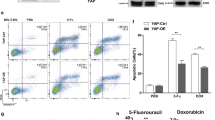
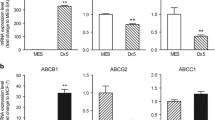
Abstract
Drug resistance is a major reason for therapy failure in cancer. Clitocine is a natural amino nucleoside isolated from mushroom and has been shown to inhibit cancer cell proliferation in vitro. In this study, we observed that clitocine can effectively induce drug-resistant human cancer cell apoptosis in vitro and inhibit tumor xenograft growth in vivo. Clitocine treatment inhibited drug-resistant human cancer cell growth in vitro in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Biochemical analysis revealed that clitocine-induced tumor growth inhibition is associated with activation of caspases 3, 8 and 9, PARP cleavage, cytochrome c release and Bax, Bak activation, suggesting that clitocine inhibits drug-resistant cancer cell growth through induction of apoptosis. Analysis of apoptosis regulatory genes indicated that Mcl-1 level was dramatically decreased after clitocine treatment. Over-expression of Mcl-1 reversed the activation of Bax and attenuated clitocine-induced apoptosis, suggesting that clitocine-induced apoptosis was at least partially by inducing Mcl-1 degradation to release Bax and Bak. Consistent with induction of apoptosis in vitro, clitocine significantly suppressed the drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft growth in vivo by inducing apoptosis as well as inhibiting cell proliferation. Taken together, our data demonstrated that clitocine is a potent Mcl-1 inhibitor that can effectively induce apoptosis to suppress drug-resistant human cancer cell growth both in vitro and in vivo, and thus holds great promise for further development as potentially a novel therapeutic agent to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Human hepatocellular carcinoma
- BCL-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- Mcl-1:
-
Myeloid cell leukaemia-1
- Bak:
-
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist-killer
- Bax:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- ΔΨm :
-
Mitochondrial transmembrane potential
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP) ribose polymerase
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- DOX:
-
Doxorubicin
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling staining
- IC50 :
-
Concentration causing a 50 % growth inhibition
References
Longley DB, Johnston PG (2005) Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol 205:275–292
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Quinn BA, Dash R, Azab B et al (2011) Targeting Mcl-1 for the therapy of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 20:1397–1411
Kazi A, Sun J, Doi K et al (2011) The BH3 alpha-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein–protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 286:9382–9392
Schwartzman RA, Cidlowski JA (1993) Apoptosis: the biochemistry and molecular biology of programmed cell death. Endocr Rev 14:133–151
Sharma A, Singh K, Mazumder S, Hill BT, Kalaycio M, Almasan A (2013) BECN1 and BIM interactions with MCL-1 determine fludarabine resistance in leukemic B cells. Cell Death Dis 4:e628
Hermanson DL, Das SG, Li Y, **ng C (2013) Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers multidrug resistance, whereas topoisomerase IIbeta downregulation introduces mitoxantrone-specific drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Pharmacol 84:236–243
Boiani M, Daniel C, Liu X, Hogarty MD, Marnett LJ (2013) The stress protein BAG3 stabilizes Mcl-1 protein and promotes survival of cancer cells and resistance to antagonist ABT-737. J Biol Chem 288:6980–6990
Doi K, Li R, Sung SS et al (2012) Discovery of marinopyrrole A (maritoclax) as a selective Mcl-1 antagonist that overcomes ABT-737 resistance by binding to and targeting Mcl-1 for proteasomal degradation. J Biol Chem 287:10224–10235
Tromp JM, Geest CR, Breij EC et al (2012) Tip** the Noxa/Mcl-1 balance overcomes ABT-737 resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 18:487–498
Yecies D, Carlson NE, Deng J, Letai A (2010) Acquired resistance to ABT-737 in lymphoma cells that up-regulate MCL-1 and BFL-1. Blood 115:3304–3313
Wang X, Chen W, Zeng W et al (2008) Akt-mediated eminent expression of c-FLIP and Mcl-1 confers acquired resistance to TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity to lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1156–1163
Rao YM, Shi HR, Ji M, Chen CH (2013) MiR-106a targets Mcl-1 to suppress cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer A2780 cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 33:567–572
Muller A, Zang C, Chumduri C, Dorken B, Daniel PT, Scholz CW (2013) Concurrent inhibition of PI3 K and mTORC1/mTORC2 overcomes resistance to rapamycin induced apoptosis by down-regulation of Mcl-1 in mantle cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer 133:1813–1824
Iglesias-Serret D, Pique M, Gil J, Pons G, Lopez JM (2003) Transcriptional and translational control of Mcl-1 during apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys 417:141–152
Gao N, Kramer L, Rahmani M, Dent P, Grant S (2006) The three-substituted indolinone cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor 3-[1-(3H-imidazol-4-yl)-meth-(Z)-ylidene]-5-methoxy-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-one (SU9516) kills human leukemia cells via down-regulation of Mcl-1 through a transcriptional mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 70:645–655
Soliera AR, Mariani SA, Audia A et al (2012) Gfi-1 inhibits proliferation and colony formation of p210BCR/ABL-expressing cells via transcriptional repression of STAT 5 and Mcl-1. Leukemia 26:1555–1563
Moss RJ, Petrie CR, Meyer RB Jr et al (1988) Synthesis, intramolecular hydrogen bonding, and biochemical studies of clitocine, a naturally occurring exocyclic amino nucleoside. J Med Chem 31:786–790
Fortin H, Tomasi S, Delcros JG, Bansard JY, Boustie J (2006) In vivo antitumor activity of clitocine, an exocyclic amino nucleoside isolated from Lepista inversa. ChemMedChem 1:189–196
Ren G, Zhao YP, Yang L, Fu CX (2008) Anti-proliferative effect of clitocine from the mushroom Leucopaxillus giganteus on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett 262:190–200
Sun J, Yeung CA, Co NN et al (2012) Clitocine reversal of P-glycoprotein associated multi-drug resistance through down-regulation of transcription factor NF-kappaB in R-HepG2 cell line. PLoS ONE 7:e40720
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH (1994) Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84:1415–1420
(2010) Bad month for cancer care in the UK. Lancet Oncol 11:701
Fisher DE (1994) Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell 78:539–542
Frankfurt OS, Krishan A (2003) Apoptosis-based drug screening and detection of selective toxicity to cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 14:555–561
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1999) Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10964–10967
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1997) Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell 91:443–446
Mehmet H (2000) Caspases find a new place to hide. Nature 403:29–30
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Wang X (2001) The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15:2922–2933
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E et al (2001) Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 410:549–554
Cande C, Cecconi F, Dessen P, Kroemer G (2002) Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): key to the conserved caspase-independent pathways of cell death? J Cell Sci 115:4727–4734
Lau WY, Lai EC (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and recent advances. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 7:237–257
Campbell KJ, Bath ML, Turner ML et al (2010) Elevated Mcl-1 perturbs lymphopoiesis, promotes transformation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, and enhances drug resistance. Blood 116:3197–3207
Nifoussi SK, Vrana JA, Domina AM et al (2012) Thr 163 phosphorylation causes Mcl-1 stabilization when degradation is independent of the adjacent GSK3-targeted phosphodegron, promoting drug resistance in cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e47060
Gillissen B, Wendt J, Richter A et al (2010) Endogenous Bak inhibitors Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL: differential impact on TRAIL resistance in Bax-deficient carcinoma. J Cell Biol 188:851–862
Dyugovskaya L, Polyakov A, Cohen-Kaplan V, Lavie P, Lavie L (2012) Bax/Mcl-1 balance affects neutrophil survival in intermittent hypoxia and obstructive sleep apnea: effects of p38MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling. J Transl Med 10:211
Ling V (1997) Multidrug resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 40(Suppl):S3–S8
Wasser SP (2002) Medicinal mushrooms as a source of antitumor and immunomodulating polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:258–274
Yassin MM, Ja WS (2003) Submerged cultured mycelium extracts of higher basidiomycetes mushrooms selectively inhibit proliferation and induce differentiation of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Int J Med Mushr 5:261–276
Zaidman BZ, Yassin M, Mahajna J, Wasser SP (2005) Medicinal mushroom modulators of molecular targets as cancer therapeutics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:453–468
Petrova RDWS, Mahajna J, Denchev CM, Nevo E (2005) Medicinal mushrooms: a new source for breast cancer therapeutics. Int J Med Mushr 7:445–446
Zaidman BZ, Wasser SP, Nevo E, Mahajna J (2007) Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms mediate Ganoderma lucidum activities in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol 31:959–967
Yassin M, Wasser SP, Mahajna J (2008) Substances from the medicinal mushroom Daedalea gibbosa inhibit kinase activity of native and T315I mutated Bcr-Abl. Int J Oncol 32:1197–1204
Tang PM, Chan JY, Zhang DM et al (2007) Pheophorbide a, an active component in Scutellaria barbata, reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance on a human hepatoma cell line R-HepG2. Cancer Biol Ther 6:504–509
Li GY, Liu JZ, Chen SG, Zhang B, Wang CB, Wang LX (2010) Tegillarca granosa extract Haishengsu inhibits the expression of P-glycoprotein and induces apoptosis in drug-resistant K562/ADM cells. Pharm Biol 48:529–533
Angelini A, Di Pietro R, Centurione L et al (2012) Inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport by S-adenosylmethionine and cynarin in multidrug-resistant human uterine sarcoma MES-SA/Dx5 cells. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 26:495–504
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Fleischer B, Schuchmann M et al (2006) Suppression of Mcl-1 via RNA interference sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards apoptosis induction. BMC Cancer 6:232
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Nature Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No.: LY12C02001 to FL) and Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (Grant No.: 2013C24012 to FL), and Siyuan Foundation (to FL and KPF). We thank Dr. Shihua Wu for assistance in purification of Clitocine.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Jg., Li, H., Li, X. et al. Clitocine targets Mcl-1 to induce drug-resistant human cancer cell apoptosis in vitro and tumor growth inhibition in vivo. Apoptosis 19, 871–882 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0969-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0969-0