Abstract
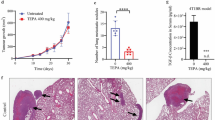
An increasing amount of evidence demonstrated that the neurotrophic receptor tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) plays a critical role in the development and progression of multiple types of cancer. However, its underlying mechanism in distant metastasis through the circulatory and lymphatic systems in colorectal cancer (CRC) is still unclear. Here we showed that downregulation of TrkB using short hairpin RNA obviously increased anoikis (detachment-induced apoptosis resulting from loss of cell–matrix interactions) sensitivity of CRC cells in vitro. Furthermore, using tail vein injection model, we confirmed that silencing TrkB significantly inhibited metastasis of CRC cells in vivo. Conversely, overexpression of TrkB obviously protected CRC cells from anoikis in vitro. Both loss- and gain-of-functional experiments indicated that TrkB could be a functional molecule in anti-anoikis of CRC cells. Mechanistically, we found that protein kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt) signaling pathway was a functional link in TrkB-induced anoikis suppression in CRC cells. Phosphorylation levels of Akt are closely related with the expression pattern of TrkB in CRC cells and inhibition of Akt activation robustly induces anoikis of CRC cells in vitro. In addition, our clinical investigation showed that high TrkB expression levels in CRC patients were associated with lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and unfavourable prognosis. Thus, based on our results, this study suggests that an important function of TrkB is to protect CRC cells from anoikis in the circulatory and lymphatic systems, and that TrkB could be a promising candidate in CRC therapy, especially in the inhibition of cancer metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, Brennan MF, Blumgart LH (1999) Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg 230:309–321
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell–matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124:619–626
Liotta LA, Kohn EC (2001) The micro environment of the tumour–host interface. Nature 411:375–379
Meredith JE, Fazeli JB, Schwartz MA (1993) The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell 4:953–961
Klein R, Nanduri V, **g SA, Lamballe F, Tapley P et al (1991) The TrkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell 66:395–403
Nakagawara A, Azar CG, Scavarda NJ, Brodeur GM (1994) Expression and function of TRK-B and BDNF in human neuroblastomas. Mol Cell Biol 14:759–767
Perez-Pinera P, Hernandez T, García-Suárez O, de Carlos F, Germana A et al (2007) The Trk tyrosine kinase inhibitor K252a regulates growth of lung adenocarcinomas. Mol Cell Biochem 295:19–26
Dionne CA, Camoratto AM, Jani JP, Emerson E, Neff N et al (1998) Cell cycle-independent death of prostate adenocarcinoma is induced by the trk tyrosine kinase inhibitor CEP-751 (KT6587). Clin Cancer Res 4:1887–1898
Miknyoczki SJ, Lang D, Huang L, Klein-Szanto AJ, Dionne CA et al (1999) Neurotrophins and Trk receptors in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: expression patterns and effects on in vitro invasive behaviour. Int J Cancer 81:417–427
Yu X, Liu L, Cai B, He Y, Wan X (2008) Suppression of anoikis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci 99:543–552
Nakamura K, Martin KC, Jackson JK, Beppu K, Woo CW et al (2006) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:4249–4255
Jaboin J, Kim CJ, Kaplan DR, Thiele CJ (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway. Cancer Res 62:6756–6763
Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J, Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E et al (2004) Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature 430:1034–1039
Yu Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Yang Z, Ou G (2010) Overexpression of TrkB promotes the progression of colon cancer. APMIS 118:188–195
Brunetto de Farias C, Rosemberg DB, Heinen TE, Koehler-Santos P, Abujamra AL et al (2010) BDNF/TrkB content and interaction with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor blockade in colorectal cancer. Oncology 79:430–439
de Farias CB, Heinen TE, dos Santos RP, Abujamra AL, Schwartsmann G et al (2012) BDNF/TrkB signaling protects HT-29 human colon cancer cells from EGFR inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425:328–332
Fujikawa H, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Saigusa S, Inoue Y et al (2012) High TrkB expression levels are associated with poor prognosis and EMT induction in colorectal cancer cells. J Gastroenterol 47:775–784
Liu LZ, Zhou XD, Qian G, Shi X, Fang J et al (2007) Akt1 amplification regulates cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells through the mammalian target of rapamycin/p70S6K1 pathway. Cancer Res 67:6325–6332
Faried LS, Faried A, Kanuma T, Aoki H, Sano T et al (2008) Expression of an activated mammalian target of rapamycin in adenocarcinoma of the cervix: a potential biomarker and molecular target therapy. Mol Carcinog 47:446–457
Yang X, Fraser M, Moll UM, Basak A, Tsang BK (2006) Akt-mediated cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer: modulation of p53 action on caspase-dependent mitochondrial death pathway. Cancer Res 66:3126–3136
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennström S, Warne PH, Downward J (1997) Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J 16:2783–2793
Schmidt M, Hövelmann S, Beckers TL (2002) A novel form of constitutively active farnesylated Akt1 prevents mammary epithelial cells from anoikis and suppresses chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Br J Cancer 87:924–932
Rhodes A, Jasani B, Barnes DM, Bobrow LG, Miller KD (2000) Reliability of immunohistochemical demonstration of oestrogen receptors in routine practice: interlaboratory variance in the sensitivity of detection and evaluation of scoring systems. J Clin Pathol 53:125–130
Chao MV (2003) Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:299–309
Nakagawara A (2001) Trk receptor tyrosine kinases: a bridge between cancer and neural development. Cancer Lett 169:107–114
Okamura K, Harada T, Wang S, Ijichi K, Furuyama K et al (2012) Expression of TrkB and BDNF is associated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 78:100–106
Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kawamura M, Kawamoto A et al (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B pathway in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 108:121–130
Iyer R, Varela CR, Minturn JE, Ho R, Simpson AM et al (2012) AZ64 inhibits TrkB and enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy and local radiation in neuroblastoma xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70:477–486
Geiger TR, Peeper DS (2005) The neurotrophic receptor TrkB in anoikis resistance and metastasis: a perspective. Cancer Res 65:7033–7036
Geiger TR, Peeper DS (2007) Critical role for TrkB kinase function in anoikis suppression tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res 67:6221–6229
Tanaka K, Mohri Y, Nishioka J, Kobayashi M, Ohi M et al (2009) Neurotrophic receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase B as an independent prognostic marker in gastric cancer patients. J Surg Oncol 99:307–310
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88:435–437
Burgering BM, Coffer PJ (2004) Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 376:599–602
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H et al (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF et al (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282:1318–1321
Lee SH, Kim HS, Park WS, Kim SY, Lee KY et al (2002) Non-small cell lung cancers frequently express phosphorylated Akt: an immunohistochemical study. APMIS 110:587–592
Itoh N, Semba S, Ito M, Takeda H, Kawata S et al (2002) Phosphorylation of Akt/PKB is required for suppression of cancer cell apoptosis and tumor progression in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 94:3127–3134
Shukla S, Maclennan GT, Marengo SR, Resnick MI, Gupta S (2005) Constitutive activation of PI3K–Akt and NF-kappaB during prostate cancer progression in autochthonous transgenic mouse model. Prostate 64:224–239
Yuan ZQ, Sun M, Feldman RI, Wang G, Ma X et al (2000) Frequent activation of AKT2 and induction of apoptosis by inhibition of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase/Akt pathway in human ovarian cancer. Oncogene 19:2324–2330
Page C, Huang M, ** X, Cho K, Lilja J et al (2000) Elevated phosphorylation of AKT and Stat3 in prostate, breast, and cervical cancer cells. Int J Oncol 17:23–28
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30901786, 81172010). We thank **aofang Zhang for her excellent technical assistance. We also thank the patients who gave consent to use their tissue for research.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Meng Fan, Jianyong Sun, Wei Wang and **g Fan have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, M., Sun, J., Wang, W. et al. Tropomyosin-related kinase B promotes distant metastasis of colorectal cancer through protein kinase B-mediated anoikis suppression and correlates with poor prognosis. Apoptosis 19, 860–870 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0968-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0968-1