Abstract
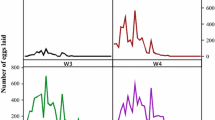
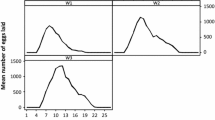
The development and biological characteristics of Haemaphysalis longicornis were investigated under field conditions in **.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre DH (1999) The life cycle of Amblyomma neumanni Ribaga, 1902 (Acari: Ixodidae) in the laboratory. Exp Appl Acarol 23:159–164
Borges L, Oliveira PR, Ribeiro M (1999) Seasonal dynamics of the free-living phase of Anocentor nitens at Pedro Leopoldo, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Vet Parasitol 87:73–81
Campbell A, Glines MV (1979) Development, survival, and oviposition of the rabbit tick, Haemaphysalis leporispalustris (Packard) (Acari: Ixodidae), at constant temperatures. J Parasitol 65:777–781
Centurier C, Klima R (1979) Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Biologie von Amblyomma variegatum (Fabricius, 1794). Z Angew Entomol 87:131–142
Chen Z, Yu ZJ, Yang XJ, Zheng HY, Liu JZ (2009) The life cycle of Hyalomma asiaticum kozlovi Olenev, 1931 (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Vet Parasitol 160:134–137
Cho SH, Kim TS, Lee HW, Tsuji M, Ishihara C, Kim JT, Wee SH, Lee CG (2002) Identification of newly isolated Babesia parasites from cattle in Korea by using the Bo-RBC-SCID mice. Korean J Parasitol 40(1):33–40
Ding XC, Yin PY (1996) Study on the biology and seasonal fleuctuations of Haemaphysalis vietnamensis in Nanshan farm, Hunan provice. J China Agric Univ 3(1):109–112
Drummond RO, Whetstone TM (1970) Oviposition of the Gulf Coast tick. J Econ Entomol 63:1548–1551
Fourie LJ, Horak IG (1994) The life cycle of Ixodes rubicundus (Acari: Ixodidae) and its adaptation to a hot, dry environment. Exp Appl Acarol 18:23–35
Fujisaki K, Kitaoka S, Morii T (1976) Comparative observations on some bionomics of Japanese ixodid ticks under laboratory cultural conditions. Natl Inst Anim Health Q 16:122–128
Gladney WJ, Dawkins CC, Price MA (1977) Amblyomma inornatum (Acarina: ixodidae): natural hosts and laboratory biology. J Med Entomol 14:85–88
Guglielmone AA, Moorhouse DE (1985) Differences in nymphs of Amblyomma triguttatum triguttatum Koch moulting to males or females. Acarologia 26:7–11
Guglielmone AA, Mangold AJ, Garcia MD (1991) The life cycle of Amblyomma parvum Aragao, 1908 (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 13:129–136
Heath ACG (1979) The temperature and humidity preferences of Haemaphysalis longicornis, Ixodes holocyclus and Rhipicephalus sanguineus (ixodidae): studies on eggs. Int J Parasitol 9(1):33–39
Heath ACG (1981) The temperature and humidity preferences of Haemaphysalis longicornis, ixodes holocyclus and Rhipicephalus sanguineus (ixodidae): studies on engorged larvae. Int J Parasitol 11(2):169–175
Hoogstraal H, Roberts F, Kohls GM, Vernon JT (1968) Review of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis Neumann (resurrected) of Australia, New Zealand, China and USSR, and its parthenogenetic and bisexual populations (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J Parasitol 54:1197–1213
Hu R, Rowley WA (2000) Relationship between weights of the engorged nymphal stage and resultant sexes in Ixodes scapularis and Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks. J Med Entomol 37(1):198–200
Ikadai H, Sasaki M, Ishida H, Matsuu A, Igarashi I, Fujisaki K, Oyamada T (2007) Molecular evidence of Babesia equi transmission in Haemaphysalis longicornis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 76(4):694–697
Inokuma H, Fujimoto T, Hosoi E, Tanaka S, Fujisaki K, Okuda M, Onishi T (2002) Tick infestation of sika deer (Cervus nippon) in the western part of Yamaguchi prefecture, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 64(7):615–617
Jiang ZJ, Bai CL (1989) Study on the oviposition in ixdid ticks. J Bei**g Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 3:81–85
Kim JE, Park HJ, Lee JY, Cho BK, Lee IY, Lee WK, Koh CJ (2003) Three cases of tick bites by Haemaphysalis longicornis. Korean J Dermatol 41(9):1198–1201
Labruna MB, Leite RC, Faccini JLH, Ferreira F (2000) Life cycle of the tick Haemaphysalis leporis-palustris (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 24:683–694
Labruna MB, Kasai N, Ferreira F, Faccini J, Gennari SM (2002) Seasonal dynamics of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on horses in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Vet Parasitol 105:65–77
Lee JL, Park HS, Jung KD, Jang WJ, Koh SE, Kong SS, Lee IY, Lee WJ, Kim BJ, Kook KH, Park KH, Lee SH (2003) Identification of the spotted fever group Rickettsiae detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis in Korea. Microbiol Immunol 47(4):301–304
Liu JZ, Jiang ZJ (1998) Studies on the bionomics of Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Acta Entomol Sin 41(3):280–283
Liu JZ, Liu ZN, Zhang Y, Yang XL, Gao ZH (2005) Biology of Dermacentor silvarum (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 36:131–138
Nava S, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA (2008) Aspects of the life cycle of Amblyomma parvum (Acari: Ixodidae) under natural conditions. Vet Parasitol 156:270–276
Oliveira PR, Borges L, Leite RC, Freitas C (2003) Seasonal dynamics of the Cayenne tick, Amblyomma cajennense on horses in Brazil. Med Vet Entomol 17:412–416
Padgett KA, Lane RS (2001) Life cycle of Ixodes pacificus (Acari: Ixodidae): timing of developmental processes under field and laboratory conditions. J Med Entomol 38:684–693
Pegram RG, Banda DS (1990) Ecology and phenology of cattle ticks in Zambia: development and survival of free-living stages. Exp Appl Acarol 8:291–301
Rechav Y, Knight MM (1981) Life cycle in the laboratory and seasonal activity of the tick Rhipicephalus glabroscutatum (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Parasitol 67:85–89
Shimada Y, Inokuma H, Beppu T, Okuda M, Onishi T (2003) Survey of ixodid tick species on domestic cats in Japan. Vet Parasitol 111:231–239
Solomon G, Kaaya GP (1998) Development, reproductive capacity and survival of Amblyomma Íariegatum and Boophilus decoloratus in relation to host resistance and climatic factors under field conditions. Vet Parasitol 75:241–253
Sutherst RW, Bourne AS (1991) Development, survival, fecundity and behavior of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis (Ixodidae) at two locations in southeast Queensland. Int J Parasitol 21:661–672
Teng KF, Jiang ZJ (eds) (1991) Economic insect Fauna of China, Fasc 39, Acari: Ixodidae. Science Press, Bei**g
Tenquisf JD, Charleston WAG (2001) A revision of the annotated checklist of ectoparasites of terrestrial mammals in New Zealand. J R Soc N Z 31(3):481–542
Vanderlingen FJ, Fourie LJ, Kok DJ, Vanzyl JM (1999) Biology of Ixodes rubicundus ticks under laboratory conditions: observations on oviposition and egg development. Exp Appl Acarol 23:513–522
Venzal JM, Estrada-Pe a A, Castro O, De Souza CG, Félix ML, Nava S, Guglielmone AA (2008) Amblyomma triste Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae): hosts and seasonality of the vector of Rickettsia parkeri in Uruguay. Vet Parasitol 155:104–109
Yano Y, Shiraishi S, Uchida TA (1987) Effects of temperature on development and growth in the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Exp Appl Acarol 3:73–78
Yao WB, Chen GD (1974) Study on the life cycle of Haemaphsalis japonica douglasi Null et Warb. Acta Entomol Sin 17(4):500–502
Yeruham I, Hadani A, Galker F (2000) The life cycle of Rhipicephalus bursa Canestrini and Fanzago, 1877 (Acarina: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Vet Parasitol 89:109–116
Zhang JX, Chen Z, Liu JZ, Yang XJ (2006) Study on oviposition and egg development of three species of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Chin J Pest Contr 22:864–867
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970406) and Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (C2007000266).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Yu, Z., Chen, Z. et al. Development and biological characteristics of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) under field conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 53, 377–388 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-010-9415-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-010-9415-3