Abstract
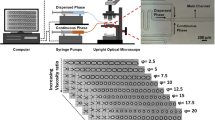
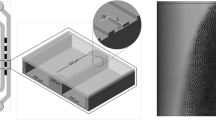
Microfluidic devices with micro-sieve plate as the dispersion medium have been widely used for the mass production of emulsions. While unfortunately, few studies have so far been made for the droplet generation rules in those devices. In this work, the droplet generation processes in micro-sieve dispersion devices are investigated with specially designed micro-sieve pore arrays. The effects of channel structure, pore arrangement, and feeding method of dispersed phase on the average size and distribution of droplets are studied carefully. It is found the dimensionless average droplet diameters (d av/d e) in micro-sieve dispersion devices can be represented by a linear relation with Ca−1/4 of continuous phase, the same as the scaling law in T-junction microchannels. The flow distribution among pores and the steric hindrance between droplets affect the diameter distribution of generated droplet very much. Monodispersed droplets with polydispersity index less than 5% can be made at Ca number larger than 0.01 and phase ratio (Q D/Q C) less than 1/6 in the present investigation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamse AJ, van Lierop R, van der Smana RGM, van der Padt A, Booma RM (2002) Analysis of droplet formation and interactions during cross-flow membrane emulsification. J Membr Sci 204:125–137
Choi J, Lee SK, Lim JM, Yang SM, Yi GR (2010) Designed pneumatic valve actuators for controlled droplet breakup and generation. Lab chip 10:456–461
Christopher GF, Noharuddin NN, Taylor JA, Anna SL (2008) Experimental observations of the squeezing-to-drip** transition in T-shaped microfluidic junctions. Phys Rev E 78:036317
Cubaud T, Mason TG (2008) Capillary threads and viscous droplets in square microchannels. Phys Fluid 20:053302
de Menech M, Garstecki P, Jousse F, Stone HA (2008) Transition from squeezing to drip** in a microfluidic T-shaped junction. J Fluid Mech 595:141–161
Engl W, Backov R, Panizza P (2008) Controlled production of emulsions and particles by milli- and microfluidic techniques. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 13:206–216
Felbel J, Reichert A, Kielpinski K, Urban M, Henkel T, Hafner N, Durst M, Weber J (2008) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in flow-through micro-reactors: thermal and fluidic concepts. Chem Eng J 135S:S298–S302
Geerken MJ, Lammertink RGH, Wessling M (2007) Interfacial aspects of water drop formation at micro-engineered orifices. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:460–469
Geerken MJ, Groenendijk MNW, Lammertink RGH, Wessling M (2008) Micro-fabricated metal nozzle plates used for water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsification. J Membr Sci 310:374–383
Gijsbertsen-Abrahamse AJ, van der Padt A, Booma RM (2003) Status of cross-flow membrane emulsification and outlook for industrial application. J Membr Sci 217:141–150
Gijsbertsen-Abrahamse AJ, van der Padt A, Booma RM (2004) Status of cross-flow membrane emulsification and outlook for industrial application. J Membr Sci 230:149–159
Guillot P, Colin A, Utada AS, Ajdari A (2007) Stability of a jet in confined pressure-driven biphasic flows at low Reynolds numbers. Phys Rev Lett 99:104502
Kjeang E, Djilali N, Sinton D (2009) Microfluidic fuel cells: a review. J Power Sources 186:353–369
Kobayashi I, Takano T, Maeda R, Wada Y, Uemura K, Nakajima M (2008) Straight-through microchannel devices for generating monodisperse emulsion droplets several microns in size. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:167–177
Lao KL, Wang JH, Lee GB (2009) A microfluidic platform for formation of double-emulsion droplets. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:709–719
Li SW, Xu JH, Wang YJ, Luo GS (2009a) Liquid-liquid two-phase flow in pore array microstructured devices for scaling-up of nanoparticle preparation. AIChE J 55:3041–3051
Li SW, Xu JH, Wang YJ, Lu YC, Luo GS (2009b) Low-temperature bonding of poly-(methyl methacrylate) microfluidic devices under an ultrasonic field. Micromech Microeng 19:015035
Li SW, Xu JH, Wang YJ, Luo GS (2009c) A new interfacial tension measurement method through a pore array micro-structured device. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:127–131
Marmottant P, Raven JP (2009) Microfluidics with foams. Soft Matter 5:3385–3388
Nie ZH, Seo MS, Xu SQ, Lewis PC, Mok M, Kumacheva E, Whitesides GM, Garstecki P, Stone HA (2008) Emulsification in a microfluidic flow-focusing device: effect of the viscosities of the liquids. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:585–594
Nisisako T, Torii T (2008) Microfluidic large-scale integration on a chip for mass production of monodisperse droplets and particles. Lab Chip 8:287–293
Panic S, Loebbecke S, Tuercke T, Antes J, Boskovi D (2004) Experimental approaches to a better understanding of mixing performance of microfluidic devices. Chem Eng J 101:409–419
Park JI, Nie ZH, Kumachev A, Abdelrahman AI, Binks BP, Stone HA, Kumacheva E (2009) A microfluidic approach to chemically driven assembly of colloidal particles at gas–liquid interfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:5300–5304
Razzaq T, Glasnov TN, Kappe CO (2009) Accessing novel process windows in a high-temperature/pressure capillary flow reactor. Chem Eng Technol 32:1702–1716
Sevonkaev I, Matijevic E (2009) Formation of magnesium fluoride particles of different morphologies. Langmuir 25:10534–10539
Steegmans MLJ, Schroen KGPH, Boom RM (2009) Characterization of emulsification at flat microchannel Y-junctions. Langmuir 25:3396–3401
Teh SY, Lin R, Hung LH, Lee AP (2008) Droplet microfluidics. Lab chip 8:98–220
van der Graaf S, Schroën CGPH, van der Sman RGM, Boom RM (2004) Influence of dynamic interfacial tension on droplet formation during membrane emulsification. J Colloid Interface Sci 277:456–463
van Steijn V, Kleijn CR, Kreutzer MT (2009) Flows around confined bubbles and their importance in triggering pinch-off. Phys Rev Lett 103:214501
Wang K, Lu YC, Xu JH, Tan J, Luo GS (2009a) Liquid-liquid micro-dispersion in a double-pore T-shaped microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:557–564
Wang K, Lu YC, Xu JH, Luo GS (2009b) Determination of dynamic interfacial tension and its effect on droplet formation in the T-shaped microdispersion process. Langmuir 25:2153–2158
Xu JH, Luo GS, Chen GG, Wang JD (2005) Experimental and theoretical approaches on droplet formation from a micrometer screen hole. J Membr Sci 266:121–131
Xu JH, Li SW, Tan J, Wang YJ, Luo GS (2006) Preparation of highly monodisperse droplet in a T-junction microfluidic device. AIChE J 52:3005–3010
Xu JH, Tan J, Li SW, Luo GS (2008a) Enhancement of mass transfer performance of liquid–liquid system by droplet flow in microchannels. Chem Eng J 141:242–249
Xu JH, Li SW, Tan J, Luo GS (2008b) Correlations of droplet formation in T-junction microfluidic devices: from squeezing to drip**. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:711–717
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21036002, 20876084) and SRFDP (20090002110070) for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Lu, Y.C., Xu, J.H. et al. Droplet generation in micro-sieve dispersion device. Microfluid Nanofluid 10, 1087–1095 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0737-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0737-6