Abstract
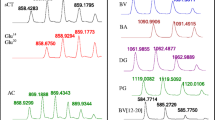
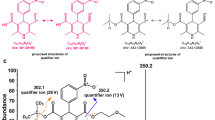
A sensitive liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–ESI–MS–MS) method was developed and validated for the quantification of cepharanthine (CEP) in beagle dog plasma. The chromatographic separation was performed on an Agilent-C18 column and the mobile phase was composed of methanol:water with 10 mM ammonium acetate (20:80, v/v). Detection was operated in the positive ion mode and the tandem mass spectrometer was tuned in the multiple reactions monitoring mode (MRM) to monitor m/z transitions 607 → 365 for CEP and 285 → 193 for the internal standard (IS) diazepam. This method exhibited a linear range of 5–2,500 ng mL−1. The precision (RSD%) and accuracy (RME%) of the assay were <8.7 and 2.4%, respectively. The limit of quantification was 5 ng mL−1 and no significant matrix effect was observed. The validated method has been successfully applied to pharmacokinetic study of CEP in beagle dog.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knodo Y, Imai Y, Hojo H, Hashimoto Y, Nozoe S (1992) Int J Immunopharmacol 14:1181–1186
Shiraishi N, Arima T, Aono K, Inouye B, Morimoto Y, Utsumi K (1980) Physiol Chem and Phy 12:299–305
Nagano M, Kanno T, Fujita H, Muranaka S, Fujiwara T, Utsumi K (2003) Physiol Chem Phy Med NMR 35:131–143
Goto M, Zeller WP, Hurley RM (1991) J Pharm Pharmacol 43:589–591
Asaumi J, Nishikawa K, Matsuoka H, Iwata M, Kawasaki S, Hiraki Y, Nishijima K (1995) Anticancer Res 15:67–70
Wu J, Suzuki H, Akhand AA, Zhou YW, Hossain K, Nakashima I (2002) Cell Signal 14:509–515
Ono M, Tanaka N, Orita K (1994) Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 35:10–16
Hirai M, Tanaka K, Shimizu T, Tanigawara Y, Yasuhara M, Hori R, Kakehi Y, Yoshida O, Ueda K, Komano T, Inui KI (1995) J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:73–78
Lin JH, Lu AYH (1997) Pharmacol Rev 49:403–449
Bory S, Bun SS, Baghdikian B, Mabrouki F, Cheng SK, Elias R, Bun H, Ollivier E (2010) Nat Prod Commun 5:877–882
White RE (2000) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:133–157
Hsieh Y (2008) Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:93–101
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Professor Qing-Duan Wang and Department of Pharmacology, Henan Institute of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, RH., Fang, ZZ., Gao, HZ. et al. Bioanalysis of Cepharanthine by LC–ESI–MS–MS and Its Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies. Chromatographia 73, 75–81 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-010-1823-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-010-1823-3