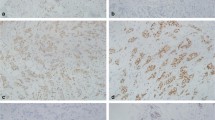
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the correlations of expression of Bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) gene and the receptors of estrogen and progestogen in breast cancer and its significance.
Methods
Immunohistochemical methods had been used to detect the expressions of BI-1 gene and receptors of estrogen and progestogen in breast cancer.
Results
The positive rates of expressions of BI-1 gene, estrogen receptor (ER) and progestogen receptor (PR) in breast cancer were 77.08%, 60.42% and 54.17%, respectively. The positive rate of expression of BI-1 gene was higher in the group with negative expression of ER than the positive group, their positive rates were 76.92% and 52.27%, respectively; but there was no statistical difference between the two groups with positive and negative expressions of PR. The positive rate of expression of BI-1 gene was also higher in the group with positive lymph node metastasis than the non-lymph node metastasis group, and their positive rates were 64.58% and 36.36%, respectively. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
BI-1 gene, in combination with ER, has guiding significance for patients with breast cancer to choose individual chemotherapy and radiotherapy after operation and can become an important indicator for judging the prognosis of breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu Q, Reed JC. Bax inhibitor-1, a mammalian apoptosis suppressor identified by functional screening in yeast. Mol Cell, 1998, 1: 337–346.
Chae HJ, Ke N, Kim HR, et al. Evolutionarily conserved cytoprotection provided by Bax inhibitor-1 homologs from animals, plants, and yeast. Gene, 2003, 323: 101–113.
Tanaka R, Ishiyama T, Uchihara T, et al. Expression of the Bax inhibitor-1 gene in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer, 2006, 106: 648–653.
Walter L, Marynen P, Szpirer J, et al. Identification of a novel conserved human gene, TEGT. Genomics, 1995, 28: 301–304.
Sanchez P, de Torres Zabala M, Grant M. AtBI-1, a plant homologue of Bax inhibitor-1, suppresses Bax-induced cell death in yeast and is rapidly upregulated during wounding and pathogen challenge. Plant J, 2000, 21: 393–399.
Reed JC. Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family. Nature, 1997, 387: 773–776.
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev, 1999, 13: 1899–1911.
Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche-Rigon M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol, 1998, 60: 619–642.
Reed JC, Jurgensmeier JM, Matsuyama S. Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1998, 1366: 127–137.
Shimizu S, Narita M, Tsujimoto Y. Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature, 1999, 399: 483–487.
Chae HJ, Kim HR, XU C, et al. BI-1 regulates an apoptosis pathway liked to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell, 2004, 15: 355–366.
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, et al. Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell, 1998, 94: 491–501.
Grzmil M, Thelen P, Hemmerlein B, et al. Bax inhibitor-1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer and its specific down-regulation by RNA interference leads to cell death in human prostate carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol, 2003, 163: 543–552.
Li M, Lv BJ, Zhang YM, et al. Study on the expression of BI-1 and relative regulators in human NSCLC cell lines. Inter J Genetics (Chinese), 2006, 29: 169–172.
Grzmil M, Kaulfuss S, Thelen P, et al. Expression and functional analysis of Bax inhibitor-1 in human breast cancer cells. J Pathol, 2006, 208: 340–349.
Iwase H, Ando Y, Ichihara S, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis on biological markers in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Breast Cancer, 2001, 8: 98–104.
Yamashita H, Kobayashi S, Iwase H, et al. Analysis of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in human breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res, 1993, 84: 871–878.
Hamilton A, Piccart M. The contribution of molecular markers to the prediction of response in the treatment of breast cancer: a review of the literature on HER-2, p53 and Bcl-2. Ann Oncol, 2000, 11: 647–663.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant of Henan Province to support the Medical High-tech Development Project (No. 20060038).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, M., Li, J. et al. Expression of BI-1 protein and its significance in breast cancer. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 8, 160–163 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-008-0101-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-008-0101-4