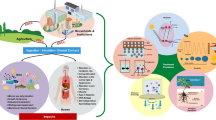
Abstract
Endocrine disruptors are hazardous chemicals with chronic health effects for most living organisms, inducing homeostasis, hormonal imbalances, cancer, reproductive and neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, vulnerability to fetus and neonates. Over 1,000 chemicals display endocrine disrupting characteristics. Endocrine disruptors are found among industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, plastic materials, fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides and fungicides. Endocrine disruptors enter human organs via ingestion, inhalation and diffusion through the skin. Here, we review the detection, toxicity, hazard identification and remediation methods of three classes of endocrine disruptors: steroid hormones, pharmaceutical and personal care products, and pesticides. Remediation methods include biological, physical, chemical, electrochemical and radiative methods. Bisphenol A was removed of 99% by biodegradation and ultraviolet with hydrogen peroxide, 98.4% by electropolymerization, 97.5% by photoelectrolysis and 80% by sand filtration. We present advanced treatment chemicals and discuss the performance of remediation using the combination of 2–3 treatment methods. In silico methods and machine learning for predicting toxicity and remediation are discussed



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abargues MR, Ferrer J, Bouzas A, Seco A (2013) Removal and fate of endocrine disruptors chemicals under lab-scale postreatment stage. removal assessment using light, oxygen and microalgae. Biores Technol 149:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.051
Abdel-Razik RK, Mosallam EM, Hamed NA, Badawy ME, Abo-El-Saad MM (2021) Testicular deficiency associated with exposure to cypermethrin, imidacloprid, and chlorpyrifos in adult rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 87:103724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2021.103724
Alaa-Eldin EA, El-Shafei DA, Abouhashem NS (2017) Individual and combined effect of chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin on reproductive system of adult male albino rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(2):1532–1543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7912-6
Alikarami M, Soltani RDC, Khataee A (2019) An innovative combination of electrochemical and photocatalytic processes for decontamination of bisphenol A endocrine disruptor form aquatic phase: Insight into mechanism, enhancers and bio-toxicity assay. Sep Purif Technol 220:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.03.056
Arditsoglou A, Voutsa D (2012) Occurrence and partitioning of endocrine-disrupting compounds in the marine environment of Thermaikos Gulf, Northern Aegean Sea. Greece Mar Pollut Bull 64(11):2443–2452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.048
Astrahan P, Korzen L, Khanin M, Sharoni Y, Israel Á (2021) Seaweeds fast EDC bioremediation: supporting evidence of EE2 and BPA degradation by the red seaweed Gracilaria sp., and a proposed model for the remedy of marine-borne phenol pollutants. Environ Pollut 278:116853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116853
Bai X, Acharya K (2019) Removal of seven endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from municipal wastewater effluents by a freshwater green alga. Environ Pollut 247:534–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.075
Bai X, Zhang B, He Y, Hong D, Song S, Huang Y, Zhang T (2020) Triclosan and triclocarbon in maternal-fetal serum, urine, and amniotic fluid samples and their implication for prenatal exposure. Environ Pollut 266:115117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115117
Barrera H, Ureña-Nuñez F, Barrios JA, Becerril E, Frontana-Uribe BA, Barrera-Díaz CE (2021) Degradation of nonylphenol ethoxylate 10 (NP10EO) in a synthetic aqueous solution using a combined treatment: electrooxidation-gamma irradiation. Fuel 283:118929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118929
Barse AV, Chakrabarti T, Ghosh TK, Pal AK, Jadhao SB (2007) Endocrine disruption and metabolic changes following exposure of cyprinus carpio to diethyl phthalate. Pestic Biochem Physiol 88(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.08.009
Baycan N, Puma GL (2018) Nanostructured catalysts for photo-oxidation of endocrine disrupting chemicals. J Photochem Photobiol A 364:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.05.010
Berslin D, Reshmi A, Sivaprakash B, Rajamohan N, Kumar PS (2021) Remediation of emerging metal pollutants using environment friendly biochar-review on applications and mechanism. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133384
Bodziach K, Staniszewska M, Falkowska L, Nehring I, Ożarowska A, Zaniewicz G, Meissner W (2021) Gastrointestinal and respiratory exposure of water birds to endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds. Sci Total Environ 754:142435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142435
Braeken L, Van der Bruggen B (2009) Feasibility of nanofiltration for the removal of endocrine disrupting compounds. Desalination 240(1–3):127–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.069
Budeli P, Ekwanzala MD, Unuofin JO, Momba MNB (2021) Endocrine disruptive estrogens in wastewater: revisiting bacterial degradation and zymoremediation. Environ Technol Innov 21:101248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101248
Cabrera-Lafaurie WA, Román FR, Hernández-Maldonado AJ (2015) Single and multi-component adsorption of salicylic acid, clofibric acid, carbamazepine and caffeine from water onto transition metal modified and partially calcined inorganic–organic pillared clay fixed beds. J Hazard Mater 282:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.009
Cajthaml T, Křesinová Z, Svobodová K, Möder M (2009) Biodegradation of endocrine-disrupting compounds and suppression of estrogenic activity by ligninolytic fungi. Chemosphere 75(6):745–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.034
Cao J, Fu B, Zhang T, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Zhao J, Luo J (2020) Fate of typical endocrine active compounds in full-scale wastewater treatment plants: distribution, removal efficiency and potential risks. Biores Technol 310:123436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123436
Cases V, Alonso V, Argandoña V, Rodriguez M, Prats D (2011) Endocrine disrupting compounds: a comparison of removal between conventional activated sludge and membrane bioreactors. Desalination 272(1–3):240–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.026
Čelić M, Škrbić BD, Insa S, Živančev J, Gros M, Petrović M (2020) Occurrence and assessment of environmental risks of endocrine disrupting compounds in drinking, surface and wastewaters in Serbia. Environ Pollut 262:114344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114344
Chen PJ, Linden KG, Hinton DE, Kashiwada S, Rosenfeldt EJ, Kullman SW (2006) Biological assessment of bisphenol A degradation in water following direct photolysis and UV advanced oxidation. Chemosphere 65(7):1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.048
Chen Y, Cheng F, Sun L, Li W, Liu G, Tang Y (2014) Computational models to predict endocrine-disrupting chemical binding with androgen or oestrogen receptors. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.08.026
Chen L, Fu W, Tan Y, Zhang X.(2021) Emerging organic contaminants and odorous compounds in secondary effluent wastewater: identification and advanced treatment. J of Hazardous Materials, 408, 124817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124817
Cho EJ, Kang JK, Moon JK, Um BH, Lee CG, Jeong S, Park SJ (2021) Removal of triclosan from aqueous solution via adsorption by kenaf-derived biochar: its adsorption mechanism study via spectroscopic and experimental approaches. J Environ Chem Eng 9(6):106343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106343
Christinelli WA, Shimizu FM, Facure MH, Cerri R, Oliveira ON Jr, Correa DS, Mattoso LH (2021) Two-dimensional MoS2-based impedimetric electronic tongue for the discrimination of endocrine disrupting chemicals using machine learning. Sens Actuators B Chem 336:129696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129696
Ciallella HL, Russo DP, Aleksunes LM, Grimm FA, Zhu H (2021) Predictive modeling of estrogen receptor agonism, antagonism, and binding activities using machine-and deep-learning approaches. Lab Invest 101(4):490–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-020-00477-2
Cruz-Morató C, Lucas D, Llorca M, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Gorga M, Petrovic M, Marco-Urrea E (2014) Hospital wastewater treatment by fungal bioreactor: removal efficiency for pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptor compounds. Sci Total Environ 493:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.117
Czech B, Shirvanimoghaddam K, Trojanowska E (2020) Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) onto a sustainable cotton based adsorbent. Sustain Chem Pharm 18:100324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100324
Daghrir R, Drogui P (2013) Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 11(3):209–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0404-8
Dai R, Han H, Wang T, Li X, Wang Z (2021) Enhanced removal of hydrophobic endocrine disrupting compounds from wastewater by nanofiltration membranes intercalated with hydrophilic MoS2 nanosheets: role of surface properties and internal nanochannels. J Membr Sci 628:119267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119267
D’Alessio M, Yoneyama B, Kirs M, Kisand V, Ray C (2015) Pharmaceutically active compounds: their removal during slow sand filtration and their impact on slow sand filtration bacterial removal. Sci Total Environ 524:124–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.014
Davididou K, Nelson R, Monteagudo JM, Durán A, Expósito AJ, Chatzisymeon E (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A under UV-LED, blacklight and solar irradiation. J Clean Prod 203:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.247
de Andrade ALC, Soares PRL, da Silva SCBL, da Silva MCG, Santos TP, Cadena MRS, Cadena PG (2017) Evaluation of the toxic effect of endocrine disruptor bisphenol A (BPA) in the acute and chronic toxicity tests with pomacea lineata gastropod. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 197:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.04.002
de Oliveira ME, Barroso BL, de Almeida J, Moraes MLL, de Arruda RC (2020) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol and estrone under UV and visible light using nanotubular oxide arrays grown on Ti-0.5 wt% W. Environ Res 191:110044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110044
de Oliveira KMG, de Sousa Carvalho EH, dos Santos Filho R, Sivek TW, Thá EL, de Souza IR, Leme DM (2021) Single and mixture toxicity evaluation of three phenolic compounds to the terrestrial ecosystem. J Environ Manag 296:113226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113226
Dietrich M, Franke M, Stelter M, Braeutigam P (2017) Degradation of endocrine disruptor bisphenol A by ultrasound-assisted electrochemical oxidation in water. Ultrason Sonochem 39:741–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.05.038
Elias KD, Ejidike IP, Mtunzi FM, Pakade VE (2021) Endocrine Disruptors-(estrone and β-estradiol) removal from water by Nutshell activated carbon: Kinetic, Isotherms and Thermodynamic studies. J Chem Thermodyn 3, 100013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctta.2021.100013
Errico S, Nicolucci C, Migliaccio M, Micale V, Mita DG, Diano N (2017) Analysis and occurrence of some phenol endocrine disruptors in two marine sites of the northern coast of Sicily (Italy). Mar Pollut Bull 120(1–2):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.04.061
Fan D, Yin W, Gu W, Liu M, Liu J, Wang Z, Shi L (2021) Occurrence, spatial distribution and risk assessment of high concern endocrine-disrupting chemicals in Jiangsu Province China. Chemosphere 285:131396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131396
Feng LJ, Yang GF, Zhu L, Xu XY (2014) Removal performance of nitrogen and endocrine-disrupting pesticides simultaneously in the enhanced biofilm system for polluted source water pretreatment. Biores Technol 170:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.004
Fernández MF, Mustieles V, Suárez B, Reina-Pérez I, Olivas-Martinez A, Vela-Soria F (2021) Determination of bisphenols, parabens, and benzophenones in placenta by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 274:129707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129707
Frankowski R, Płatkiewicz J, Stanisz E, Grześkowiak T, Zgoła-Grześkowiak A (2021) Biodegradation and photo-fenton degradation of bisphenol A, bisphenol S and fluconazole in water. Environ Pollut 289:117947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117947
Fuhrman VF, Tal A, Arnon S (2015) Why endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) challenge traditional risk assessment and how to respond. J Hazard Mater 286:589–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.012
Gani KM, Kazmi AA (2020) Ecotoxicological risk evaluation and regulatory compliance of endocrine disruptor phthalates in a sustainable wastewater treatment scheme. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(8):7785–7794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07418-7
Gerent GG, Spinelli A (2019) Ag–Au core-partial shell bimetallic nanoparticles applied in electrochemical determination of the potential endocrine disruptor oryzalin. J Electroanal Chem 855:113484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113484
Grisoni F, Consonni V, Ballabio D (2019) Machine learning consensus to predict the binding to the androgen receptor within the CoMPARA project. J Chem Inf Model 59(5):1839–1848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00794
Guo Y, Rene ER, Han B, Ma W (2021) Enhanced fluoroglucocorticoid removal from groundwater in a bio-electrochemical system with polyaniline-loaded activated carbon three-dimensional electrodes: performance and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126197
Haubruge E, Petit F, Gage MJ (2000) Reduced sperm counts in guppies (poecilia reticulata) following exposure to low levels of tributyltin and bisphenol A. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 267(1459):2333–2337. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2000.1288
Herreros MA, Gonzalez-Bulnes A, Inigo-Nunez S, Letelier C, Contreras-Solis I, Ros-Rodriguez JM, Encinas T (2010) Pregnancy-associated changes in plasma concentration of the endocrine disruptor di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in a sheep model. Theriogenology 73(2):141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2009.07.029
Hom-Diaz A, Llorca M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Vicent T, Barceló D, Blánquez P (2015) Microalgae cultivation on wastewater digestate: β-estradiol and 17α-ethynylestradiol degradation and transformation products identification. J Environ Manag 155:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.003
Hou L, Xu H, Ying G, Yang Y, Shu H, Zhao J, Cheng X (2017) Physiological responses and gene expression changes in the western mosquitofish (gambusia affinis) exposed to progesterone at environmentally relevant concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 192:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.011
Huang Y, Su L, Zhang S, Zhao Q, Zhang X, Li X, Wei X (2020) Opposite pH-dependent roles of hydroxyl radicals in ozonation and UV photolysis of genistein. Sci Total Environ 709:136243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136243
Janicki T, Krupiński M, Długoński J (2016) Degradation and toxicity reduction of the endocrine disruptors nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol and 4-cumylphenol by the non-ligninolytic fungus umbelopsis isabellina. Biores Technol 200:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.034
Jun BM, Kim S, Heo J, Her N, Jang M, Park CM, Yoon Y (2019) Enhanced sonocatalytic degradation of carbamazepine and salicylic acid using a metal-organic framework. Ultrason Sonochem 56:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.04.019
Jung JW, Kang JS, Choi J, Park JW (2020) Chronic toxicity of endocrine disrupting chemicals used in plastic products in Korean resident species: Implications for aquatic ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:110309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110309
Khan K, Roy K, Benfenati E (2019) Ecotoxicological QSAR modeling of endocrine disruptor chemicals. J Hazard Mater 369:707–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.019
Kim Y, Joo H, Her N, Yoon Y, Sohn J, Kim S, Yoon J (2015) Simultaneously photocatalytic treatment of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) and endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) using rotating reactor under solar irradiation. J Hazard Mater 288:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.021
Kittappa S, Jang M, Ramalingam M, Ibrahim S (2020) Amine functionalized magnetic nano-composite materials for the removal of selected endocrine disrupting compounds and its mechanism study. J Environ Chem Eng, 8(4): 103839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103839
Kim JH, Kwak JM, Kang H (2021a) Web-based behavioral intervention to reduce exposure to phthalate metabolites, bisphenol A, triclosan, and parabens in mothers with young children: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Hyg Environ Health 236:113798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113798
Kim M, Song YE, **ong JQ, Kim KY, Jang M, Jeon BH, Kim JR (2021b) Electrochemical detection and simultaneous removal of endocrine disruptor, bisphenol A using a carbon felt electrode. J Electroanal Chem 880:114907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114907
Kovačič A, Česen M, Laimou-Geraniou M, Lambropoulou D, Kosjek T, Heath D, Heath E (2019) Stability, biological treatment and UV photolysis of 18 bisphenols under laboratory conditions. Environ Res 179:108738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108738
Lara LZ, Bertoldi C, Alves NM, Fernandes AN (2021) Sorption of endocrine disrupting compounds onto polyamide microplastics under different environmental conditions: behaviour and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 796:148983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148983
Lee YM, Lee G, Kim MK, Zoh KD (2020) Kinetics and degradation mechanism of benzophenone-3 in chlorination and UV/chlorination reactions. Chem Eng J 393:124780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124780
Liu YH., Zhang SH, Ji G X, Wu SM, Guo RX, Cheng J, Chen JQ (2017) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of suspected endocrine-disrupting chemicals in surface water and suspended particulate matter of Yangtze River Nan**g section. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135, 90–97.
Li D, Bi R, Chen H, Mu L, Zhang L, Chen Q, **e L (2017) The acute toxicity of bisphenol A and lignin-derived bisphenol in algae, daphnids, and Japanese medaka. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(30):23872–23879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0018-y
Li J, He J, Aziz MT, Song X, Zhang Y, Niu Z (2021a) Iodide promotes bisphenol A (BPA) halogenation during chlorination: evidence from 30 X-BPAs (X= Cl, Br, and I). J Hazard Mater 414:125461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125461
Li M, Yang T, Gao L, Xu H (2021b) An inadvertent issue of human retina exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: a safety assessment. Chemosphere 264:128484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128484
Li X, Liu X, Jia Z, Wang T, Zhang H (2021c) Screening of estrogenic endocrine-disrupting chemicals in meat products based on the detection of vitellogenin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chemosphere 263:128251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128251
Lin X, Ni Y, Kokot S (2015) An electrochemical DNA-sensor developed with the use of methylene blue as a redox indicator for the detection of DNA damage induced by endocrine-disrupting compounds. Anal Chim Acta 867:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.050
Liu H, Yang X, Lu R (2016) Development of classification model and QSAR model for predicting binding affinity of endocrine disrupting chemicals to human sex hormone-binding globulin. Chemosphere 156:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.077
Llorca M, Badia-Fabregat M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Caminal G, Vicent T, Barceló D (2017) Fungal treatment for the removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from reverse osmosis concentrate: identification and monitoring of transformation products of benzotriazoles. Chemosphere 184:1054–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.053
Loffredo E, Parlavecchia M (2021) Use of plant-based sorbents and mycodegradation for the elimination of endocrine disrupting chemicals from soil: a novel facile and low-cost method. Environ Technol Innov 21:101358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101358
López-Velázquez K, Guzmán-Mar JL, Montalvo-Herrera TJ, Mendiola-Alvarez SY, Villanueva-Rodríguez M (2021) Efficient photocatalytic removal of four endocrine-disrupting compounds using N-doped BiOBr catalyst under UV-vis radiation. J Environ Chem Eng 9(5):106185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106185
Lu S, Yu Y, Ren L, Zhang X, Liu G, Yu Y (2018) Estimation of intake and uptake of bisphenols and triclosan from personal care products by dermal contact. Sci Total Environ 621:1389–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.088
Lu J, Wu J, Zhang C, Zhang Y (2020a) Possible effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the pollution of coastal water: occurrence, source, and risks of endocrine disrupting chemicals in coastal groundwater and adjacent seawater influenced by reclaimed water irrigation. Chemosphere 250:126323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126323
Lu J, Zhang C, Wu J, Zhang Y, Lin Y (2020b) Seasonal distribution, risks, and sources of endocrine disrupting chemicals in coastal waters: will these emerging contaminants pose potential risks in marine environment at continental-scale? Chemosphere 247:125907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125907
Lu S, Lin C, Lei K, **n M, Wang B, Ouyang W, He M (2021) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in a typical urbanized bay of Yellow Sea, China: distribution, risk assessment, and identification of priority pollutants. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117588
Luan H, Zhao H, Li J, Zhou Y, Fang J, Liu H, Cai Z (2021) Machine learning for investigation on endocrine-disrupting chemicals with gestational age and delivery time in a longitudinal cohort. Research. https://doi.org/10.34133/2021/9873135
Ma W, Nie C, Chen B, Cheng X, Lun X, Zeng F (2015) Adsorption and biodegradation of three selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in river-based artificial groundwater recharge with reclaimed municipal wastewater. J Environ Sci 31:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.12.006
Machtinger R, Berman T, Adir M, Mansur A, Baccarelli AA, Racowsky C, Nahum R (2018) Urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites, bisphenols and personal care product chemical biomarkers in pregnant women in Israel. Environ Int 116:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.022
Mallerman J, Itria R, Babay P, Saparrat M, Levin L (2019) Biodegradation of nonylphenol polyethoxylates by litter-basidiomycetous fungi. J Environ Chem Eng 7(5):103316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103316
Minerali E, Foil DH, Zorn KM, Ekins S (2020) Evaluation of assay central machine learning models for rat acute oral toxicity prediction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(42):16020–16027. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c06348
Monisha RS, Mani RL, Sivaprakash B, Rajamohan N, Vo DVN (2021) Green remediation of pharmaceutical wastes using biochar: a review. Environ Chem Lett 1:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01348-y
Mukherjee R, Beykal B, Szafran AT, Onel M, Stossi F, Mancini MG, Pistikopoulos EN (2020) Classification of estrogenic compounds by coupling high content analysis and machine learning algorithms. PLoS Comput Biol 16(9):e1008191. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008191
Munier M, Grouleff J, Gourdin L, Fauchard M, Chantreau V, Henrion D, Rodien P (2016) In vitro effects of the endocrine disruptor p, p’-DDT on human follitropin receptor. Environ Health Perspect 124(7):991–999. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1510006
Murack PJ, Parrish J, Barry TP (2011) Effects of progesterone on sperm motility in fathead minnow (pimephales promelas). Aquat Toxicol 104(1–2):121–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.04.006
Nakada N, Shinohara H, Murata A, Kiri K, Managaki S, Sato N, Takada H (2007) Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res 41(19):4373–4382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.038
Nice HE, Morritt D, Crane M, Thorndyke M (2003) Long-term and transgenerational effects of nonylphenol exposure at a key stage in the development of crassostrea gigas. possible endocrine disruption? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 256:293–300. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps256293
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Tillmann M, Markert B (2000) Effects of endocrine disruptors on prosobranch snails (mollusca: gastropoda) in the laboratory. part I: bisphenol A and octylphenol as xeno-estrogens. Ecotoxicology 9(6):383–397. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008972518019
Ohtani H, Miura I, Ichikawa Y (2000) Effects of dibutyl phthalate as an environmental endocrine disruptor on gonadal sex differentiation of genetic males of the frog Rana rugosa. Environ Health Perspect 108(12):1189–1193. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.001081189
Olmez-Hanci T, Dursun D, Aydin E, Arslan-Alaton I, Girit B, Mita L, Guida M (2015) S2O82−/UV-C and H2O2/UV-C treatment of Bisphenol A: assessment of toxicity, estrogenic activity, degradation products and results in real water. Chemosphere 119:S115–S123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.020
Omran NE, Salama WM (2016) The endocrine disruptor effect of the herbicides atrazine and glyphosate on biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Toxicol Ind Health 32(4):656–665. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713506959
Oskar S, Wolff MS, Teitelbaum SL, Stingone JA (2021) Identifying environmental exposure profiles associated with timing of menarche: a two-step machine learning approach to examine multiple environmental exposures. Environ Res 195:110524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110524
Park Y, Sun Z, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2014) Bisphenol A sorption by organo-montmorillonite: implications for the removal of organic contaminants from water. Chemosphere 107:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.050
Park HJ, Lee WY, Do JT, Park C, Song H (2021) Evaluation of testicular toxicity upon fetal exposure to bisphenol A using an organ culture method. Chemosphere 270:129445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129445
Pereira VJ, Galinha J, Crespo MTB, Matos CT, Crespo JG (2012) Integration of nanofiltration, UV photolysis, and advanced oxidation processes for the removal of hormones from surface water sources. Sep Purif Technol 95:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.04.013
Petrie B, Camacho-Muñoz D (2021) Analysis, fate and toxicity of chiral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in wastewaters and the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(1):43–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01065-y
Piir G, Sild S, Maran U (2021) Binary and multi-class classification for androgen receptor agonists, antagonists and binders. Chemosphere 262:128313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128313
Rajamohan N, Sivaprakash B (2008) Biosorption of heavy metal using brown seaweed in a regenerable continuous column. Asia-Pacific J Chem Eng 3(5):572–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.202
Rajamohan N, Sivaprakash B (2010) Biosorption of inorganic mercury onto marine alga sargassum tenerrimum: batch and column studies. Int J Environ Technol Manag 12(2–4):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJETM.2010.031530
Romero V, Fernandes, SP, Kovář P, Pšenička M, Kolen'ko YV, Salonen L M, Espiña B (2020) Efficient adsorption of endocrine-disrupting pesticides from water with a reusable magnetic covalent organic framework. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 307, 110523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110523
Rosenfeldt EJ, Chen PJ, Kullman S, Linden KG (2007) Destruction of estrogenic activity in water using UV advanced oxidation. Sci Total Environ 377(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.096
Russo DP, Zorn KM, Clark AM, Zhu H, Ekins S (2018) Comparing multiple machine learning algorithms and metrics for estrogen receptor binding prediction. Mol Pharm 15(10):4361–4370. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00546
Sakhteman A, Failli M, Kublbeck J, Levonen AL, Fortino V (2021) A toxicogenomic data space for system-level understanding and prediction of EDC-induced toxicity. Environ Int 156:106751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106751
Sayed AEDH, Mahmoud UM, Mekkawy IA (2012) Reproductive biomarkers to identify endocrine disruption in clarias gariepinus exposed to 4-nonylphenol. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.041
Singam ERA, Tachachartvanich P, Fourches D, Soshilov A, Hsieh JC, La Merrill MA, Durkin KA (2020) Structure-based virtual screening of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) as endocrine disruptors of androgen receptor activity using molecular docking and machine learning. Environ Res 190:109920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109920
Singh S, Kumar V, Chauhan A, Datta S, Wani AB, Singh N, Singh J (2018) Toxicity, degradation and analysis of the herbicide atrazine. Environ Chem Lett 16(1):211–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0665-8
Sivaprakash B, Rajamohan N (2011) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on the biosorption of As (III) and As (V) by the marine algae turbinaria conoides. Res J Environ Sci 5(10):779. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2011.779.789
Song M, Liang D, Liang Y, Chen M, Wang F, Wang H, Jiang G (2014) Assessing developmental toxicity and estrogenic activity of halogenated bisphenol A on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 112:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.084
Staniszewska M, Koniecko I, Falkowska L, Krzymyk E (2015) Occurrence and distribution of bisphenol A and alkylphenols in the water of the gulf of Gdansk (Southern Baltic). Mar Pollut Bull 91(1):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.027
Su C, Cui Y, Liu D, Zhang H, Baninla Y (2020) Endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment of China: which chemicals are the prioritized ones? Sci Total Environ 720:137652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137652
Suyamud B, Thiravetyan P, Panyapinyopol B, Inthorn D (2018) Dracaena sanderiana endophytic bacteria interactions: effect of endophyte inoculation on bisphenol A removal. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.066
Tan TL, Lai CW, Hong SL, Rashid SA (2018) New insights into the photocatalytic endocrine disruptors dimethyl phathalate esters degradation by UV/MWCNTs-TiO2 nanocomposites. J Photochem Photobiol A 364:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.05.019
Tanner EM, Hallerbäck MU, Wikström S, Lindh C, Kiviranta H, Gennings C, Bornehag CG (2020) Early prenatal exposure to suspected endocrine disruptor mixtures is associated with lower IQ at age seven. Environ Int 134:105185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105185
Torres T, Cunha I, Martins R, Santos MM (2016) Screening the toxicity of selected personal care products using embryo bioassays: 4-MBC, propylparaben and triclocarban. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101762
Torres NH, Santos GDOS, Ferreira LFR, Américo-Pinheiro JHP, Eguiluz KIB, Salazar-Banda GR (2021) Environmental aspects of hormones estriol, 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol: Electrochemical processes as next-generation technologies for their removal in water matrices. Chemosphere 267:128888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128888
Trujillo-Rodríguez MJ, Gomila RM, Martorell G, Miró M (2021) Microscale extraction versus conventional approaches for handling gastrointestinal extracts in oral bioaccessibility assays of endocrine disrupting compounds from microplastic contaminated beach sand. Environ Pollut 272, 115992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115992
Verma D, Yadav AK, Mukherjee MD, Solanki PR (2021) Fabrication of a sensitive electrochemical sensor platform using reduced graphene oxide-molybdenum trioxide nanocomposite for BPA detection: an endocrine disruptor. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105504
Vlassi E, Bempelou E, Liapis K, Arapis G (2020) Consumer safety evaluation after monitoring of endocrine disruptor pesticide residues: a case study of Thessaly. Cent Greece Toxicol Environ Chem 102(1–4):105–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2020.1770256
Wang S, Zhu Z, He J, Yue X, Pan J, Wang Z (2018) Steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in surface water of Bahe River, China: distribution, bioaccumulation, risk assessment and estrogenic effect on hemiculter leucisculus. Environ Pollut 243:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.063
Wang Q, Yang H, Yang M, Yu Y, Yan M, Zhou L, Li Y (2019) Toxic effects of bisphenol A on goldfish gonad development and the possible pathway of BPA disturbance in female and male fish reproduction. Chemosphere 221:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.033
Wang P, Sun Q, Wan R, Du Q, **a X (2020) Progesterone affects the transcription of genes in the circadian rhythm signaling and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axes and changes the sex ratio in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 77:103378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103378
Wee SY, Aris AZ, Yusoff FM, Praveena SM (2019) Occurrence and risk assessment of multiclass endocrine disrupting compounds in an urban tropical river and a proposed risk management and monitoring framework. Sci Total Environ 671:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.243
Wee SY, Aris AZ, Yusoff FM, Praveena SM (2021) Tap water contamination: multiclass endocrine disrupting compounds in different housing types in an urban settlement. Chemosphere 264:128488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128488
Wei Q, Zhang P, Pu H, Sun DW (2021) A fluorescence aptasensor based on carbon quantum dots and magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of 17β-estradiol. Food Chem 373:131591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131591
Wirasnita R, Mori K, Toyama T (2018) Effect of activated carbon on removal of four phenolic endocrine-disrupting compounds, bisphenol A, bisphenol F, bisphenol S, and 4-tert-butylphenol in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 210:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.060
Wu H, Niu X, Yang J, Wang C, Lu M (2016) Retentions of bisphenol A and norfloxacin by three different ultrafiltration membranes in regard to drinking water treatment. Chem Eng J 294:410–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.117
Xu F, Chen J, Kalytchuk S, Chu L, Shao Y, Kong D, Teoh WY (2017) Supported gold clusters as effective and reusable photocatalysts for the abatement of endocrine-disrupting chemicals under visible light. J Catal 354:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.07.027
Xue W, **ao K, Liang P, Huang X (2018) Roles of membrane and organic fouling layers on the removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in microfiltration. J Environ Sci 72:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.01.004
Yan X, He B, Hu L, Gao J, Chen S, Jiang G (2018) Insight into the endocrine disrupting effect and cell response to butyltin compounds in H295R cell: Evaluated with proteomics and bioinformatics analysis. Sci Total Environ 628:1489–1496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.165
Yi X, Tran NH, Yin T, He Y, Gin KYH (2017) Removal of selected PPCPs, EDCs, and antibiotic resistance genes in landfill leachate by a full-scale constructed wetlands system. Water Res 121:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.008
Yilmaz B, Terekeci H, Sandal S, Kelestimur F (2020) Endocrine disrupting chemicals: exposure, effects on human health, mechanism of action, models for testing and strategies for prevention. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 21(1):127–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-019-09521-z
Yin N, Yao X, Qin Z, Wang YL, Faiola F (2015) Assessment of bisphenol A (BPA) neurotoxicity in vitro with mouse embryonic stem cells. J Environ Sci 36:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.06.004
Yoon Y, Westerhoff P, Snyder SA, Wert EC, Yoon J (2007) Removal of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals by nanofiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 202(1–3):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.12.033
Zbair M, Bottlinger M, Ainassaari K, Ojala S, Stein O, Keiski RL, Brahmi R (2020) Hydrothermal carbonization of argan nut shell: functional mesoporous carbon with excellent performance in the adsorption of bisphenol A and diuron. Waste and biomass valorization, 11(4): 1565–1584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-00554-0
Zhang Q, Yan L, Wu Y, Ji L, Chen Y, Zhao M, Dong X (2017) A ternary classification using machine learning methods of distinct estrogen receptor activities within a large collection of environmental chemicals. Sci Total Environ 580:1268–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.088
Zhang C, Lu J, Wu J, Luo Y (2019) Phycoremediation of coastal waters contaminated with bisphenol A by green tidal algae ulva prolifera. Sci Total Environ 661:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.132
Zhang C, Lu J, Wu J (2021) Enhanced removal of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals from coastal waters by intertidal macroalgae. J Hazard Mater 411:125105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125105
Zhao L, Zhang X, Liu Z, Deng C, Xu H, Wang Y, Zhu M (2021) Carbon nanotube-based electrocatalytic filtration membrane for continuous degradation of flow-through Bisphenol A. Sep Purif Technol 265:118503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118503
Zhou R, Cheng W, Feng Y, Wei H, Liang F, Wang Y (2017) Interactions between three typical endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in binary mixtures exposure on myocardial differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell. Chemosphere 178:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.040
Zorn KM, Foil DH, Lane TR, Hillwalker W, Feifarek DJ, Jones F, Ekins S (2020) Comparing machine learning models for aromatase (P450 19A1). Environ Sci Technol 54(23):15546–15555. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c05771
Zorzo CF, Inticher JJ, Borba FH, Cabrera LC, Dugatto JS, Baroni S, Bergamasco R (2021) Oxidative degradation and mineralization of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol-A by an eco-friendly system based on UV-solar/H2O2 with reduction of genotoxicity and cytotoxicity levels. Sci Total Environ 770:145296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145296
Funding
The authors declare that no funding is received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no competing financial interests declared by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Monisha, R.S., Mani, R.L., Sivaprakash, B. et al. Remediation and toxicity of endocrine disruptors: a review. Environ Chem Lett 21, 1117–1139 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01455-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01455-4