Abstract
Objectives
Anti-cytokine therapy is reportedly useful in amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases. However, to date no studies have directly compared the utility of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition to that of interleukin-6. The aim of our retrospective study was to compare the clinical utility of tocilizumab (TCZ) and anti-TNF (TNF inhibitor) therapy.
Methods
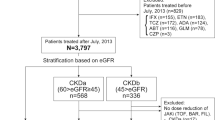
We studied 42 patients treated with anti-cytokine agents at our hospital: 31 had received a single agent, ten had received two agents and one had received three agents. Patients were divided into a TCZ group (22 patients) and a TNF inhibitor group (32 patients). The main parameters compared were treatment retention rate, serum amyloid A (SAA) profile, renal function profile and clinical disease activity index.
Results
The 5-year retention rates were 90.4 (TCZ group) and 34.3 % (TNF inhibitor group) (p = 0.0154, log-rank test). The median SAA fell from 219.2 μg/mL at treatment initiation to 5.0 μg/mL at last observation (TCZ), and from 143.6 to 38.1 μg/mL (TNF inhibitor) (p = 0.0194). Estimated glomerular filtration rate was improved in 72.7 (TCZ) and 34.4 % (TNF inhibitor) of patients (p = 0.0062). The rates of clinical remission or low disease activity at last observation for the TCZ and TNF inhibitor groups were 72.7 and 40.7 % (p = 0.0201), respectively.
Conclusions
Based on these results, we conclude that TCZ was of greater clinical utility than anti-TNF therapy in our patients with AA amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gillmore JD, Lovat LB, Persey MR, Pepys MB, Hawkins PN. Amyloid load and clinical outcome in AA amyloidosis in relation to circulating concentration of serum amyloid A protein. Lancet. 2001;358:24–9.
Lachmann HJ, Goodman HJ, Gilbertson JA, Gallimore JR, Sabin CA, Gillmore JD, et al. Natural history and outcome in systemic AA amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2361–71.
Elkayam O, Hawkins PN, Lachmann H, Yaron M, Caspi D. Rapid and complete resolution of proteinuria due to renal amyloidosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2571–3.
Gottenberg JE, Merle-Vincent F, Bentaberry F, Allanore Y, Berenbaum F, Fautrel B, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis α therapy in fifteen patients with AA amyloidosis secondary to inflammatory arthritides: a follow up report of tolerability and efficacy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2019–24.
Kuroda T, Wada Y, Kobayashi D, Murakami S, Sakai T, Hirose S, et al. Effective anti-TNF-α therapy can induce rapid resolution and sustained decrease of gastroduodenal mucosal amyloid deposits in reactive amyloidosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:2409–15.
Nakamura T, Higashi S, Tomoda K, Tsukano M, Shono M. Etanercept can induce resolution of renal deterioration in patients with amyloid A amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:1395–401.
Fernándes-Nebro A, Olivé A, Castro MC, Varela AH, Riera E, Irigoyen MV, et al. Long-term TNF-alpha blockade in patients with amyloid A amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases. Am J Med. 2010;123:454–61.
Okuda Y, Takasugi K. Successful use of a humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, to treat amyloid A amyloidosis complicating juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2997–3000.
Sato H, Sakai T, Sugaya T, Otaki Y, Aoki K, Ishii K, et al. Tocilizumab dramatically ameliorated life-threatening diarrhea due to secondary amyloidosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:1113–6.
Inoue D, Arima H, Kawanami C, Takiuchi Y, Nagano S, Kimura T, et al. Excellent therapeutic effect of tocilizumab on intestinal amyloid A deposition secondary to active rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:1195–7.
Nishida S, Hagihara K, Shima Y, Kawai M, Kuwahara Y, Arimitsu J, et al. Rapid improvement of AA amyloidosis with humanised anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1235–6.
Kishida D, Okuda Y, Onishi M, Takebayashi M, Matoba K, Jouyama K, et al. Successful tocilizumab treatment in a patient with adult-onset Still’s disease complicated by chronic active hepatitis B and amyloid A amyloidosis. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21:215–8.
Ubara Y, J Hoshi J, Suwabe T. Renal amyloidosis (in Japanese). Medicina (ISSN 0025-7699). 2009;46:1980–3.
Puchtler H, Sweat F, Levine M. On the binding of Congo red by amyloid. J Histochem Cytochem. 1962;10:355–64.
Linke RP. Monoclonal antibodies against amyloid fibril protein AA. Production, specificity, and use for immunohistochemical localization and classification of AA-type amyloidosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984;32:322–8.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Hagihara K, Nishikawa T, Isobe T, Song J, Sugamata Y, Yoshizaki K. IL-6 plays a critical role in the synergistic induction of human serum amyloid A (SAA) gene when stimulated with proinflammatory cytokines as analyzed with an SAA isoform real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;314:363–9.
Hagihara K, Nishikawa T, Sugamata Y, Song J, Isobe T, Taga T, et al. Essential role of STAT3 in cytokine-driven NF-kappaB-mediated serum amyloid A gene expression. Genes Cells. 2005;10:1051–63.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Amyloidosis Research Committee of the Intractable Disease Division of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Okuda, Y., Ohnishi, M., Matoba, K. et al. Comparison of the clinical utility of tocilizumab and anti-TNF therapy in AA amyloidosis complicating rheumatic diseases. Mod Rheumatol (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0846-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0846-7