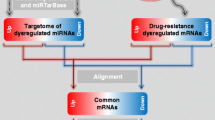
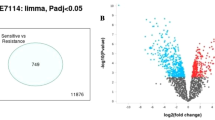
Abstract
Targeted therapy in the form of selective breakpoint cluster region-abelson (BCR/ABL) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (imatinib mesylate) has successfully been introduced in the treatment of the chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, acquired resistance against imatinib mesylate (IM) has been reported in nearly half of patients and has been recognized as major issue in clinical practice. Multiple resistance genes and microRNAs (miRNAs) are thought to be involved in the IM resistance process. These resistance genes and miRNAs tend to interact with each other through a regulatory network. Therefore, it is crucial to study the impact of these interactions in the IM resistance process. The present study focused on miRNA and gene network analysis in order to elucidate the role of interacting elements and to understand their functional contribution in therapeutic failure. Unlike previous studies which were centered only on genes or miRNAs, the prime focus of the present study was on relationships. To this end, three regulatory networks including differentially expressed, related, and global networks were constructed and analyzed in search of similarities and differences. Regulatory associations between miRNAs and their target genes, transcription factors and miRNAs, as well as miRNAs and their host genes were also macroscopically investigated. Certain key pathways in the three networks, especially in the differentially expressed network, were featured. The differentially expressed network emerged as a fault map of IM-resistant CML. Theoretically, the IM resistance process could be prevented by correcting the included errors. The present network-based approach to study resistance miRNAs and genes might help in understanding the molecular mechanisms of IM resistance in CML as well as in the improvement of CML therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- IM:
-
Imatinib mesylate
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- TFBSs:
-
Transcription factor binding sites
References
A J, Qian S, Wang G, Yan B, Zhang S, Huang Q, Ni L, Zha W, Liu L, Cao B, Hong M, Wu H, Lu H, Shi J, Li M, Li J (2010) Chronic myeloid leukemia patients sensitive and resistant to imatinib treatment show different metabolic responses. PLoS One 5:e13186. DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0013186
Alikian M, Gerrard G, Subramanian PG, Mudge K, Foskett P, Khorashad JS, Lim AC, Marin D, Milojkovic D, Reid A, Rezvani K, Goldman J, Apperley J, Foroni L (2012) BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations: methodology and clinical evaluation. Am J Hematol 87:298–304. doi:10.1002/ajh.22272
Augis V, Airiau K, Josselin M, Turcq B, Mahon FX, Belloc F (2013) A single nucleotide polymorphism in cBIM is associated with a slower achievement of major molecular response in chronic myeloid leukaemia treated with imatinib. PLoS One 8:e78582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078582
Barabasi AL, Oltvai ZN (2004) Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat Rev Genet 5:101–113. doi:10.1038/nrg1272
Baskerville S, Bartel DP (2005) Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 11:241–247. doi:10.1261/rna.7240905
Budak H, Akpinar BA (2015) Plant miRNAs: biogenesis, organization and origins. Funct Integr Genomics 15:523–531. doi:10.1007/s10142-015-0451-2
Cao G, Huang B, Liu Z, Zhang J, Xu H, **a W, Li J, Li S, Chen L, Ding H, Zhao Q, Fan M, Shen B, Shao N (2010) Intronic miR-301 feedback regulates its host gene, ska2, in A549 cells by targeting MEOX2 to affect ERK/CREB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396:978–982. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.037
Chekmenev DS, Haid C, Kel AE (2005) P-Match: transcription factor binding site search by combining patterns and weight matrices. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W432–W437. doi:10.1093/nar/gki441
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, Tsai TR, Ho SY, Jian TY, Wu HY, Chen PR, Lin NC, Huang HT, Yang TL, Pai CY, Tai CS, Chen WL, Huang CY, Liu CC, Weng SL, Liao KW, Hsu WL, Huang HD (2016) miRTarBase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D239–D247. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1258
Cunningham F, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K, Billis K, Brent S, Carvalho-Silva D, Clapham P, Coates G, Fitzgerald S, Gil L, Giron CG, Gordon L, Hourlier T, Hunt SE, Janacek SH, Johnson N, Juettemann T, Kahari AK, Keenan S, Martin FJ, Maurel T, McLaren W, Murphy DN, Nag R, Overduin B, Parker A, Patricio M, Perry E, Pignatelli M, Riat HS, Sheppard D, Taylor K, Thormann A, Vullo A, Wilder SP, Zadissa A, Aken BL, Birney E, Harrow J, Kinsella R, Muffato M, Ruffier M, Searle SM, Spudich G, Trevanion SJ, Yates A, Zerbino DR, Flicek P (2015) Ensembl 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D662–D669. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1010
Dang CV, O’Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen T, Osthus RC, Li F (2006) The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol 16:253–264. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.014
Elghannam DM, Ibrahim L, Ebrahim MA, Azmy E, Hakem H (2014) Association of MDR1 gene polymorphism (G2677T) with imatinib response in Egyptian chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Hematology 19:123–128. doi:10.1179/1607845413Y.0000000102
Esposito N, Colavita I, Quintarelli C, Sica AR, Peluso AL, Luciano L, Picardi M, Del Vecchio L, Buonomo T, Hughes TP, White D, Radich JP, Russo D, Branford S, Saglio G, Melo JV, Martinelli R, Ruoppolo M, Kalebic T, Martinelli G, Pane F (2011) SHP-1 expression accounts for resistance to imatinib treatment in Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells derived from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 118:3634–3644. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-03-341073
Guo Z, Maki M, Ding R, Yang Y, Zhang B, **ong L (2014) Genome-wide survey of tissue-specific microRNA and transcription factor regulatory networks in 12 tissues. Sci Rep 4:5150. doi:10.1038/srep05150
Hobert O (2008) Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 319:1785–1786. doi:10.1126/science.1151651
Hsu SD, Lin FM, Wu WY, Liang C, Huang WC, Chan WL, Tsai WT, Chen GZ, Lee CJ, Chiu CM, Chien CH, Wu MC, Huang CY, Tsou AP, Huang HD (2011) miRTarBase: a database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D163–D169. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1107
Jelinek J, Gharibyan V, Estecio MR, Kondo K, He R, Chung W, Lu Y, Zhang N, Liang S, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE, Issa JP (2011) Aberrant DNA methylation is associated with disease progression, resistance to imatinib and shortened survival in chronic myelogenous leukemia. PLoS One 6:e22110. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022110
Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M, Zhang X, Li M, Wang G, Liu Y (2009) miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D98–D104. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn714
Kim DH, Xu W, Kamel-Reid S, Liu X, Jung CW, Kim S, Lipton JH (2010) Clinical relevance of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) and VEGF receptor (VEGFR2) gene polymorphism on the treatment outcome following imatinib therapy. Ann Oncol 21:1179–1188. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp452
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2011) miRBase: integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D152–D157. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1027
Li H, Yang BB (2014) MicroRNA-in drug resistance. Oncoscience 1:3–4
Lin S, Pan L, Guo S, Wu J, ** L, Wang JC, Wang S (2013) Prognostic role of microRNA-181a/b in hematological malignancies: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8:e59532. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059532
Liu L, Wang S, Chen R, Wu Y, Zhang B, Huang S, Zhang J, **ao F, Wang M, Liang Y (2012) Myc induced miR-144/451 contributes to the acquired imatinib resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia cell K562. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425:368–373. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.098
Lounnas N, Frelin C, Gonthier N, Colosetti P, Sirvent A, Cassuto JP, Berthier F, Sirvent N, Rousselot P, Dreano M, Peyron JF, Imbert V (2009) NF-kappaB inhibition triggers death of imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells including T315I Bcr-Abl mutants. Int J Cancer 125:308–317. doi:10.1002/ijc.24294
Lu M, Zhang Q, Deng M, Miao J, Guo Y, Gao W, Cui Q (2008) An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS One 3:e3420. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003420
Machova Polakova K, Lopotova T, Klamova H, Burda P, Trneny M, Stopka T, Moravcova J (2011) Expression patterns of microRNAs associated with CML phases and their disease related targets. Mol Cancer 10:41. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-41
Martinez NJ, Walhout AJ (2009) The interplay between transcription factors and microRNAs in genome-scale regulatory networks. Bioessays 31:435–445. doi:10.1002/bies.200800212
Matsumura I, Tanaka H, Kanakura Y (2003) E2F1 and c-Myc in cell growth and death. Cell Cycle 2:333–338
Mohamad Ashari ZS, Sulong S, Hassan R, Husin A, Sim GA, Abdul Wahid SF (2014) Low level of TERC gene amplification between chronic myeloid leukaemia patients resistant and respond to imatinib mesylate treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:1863–1869
Mosakhani N, Mustjoki S, Knuutila S (2013) Down-regulation of miR-181c in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Mol Cytogenet 6:27. doi:10.1186/1755-8166-6-27
Porro A, Iraci N, Soverini S, Diolaiti D, Gherardi S, Terragna C, Durante S, Valli E, Kalebic T, Bernardoni R, Perrod C, Haber M, Norris MD, Baccarani M, Martinelli G, Perini G (2011) c-MYC oncoprotein dictates transcriptional profiles of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Mol Cancer Res 9:1054–1066. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0510
Ruepp A, Kowarsch A, Theis F (2012) PhenomiR: microRNAs in human diseases and biological processes. Methods Mol Biol 822:249–260. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-427-8_17
San Jose-Eneriz E, Agirre X, Jimenez-Velasco A, Cordeu L, Martin V, Arqueros V, Garate L, Fresquet V, Cervantes F, Martinez-Climent JA, Heiniger A, Torres A, Prosper F, Roman-Gomez J (2009) Epigenetic down-regulation of BIM expression is associated with reduced optimal responses to imatinib treatment in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 45:1877–1889. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.04.005Schoch
Schoch C, Haferlach T, Kern W, Schnittger S, Berger U, Hehlmann R, Hiddemann W, Hochhaus A (2003) Occurrence of additional chromosome aberrations in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia 17:461–463. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402813
Sun QC, Liu MB, Shen HJ, Jiang Z, Xu L, Gao LP, Ni JL, Wu SL (2013) Inhibition by imatinib of expression of O-glycan-related glycosyltransferases and tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens in the K562 human leukemia cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:2447–2451
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU, Ganser A, Eder M, Scherr M (2007) Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 109:4399–4405. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-09-045104
Virgili A, Koptyra M, Dasgupta Y, Glodkowska-Mrowka E, Stoklosa T, Nacheva EP, Skorski T (2011) Imatinib sensitivity in BCR-ABL1-positive chronic myeloid leukemia cells is regulated by the remaining normal ABL1 allele. Cancer Res 71:5381–5386. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0068
Vita M, Henriksson M (2006) The Myc oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:318–330. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.015
Wang J, Lu M, Qiu C, Cui Q (2010) TransmiR: a transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D119–D122. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp803
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Cowan-Jacob SW, Hochhaus A, Griffin JD (2007) Second generation inhibitors of BCR-ABL for the treatment of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 7:345–356. doi:10.1038/nrc2126
**ao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X, Li T (2009) miRecords: an integrated resource for microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D105–D110. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn851
Yu W, Clyne M, Khoury MJ, Gwinn M (2010) Phenopedia and Genopedia: disease-centered and gene-centered views of the evolving knowledge of human genetic associations. Bioinformatics 26:145–146. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp618
Zhao P, Ding D, Zhang F, Zhao X, Xue Y, Li W, Fu Z, Li H, Tang J (2015) Investigating the molecular genetic basis of heterosis for internode expansion in maize by microRNA transcriptomic deep sequencing. Funct Integr Genomics 15:261–270. doi:10.1007/s10142-014-0411-2
Zheng T, Wang J, Chen X, Liu L (2010) Role of microRNA in anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer 126:2–10. doi:10.1002/ijc.24782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of Functional & Integrative Genomics entitled “miRNA in model and complex organisms” (Issue Editors: Hikmet Budak and Baohong Zhang).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltani, I., Gharbi, H., Hassine, I.B. et al. Regulatory network analysis of microRNAs and genes in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Funct Integr Genomics 17, 263–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0520-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0520-1