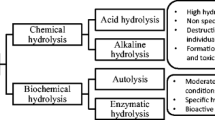
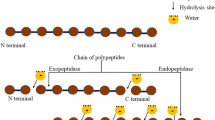
Abstract
Marine products have gained popularity due to their valuable components, especially protein, despite generating significant waste. Protein hydrolysates are widely recognized as the most effective method for transforming these low-value raw materials into high-value products. Fish protein hydrolysate (FPH), sourced from various aquatic wastes such as bones, scales, skin, and others, is rich in protein for value-added products. However, the hydrophobic peptides have limitations like an unpleasant taste and high solubility. Microencapsulation techniques provide a scientific approach to address these limitations and safeguard bioactive peptides. This review examines current research on FPH production methods and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Enzymatic hydrolysis using commercial enzymes is identified as the optimal method, and the antioxidant and antibacterial properties of FPH are substantiated. Microencapsulation using nanoliposomes effectively extends the inhibitory activity and enhances antioxidant and antibacterial capacities. Nevertheless, more research is needed to mitigate the bitter taste associated with FPH and enhance sensory attributes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Aspevik T, Oterhals Å, Rønning SB, Altintzoglou T, Wubshet SG, Gildberg A, Afseth NK, Whitaker RD, Lindberg D. Valorization of proteins from co- and by-products from the fish and meat industry. Topics in Current Chemistry. 385: 1-27 (2017)
Azizi M, Sharifan A, Hoseini E, Ghavami A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of Whitefish Viscera of Caspian sea (Caspiankutum) and evaluation of antioxidant properties of hydrolyzed protein. Iranian Journal of Biosystems Engineering. 52: 379-390 (2021)
Bahram S, Khezri M, Javadian S. Evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of hydrolyzed protein of Saurida tumbil. Experimental animal Biology. 9: 23-35 (2020)
Bhaskar N, Benila T, Radha C, Lalitha RG. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of visceral waste proteins of Catla (Catla catla) for preparing protein hydrolysate using a commercial protease. Bioresource Technology. 99: 259-267 (2008)
Bi J, Tian C, Jiang J, Zhang GL, Hao H, Hou HM. Antibacterial activity and potential application in food packaging of peptides derived from turbot viscera hydrolysate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 68: 9968-9977 (2020)
Blanco M, Vazquez JA, Perez-Martin RI, Sotelo CG. Hydrolysates of fish skin collagen: an opportunity for valorizing fish industry byproducts. Marine Drugs. 15: 131 (2017)
Borah AJ, Agarwal M, Poudyal M, Goyal A, Moholkar VS. Mechanistic investigation in ultrasound-induced enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of invasive biomass species. Bioresource Technology. 213: 342-349 (2016)
Burey P, Bhandari BR, Howes T, Gidley MJ. Hydrocolloid gel particles: formation, characterization, and application. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 48: 361-377 (2008)
Carneiro HC, Tonon RV, Grosso CR, Hubinger MD. Encapsulation efficiency and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil microencapsulated by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. Journal of Food Engineering. 115: 443-451 (2013)
Cheung RCF, Ng TB, Wong JH. Marine peptides: bioactivities and applications. Marine Drugs. 13: 4006-4043 (2015)
Chotphruethipong L, Hutamekalin P, Sukketsiri W, Benjakul S. Effects of sonication and ultrasound on properties and bioactivities of liposomes loaded with hydrolyzed collagen from defatted sea bass skin conjugated with epigallocatechin gallate. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 45: e13809 (2021)
Da Rocha M, Aleman A, Baccan GC, Lopez-Caballero ME, Gomez-Guillen C, Montero P, Prentice C. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects of underutilized fish protein hydrolysate. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology. 27: 592-608 (2018)
Da Rosa Zavareze E, Telles AC, Mello El Halal SL, da Rocha M, Colussi R, Marques de Assis L, Prentice-Hernandez C. Production and characterization of encapsulated antioxidative protein hydrolysates from Whitemouth croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) muscle and byproduct. LWT - Food Science and Technology. 59: 841-848 (2014)
Das A, Nayak Y, Dash S. Fish protein hydrolysate production, treatment methods and current potential uses: a review. International Journal of Fish Aquatic Studies. 9: 195-200 (2021)
Divyasree R, Divya K, Aarti S, Bhavani K, Vamsidhar M, Bhanja S. B, Sudhakar M, Panigrahi BB. A comprehensive review on Liposomes: a novel drug delivery system. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 13: 628-644 (2022)
Dorvaj Z, Javadian SR, Oveissipour M, Nemati M. Use of protein hydrolysates from caspian sea sprat (Clupeonella Cultiventris) as a nitrogen source for bacteria growth media (Vibrio anguillarum, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis). Journal of Aquatic Animals & Fisheries. 4: 11-18 (2013)
Ediriweera TK, Aruppala AL, Abeyrathne ED. Analysis of bioactive properties of fish protein hydrolysates from Scomber japonicus fin wastes. Journal of Technological Value Addition. 1: 31-35 (2019)
Ennaas N, Hammami R, Beaulieu L, Fliss I. Purification and characterisation of four antibacterial peptides from protamex hydrolysate of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus)by-products. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 462: 195-200 (2015)
Eskandari V, Sadeghi M, Hadi A. Physical and chemical properties of nano-liposome, application in nano medicine. Journal of Computational Applied Mechanics. 52: 751-767 (2021)
Food and Agriculture Organization. The State of Food and Agriculture 2018. Migration, Agriculture, and Rural Development. Rome. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO (2018)
Fathi M, Mozafari MR, Mohebbi M. Nanoencapsulation of food ingredients using lipid-based delivery systems. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 23: 13-27 (2012)
Golpaigani MH, Ariaii P, Ahmadi M, Panigrahi BB. Preservation effect of protein hydrolysate of rainbow trout roe with a composite coating on the quality of fresh meat during storage at 4±1 °C. Food Measurement. 17: 2416-2428 (2023)
Halim NRA, Yusof HM, Sarbon NM. Functional and bioactive properties of fish protein hydrolysates and peptides: a comprehensive review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 51: 24-33 (2016)
Hamzeh A, Rezaei M, Khodabandeh S, Noruzinia M, Mac Regenstein J. Antiproliferative and antioxidative activities of cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) protein hydrolysates as affected by the degree of hydrolysis. Food Measurement. 12: 721-727 (2018)
Hamzeh A, Rezaei M, Khodabandeh S, Motamedzadegan A, Noruzinia M, Mac Regenstein J. Optimization of antioxidant peptides production from the mantle of cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) using RSM and fractionation. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology. 28: 392-401 (2019)
Hasani K, Ariaii P, Ahmadi M. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-cancer properties of protein hydrolysates from Indian mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) waste prepared using commercial enzyme. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics. 28: 86 (2022)
Hasani S, Shahidi M, Ojagh SM. The production and evaluation of nanoliposomes containing bioactive peptides derived from fish wastes using the alkalase enzyme. Research and Innovation in Food Science and Technology. 8: 31-44 (2019)
Hosseini SF, Ramezanzade L, McClements DJ. Recent advances in nanoencapsulation of hydrophobic marine bioactives: bioavailability, safety, and sensory attributes of nano-fortified functional foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 109: 322-339 (2021)
Hosseini SF, Ramezanzade L, Nikkhah M. Nano-liposomal entrapment of bioactive peptidic fraction from fish gelatin hydrolysate. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 105: 1455-1463 (2017)
Hosseini SF, Soleimani MR, Nikkhah M. Chitosan/sodium tripolyphosphate NPs as efficient vehicles for antioxidant peptidic fraction from common kilka. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 111: 730-737 (2018)
Hou Y, Wu Z, Dai Z, Wang G, Wu G. Protein hydrolysates in animal nutrition: Industrial production, bioactive peptides, and functional significance. Journal of Animal and Science Biotechnology. 7: 24 (2017)
Islam MS, Wang H, Admassu H, Sulieman AA, Wei FA. Health benefits of bioactive peptides produced from muscle proteins: antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic activities. Process Biochemistry. 116: 116-125 (2022)
Jamshidi A, Shabanpour B, Pourashouri P, Raeisi M. Optimization of encapsulation of fish protein hydrolysate and fish oil in W 1 / O / W 2 double emulsion: evaluation of sensory quality of fortified yogurt. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation. 43: e14063 (2019)
Jamshidi A, Antequera T, Solomando JC, et al. Microencapsulation of oil and protein hydrolysate from fish within a high-pressure homogenized double emulsion. Journal of Food and Science Technology. 57: 60-69 (2020)
Jiang H, Tong T, Sun J, Xu Y, Zhao Z, Liao D. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) muscle protein hydrolysate. Food Chemistry. 154: 158-163 (2014)
Kristinsson HG, Rasco BA. Fish protein hydrolysates: production, biochemical and functional properties. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 40: 43-81 (2000)
Krobthong S, Yingchutrakul Y, Visessanguan W, Mahatnirunkul T, Samutrtai P, Chaichana C, Papan P, Choowongkomon K. Study of the lipolysis effect of nanoliposome-encapsulated ganoderma lucidum protein hydrolysates on adipocyte cells using proteomics approach. Foods. 10: 2157 (2021)
Liao X, Zhu Z, Wu S, Chen M, Huang R, Wang J, Wu Q, Ding Y. Preparation of antioxidant protein hydrolysates from Pleurotus geesteranus and their protective effects on H2O2 oxidative damaged PC12 cells. Molecules. 25: 5408 (2022)
Li T, Wang X, Wang Y, Fan T, Xu Y, Fan Z. Characterisation of antimicrobial peptides isolated from the processing by-products of African catfish Clarias gariepinus. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics. 23: 227-233 (2017)
Li Z, Paulson AT, Gill TA. Encapsulation of bioactive salmon protein hydrolysates with chitosan-coated liposomes. Journal of Functional Foods. 19: 733-743 (2015)
Li-Chan ECY, Lacroix IME. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV and α-glucosidase activities by pepsin-treated whey proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 61: 7500-7506 (2013)
Liu BY, Zhu KX, Guo XN, Peng W, Zhou HM. Changes in the enzyme-induced release of bitter peptides from wheat gluten hydrolysates. RSC Advances. 6: 102249-102257 (2016)
Liu B, Li N, Chen F, Zhang J, Sun X, Xu L, Fang F. Review on the release mechanism and debittering technology of bitter peptides from protein hydrolysates. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 21: 5153-5170 (2022)
McClements DJ, Decker EA, Weiss J. Emulsion-based delivery systems for lipophilic bioactive components. Journal of Food Science. 72:109-124 (2007)
McClements DJ, Öztürk B. Utilization of nanotechnology to improve the handling, storage and biocompatibility of bioactive lipids in food applications. Foods. 10: 1-17 (2021)
Mirzapour Z, Ariaii P, Safari R, et al. Evaluation the effect hydrolyzed canola meal protein with composite coating on physicochemical and sensory properties of chicken nugget. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics. 28: 97 (2022)
Mohan A, Rajendran SR, He QS, Bazinet L, Udenigwe CC. Encapsulation of food protein hydrolysates and peptides: a review. RSC Advances. 5: 79270-79278 (2015)
Mosquera M, Giménez B, da Silva IM, Boelter JF, Montero P, Gómez-Guillén MC, Brandelli A. Nanoencapsulation of an active peptidic fraction from sea bream scales collagen. Food Chemistry. 156: 144-150 (2014)
Mozafari MR, Khosravi-Darani K, Borazan GG, Cui J, Pardakhty A, Yurdugul S. Encapsulation of food ingredients using nanoliposome technology. International Journal of Food Properties. 11: 833-844 (2008)
Najafian L, Babji AS. A review of fish-derived antioxidant and antimicrobial peptides: their production, assessment, and applications. Peptides. 33: 178-185 (2012)
Nemati M, Javadian SR, Ovissipour M, Keshavarz M. A study on the properties of alosa (Alosa caspia) by-products protein hydrolysates using commercial enzymes. World Applied Sciences Journal. 18(7): 950-956 (2012)
Nemati M, Javadian SR, Keshavarz M. Production of protein hydrolysates from Caspian shad (Alosa caspia) by-products using Alcalase enzyme. Journal of Marine Biology. 11: 87-95 (2019)
Nirmal NP, Santivarangkna C, Rajput MS, Benjakul S, Maqsood S. Valorization of fish byproducts: sources to end-product applications of bioactive protein hydrolysate. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 21: 1803-1842 (2022)
Otchere E, McKay BM, English MM, Aryee ANA. Current trends in nano-delivery systems for functional foods: a systematic review. PeerJ. 11: e14980 (2023)
Ovissipour M, Rasco B, Shiroodi SG, Modanlow M, Gholami S, Nemati M. Antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysates from whole anchovy sprat (Clupeonella engrauliformis) prepared using endogenous enzymes and commercial proteases. Journal of Food Science and Agriculture. 93: 1718-1726 (2013)
Ovissipour M, Safari R, Motamedzadegan A, Shabanpour B. Chemical and biochemical hydrolysis of Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) visceral protein. Food and Bioprocess Technology. 5: 460-465 (2012)
Ovissipour M, Taghiof M, Motamedzadegan A, Rasco B, Esmaeili Mulla A. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of visceral waste proteins of beluga sturgeons Huso huso using Alcalase. International Aquatic Research. 1: 31-38 (2009)
Pavlović N, Mijalković J, Đorđević V, Pecarski D, Bugarski B, Knežević-Jugović Z. Ultrasonication for production of nanoliposomes with encapsulated soy protein concentrate hydrolysate: Process optimization, vesicle characteristics and in vitro digestion. Food Chemistry X. 15:100370 (2022)
Paulo F, Santos L. Inclusion of hydroxytyrosol in ethyl cellulose microparticles: In vitro release studies under digestion conditions. Food Hydrocolloids. 84: 104-116 (2018)
Pezeshk S, Ojagh SM, Rezaei M, Shabanpour B. Fractionation of protein hydrolysates of fish waste using membrane ultrafiltration: investigation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Probiotics & Antimicrobial Protiens. 11: 1015-1022 (2019)
Perez Espitia PJ, de Fátima Ferreira Soares N, dos Reis Coimbra JS, de Andrade NJ, Souza Cruz R, Medeiros A, Antonio E. Bioactive peptides: synthesis, properties, and applications in the packaging and preservation of food. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 11: 187-204 (2021)
Poyato C, Navarro-Blasco I, Calvo MI, Cavero RY, Astiasarán I, Ansorena D. Oxidative stability of O/W and W/O/W emulsions: effect of lipid composition and antioxidant polarity. Food Research International. 51: 132-140 (2013)
Qin D, Bo W, Zheng X, Hao Y, Li B, Zheng J, Liang G. DFBP: a comprehensive database of food-derived bioactive peptides for peptidomics research. Bioinformatics. 38: 3275-3280 (2022)
Rabiei S, Rezaei M, Asgharzade S, Nikoo M, Rafieian-Kopaei M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic properties of protein hydrolysates obtained from enzymatic hydrolysis of Klunzinger’s mullet (Liza klunzingeri) muscle. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 55: e18304, 1-10 (2019)
Ramezanzade L, Hosseini SF, Akbari-Adergani B, Yaghmur A. Cross-linked chitosan-coated liposomes for encapsulation of fish-derived peptide. LWT - Food Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112057 (2021)
Ramezanzade L, Hosseini SF, Nikkhah M. Biopolymer-coated nanoliposomes as carriers of rainbow trout skin-derived antioxidant peptides. Food Chemistry. 234: 220-229 (2017)
Reyhani Poul S, Yeganeh S. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of chitosan-coated nanoliposome loaded with bioactive peptides produced from shrimp wastes hydrolysis. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences. 21: 987-1003 (2022)
Roshan SA, Ovissipour M, Keshavarz M, Nemati M. Optimization of the production of protein hydrolysates from common Kilka (Clupeonella cultiventris) using protease enzyme (Promod). Journal of Marine Biology. 7: 83-90 (2015)
Sepúlveda CT, Alemán A, Zapata JE, Montero MP, Gómez-Guillén MC. Characterization and storage stability of spray dried soy-rapeseed lecithin/trehalose liposomes loaded with a tilapia viscera hydrolysate. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102708 (2021)
Sapei L, Naqvi MA, Rousseau D. Stability and release properties of double emulsions for food applications. Food Hydrocolloids. 27: 316-323 (2012)
Shahidi F, Han XQ, Synowiecki J. Production and characteristic of protein hydrolysates from capelin (Mallotus villosus). Food Chemistry. 53: 275-233 (1995)
Shahidi F, Zhong Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. Journal of Functional Foods. 18: 757-781 (2015)
Shahosseini SR, Javadian SR, Safari R. Effects of molecular weights-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis on antioxidant and anticancer activities of liza abu muscle protein hydrolysates. International Journal for Peptide Research & Therapeutics. 28: 72 (2022)
Shahosseini SR, Javadian SR, Safari R. Evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Liza abu viscera protein hydrolysate. Journal of Innovation in Food Science and Technology. 15: 143-155 (2023)
Sharma K, Nilsuwan K, Ma L, Benjakul S. Effect of liposomal encapsulation and ultrasonication on debittering of protein hydrolysate and Plastein from Salmon Frame Food. 12: 761 (2023)
Siddik MA, Howieson J, Fotedar R, Partridge GJ. Enzymatic fish protein hydrolysates in finfish aquaculture: a review. Reviews in Aquaculture. 13: 406-430 (2021)
Slizyte R, Mozuraityte R, Remman T, Rustad T. Two-stage processing of salmon backbones to obtain high-quality oil and proteins. International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 53: 2387-2395 (2018)
Srikanya A, Dhanapal K, Sravani K, Madhavi K, Yeshdas B, Kumar PG. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of protein hydrolysate prepared from tilapia fish waste by enzymatic treatment. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences. 7: 2891-2899 (2018)
Tejpal CS, Vijayagopal P, Elavarasan K, Linga Prabu D, Lekshmi RG, Asha KK, et al. Antioxidant, functional properties and amino acid composition of pepsin-derived protein hydrolysates from whole tilapia waste as influenced by preprocessing ice storage. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 54: 4257-4267 (2017)
Tkaczewska J, Borawska-Dziadkiewicz J, Kulawik P, Duda I, Morawska M, Mickowska B. The effects of hydrolysis conditions on the antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysate from Cyprinus carpio skin gelatin. LWT - Food Science and Technology. 117: 108616 (2020)
Vazquez JA, Blanco M, Massa AE, Amado IR, Perez-Martin RI. Production of fish protein hydrolysates from Scyliorhinus canicula discards with antihypertensive and antioxidant activities by enzymatic hydrolysis and mathematical optimization using response surface methodology. Marine Drugs. 15: 306 (2017)
Villamil O, Váquiro H, Solanilla J.F. Fish viscera protein hydrolysates: Production, potential applications and functional and bioactive properties. Food Chemistry. 224: 160-171 (2017)
Wald M, Schwarz K, Rehbein H, Bußmann B, Beermann C. Detection of antibacterial activity of an enzymatic hydrolysate generated by processing rainbow trout by-products with trout pepsin. Food Chemistry. 205: 221-228 (2016)
Wu D, Zhou L, Gao M, Wang M, Wang B, He J, et al. Effects of stickwater hydrolysates on growth performance for yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquaculture. 488: 161-173 (2018)
Yaghoubzadeh Z, Peyravii Ghadikolaii F, Kaboosi H, et al. Antioxidant activity and anticancer effect of bioactive peptides from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skin hydrolysate. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics. 26: 625-632 (2020)
Ziyaei K, Hosseini SV. The review of hydrolyzed protein from fishery by-product: Production methods, application, Biological Properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology (Iran). 18:383-395 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nemati, M., Shahosseini, S.R. & Ariaii, P. Review of fish protein hydrolysates: production methods, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity and nanoencapsulation. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 1789–1803 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-024-01554-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-024-01554-8