Abstract
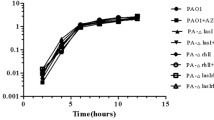
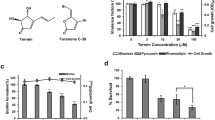
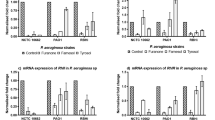
Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) plays a role in the regulation of virulence genes and it is intertwined in the las/rhl quorum sensing (QS) circuits of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PQS is synthesized from anthranilate by pqsA-D and pqsH whose expression is influenced by the las/rhl systems. Since anthranilate can be degraded by functions of antABC and catBCA, PQS synthesis might be regulated by the balance between the expression of the pqsA-D/phnAB, pqsH, antABC, and catBCA gene loci. antA and catA are repressed by LasR during log phase and activated by RhlR in late stationary phase, whereas pqsA-E/phnAB is activated by LasR in log phase and repressed by RhlR. QscR represses both but each repression occurs in a different growth phase. This growth phase-differential regulation appears to be accomplished by the antagonistic interplay of LasR, RhlR, and QscR, mediated by two intermediate regulators, AntR and PqsR, and their cofactors, anthranilate and PQS, where the expressions of antR and pqsR and the production of anthranilate and PQS are growth phase-differentially regulated by QS systems. Especially, the anthranilate level increases in an RhlR-dependent manner at late stationary phase. From these results, we suggest that RhlR and LasR regulate the anthranilate metabolism in a mutually antagonistic and growth phase-differential manner by affecting both the expressions and activities of AntR and PqsR, and that QscR also phase-differentially represses both LasR and RhlR functions in this regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aendekerk, S., Diggle, S.P., Song, Z., Hoiby, N., Cornelis, P., Williams, P., and Camara, M. (2005). The MexGHI-OpmD multidrug efflux pump controls growth, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 4-quinolone-dependent cell-to-cell communication. Microbiology 151, 1113–1125.
Brint, J.M., and Ohman, D.E. (1995). Synthesis of multiple exoproducts in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is under the control of RhlRRhlI, another set of regulators in strain PAO1 with homology to the autoinducer-responsive LuxR-LuxI family. J. Bacteriol. 177, 7155–7163.
Calfee, M.W., Coleman, J.P., and Pesci, E.C. (2001). Interference with Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis inhibits virulence factor expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11633–11637.
Chugani, S.A., Whiteley, M., Lee, K.M., D’Argenio, D., Manoil, C., and Greenberg, E.P. (2001). QscR, a modulator of quorumsensing signal synthesis and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 2752–2757.
Deziel, E., Lepine, F., Milot, S., He, J., Mindrinos, M.N., Tompkins, R.G., and Rahme, L.G. (2004). Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1339–1344.
Diggle, S.P., Winzer, K., Chhabra, S.R., Worrall, K.E., Camara, M., and Williams, P. (2003). The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 50, 29–43.
Essar, D.W., Eberly, L., Hadero, A., and Crawford, I.P. (1990). Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J. Bacteriol. 172, 884–900.
Farinha, M.A., and Kropinski, A.M. (1990). Construction of broadhost-range plasmid vectors for easy visible selection and analysis of promoters. J. Bacteriol. 172, 3496–3499.
Farrow, J.M., 3rd, and Pesci, E.C. (2007). Two distinct pathways supply anthranilate as a precursor of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal. J. Bacteriol. 189, 3425–3433.
Fuqua, C., Parsek, M.R., and Greenberg, E.P. (2001). Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 35, 439–468.
Gallagher, L.A., McKnight, S.L., Kuznetsova, M.S., Pesci, E.C., and Manoil, C. (2002). Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6472–6380.
Jacobs, M.A., Alwood, A., Thaipisuttikul, I., Spencer, D., Haugen, E., Ernst, S., Will, O., Kaul, R., Raymond, C., Levy, R., et al. (2003). Comprehensive transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 14339–14344.
Kim, C., Kim, J., Park, H.Y., Park, H.J., Kim, C.K., Yoon, J., and Lee, J.H. (2009). Development of inhibitors against TraR quorumsensing system in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by molecular modeling of the ligand-receptor interaction. Mol. Cells 28, 447–453.
Latifi, A., Foglino, M., Tanaka, K., Williams, P., and Lazdunski, A. (1996). A hierarchical quorum-sensing cascade in Pseudomonas aeruginosa links the transcriptional activators LasR and RhIR (VsmR) to expression of the stationary-phase sigma factor RpoS. Mol. Microbiol. 21, 1137–1146.
Ledgham, F., Ventre, I., Soscia, C., Foglino, M., Sturgis, J.N., and Lazdunski, A. (2003). Interactions of the quorum sensing regulator QscR: interaction with itself and the other regulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR and RhlR. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 199–210.
Lee, J.H., Lequette, Y., and Greenberg, E.P. (2006). Activity of purified QscR, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum-sensing transcription factor. Mol. Microbiol. 59, 602–609.
Lequette, Y., Lee, J.H., Ledgham, F., Lazdunski, A., and Greenberg, E.P. (2006). A distinct QscR regulon in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing circuit. J. Bacteriol. 188, 3365–3370.
Mavrodi, D.V., Bonsall, R.F., Delaney, S.M., Soule, M.J., Phillips, G., and Thomashow, L.S. (2001). Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 183, 6454–6465.
Mavrodi, D.V., Blankenfeldt, W., and Thomashow, L.S. (2006). Phenazine compounds in fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. biosynthesis and regulation. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 44, 417–445.
McGrath, S., Wade, D.S., and Pesci, E.C. (2004). Dueling quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa control the production of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 230, 27–34.
McKnight, S.L., Iglewski, B.H., and Pesci, E.C. (2000). The Pseudomonas quinolone signal regulates rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 182, 2702–2708.
Newman, J.R., and Fuqua, C. (1999). Broad-host-range expression vectors that carry the L-arabinose-inducible Escherichia coli araBAD promoter and the araC regulator. Gene 227, 197–203.
Oglesby, A.G., Farrow, J.M., 3rd, Lee, J.H., Tomaras, A.P., Greenberg, E.P., Pesci, E.C., and Vasil, M.L. (2008). The influence of iron on Pseudomonas aeruginosa physiology: a regulatory link between iron and quorum sensing. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 15558–15567.
Pearson, J.P., Pesci, E.C., and Iglewski, B.H. (1997). Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of elastase and rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol. 179, 5756–5767.
Pesci, E.C., Pearson, J.P., Seed, P.C., and Iglewski, B.H. (1997). Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 179, 3127–3132.
Pesci, E.C., Milbank, J.B., Pearson, J.P., McKnight, S., Kende, A.S., Greenberg, E.P., and Iglewski, B.H. (1999). Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 11229–11234.
Sambrook, J.E., Fritsch, F., and Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. (Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press).
Schuster, M., and Greenberg, E.P. (2006). A network of networks: quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 296, 73–81.
Schuster, M., and Greenberg, E.P. (2007). Early activation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals the architecture of a complex regulon. BMC Genomics 8, 287.
Schuster, M., Lostroh, C.P., Ogi, T., and Greenberg, E.P. (2003). Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: a transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 185, 2066–2079.
Stover, C.K., Pham, X.Q., Erwin, A.L., Mizoguchi, S.D., Warrener, P., Hickey, M.J., Brinkman, F.S., Hufnagle, W.O., Kowalik, D.J., Lagrou, M., et al. (2000). Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406, 959–964.
Van Delden, C., and Iglewski, B.H. (1998). Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 4, 551–560.
Venturi, V. (2006). Regulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30, 274–291.
Wade, D.S., Calfee, M.W., Rocha, E.R., Ling, E.A., Engstrom, E., Coleman, J.P., and Pesci, E.C. (2005). Regulation of Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 187, 4372–4380.
**ao, G., Deziel, E., He, J., Lepine, F., Lesic, B., Castonguay, M.H., Milot, S., Tampakaki, A.P., Stachel, S.E., and Rahme, L.G. (2006). MvfR, a key Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity LTTR-class regulatory protein, has dual ligands. Mol. Microbiol. 62, 1689–1699.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-3322-2
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y., Park, HY., Park, S.J. et al. Growth phase-differential quorum sensing regulation of anthranilate metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Mol Cells 32, 57–65 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-2322-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-011-2322-6