Abstract
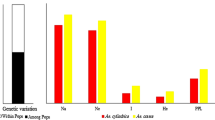
Aegilops geniculata Roth is an annual grass relative to cultivated wheats and is widely distributed in North Africa. In order to understand the diversity of this species, 14 populations collected in different bioclimatic areas in northern Algeria were analyzed using morphological and biochemical characters. Principal component analyses (PCA) based on the inflorescence characters and ecological parameters allowed the separation of populations in two mainly bioclimatic clusters characterized by different morphological patterns. Populations originated from humid and sub-humid coastal areas were characterized by vigorous spikes. Samples collected from intermediate and high mountains with humid and semi-arid conditions had long and lanceolate spikes. Individuals with small and narrow spikes were characteristics of steppic highlands in semi-arid conditions and high mountains with humid bioclimate. Individuals were distinguished successively by spike width, spike length, rachis length and awns number. Electrophoretic analyses of high molecular weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS) based on the phenotypic variability and genetic distances revealed a significant variation within and between populations associated with bioclimatic conditions, in particular winter temperature. Genetic diversity was higher in populations growing under warm bioclimates than in those from cold bioclimates. These results suggest that a part of the variation for HMW glutenin variability is adaptive.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aïnouche ML, Misset M-T, Huon A (1995) Genetic diversity in Mediterranean diploid and tetraploid Bromus L. (Section Bromus Sm) populations. Genome 38:879–888
Aïnouche ML, Bayer RJ, Gouret JP, Defontaine A, Misset MT (1999) The allotetraploid invasive weed Bromus hordeaceus L. (Poaceae): genetic diversity, origin and molecular evolution. Folia Geobot 34:405–419
Amirouche R, Misset M-T (2003) Hordein polymorphism in diploid and tetraploid Mediterranean populations of the Hordeum murinum L. complex. Pl Syst Evol 242:83–99
Amirouche N, Misset M-T (2007) Morphological variation and distribution of cytotypes in the diploid-tetraploid complex of the genus Dactylis L. (Poaceae) from Algeria. Pl Syst Evol 264:157–174
Baalbaki R, Hajj-Hassan N, Zurayk R (2006) Aegilops species from semiarid areas of Lebanon: variation in quantitative attributes under water stress. Crop Sci 46:799–806
Badaeva ED, Amosova AV, Samatadze TE, Zoshchuk SA, Chikida N, Zelenin AV, Raupp WJ, Friebe B, Gill BS (2004) Genome differentiation in Aegilops. 4. Evolution of U-genome cluster. Pl Syst Evol 246:45–76
Battandier JA, Trabut L (1902) Flore analytique et synoptique de l’Algérie et de la Tunisie. edn. Vve Girault, Alger. pp 410
De Bustos A, Jouve N (2006) Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the genes coding for high molecular wei glutenin subunits in three diploid species of Aegilops. Int J Pl Sci 167:359–366
Eig A (1929) Monographisch-kritische Übersicht der Gattung Aegilops. Feddes Repert 55:1–228 in German
Farooq S, Shah TM, Asghar M (1996) Intergeneric hybridization for wheat improvement: V. Production of and metaphase 1 chromosome analysis in F1 hybrids of wheat (Triticum aestivum) with Aegilops ovata L. Cereal Res Commun 24:155–161
Feldman M (1965) Further evidence for natural hybridization between tetraploid species of Aegilops. sect. Pleionathera. Evolution 19:162–174
Fernandez-Calvin B, Orellana J (1990) High molecular weight glutenin subunit variation in the Sitopsis section of Aegilops. Implications for the origin of the B genome of wheat. Heredity 65:455–463
Gill BS, Sharma HC, Raupp WJ, Browder IE, Hatchett JH, Harvey TL, Moseman JG, Waines JG (1985) Evaluation of Aegilops species for resistance to wheat powdery mildew, wheat leaf rust, Hussian fly, and greenbug. Plant Dis 69:314–316
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1997) Effects of life history on genetic diversity in plants species. In: Silvertown J, Franco M, Harper JL (eds) Plant life histories-ecology phylogeny and evolution. Cambridge University Press, London, p 313
Hammer K (1980) Vorarbeiten zur Monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzen-Sortimenten: Aegilops L. Kulturpflanze 28:33–180
Hegde SG, Valkoun J, Waines JG (2000) Genetic diversity in wild wheats and goatgrass. Theor Appl Genet 101:309–316
Hegde SG, Valkoun J, Waines JG (2002) Genetic diversity in wild and weedy Aegilops, Amblyopyrum, and Secale species—A preliminary survey. Crop Sci 42:608–614
Kimber G, Feldman M (1987) Wild wheat. An introduction. Special Report 353, College of Agriculture, University of Missouri, Columbia, p 142, Kimber and Sears 1984
Law CN, Payne PI (1983) Genetical aspects of breeding for improved grain protein content and type in wheat. J Cereal Sci 1:79–93
Lawrence GJ, Shepherd KW (1981) Chromosomal location of genes controlling seed protein in species related to wheat. Theor Appl Genet 59:25–31
Maire R (1955) Flore de l’Afrique du Nord. Eds Le Chevalier, vol III, Paris, pp 65–69
Monte JV, Casanova C, Soler C (1999) Genetic variation in Spanish populations of the genus Aegilops revealed by RAPDs. Agronomie 19:419–427
Nevo E, Goldberg E, Beiles A, Brown AHD, Zohary D (1982) Genetic diversity and environmental associations of wild wheat. Triticum dicoccoides in Israel. Theor Appl Genet 78:260–264
Nieto-Taladriz MT, Branlard G, Dardevet M (1994) Polymorphism of omega-gliadin in durum wheat as revealed by the two-step APAGE/SDS-PAGE technique. Theor Appl Genet 87:1001–1008
Pazy B, Zohary D (1965) The process of introgression between Aegilops polyploids. Natural hybridization between A. variabilis, A. ovata and A. biuncialis. Evolution 19:385–394
Perrino P, Laghetti G, Cifarelli S, Volpe N, Spagnoletti-Chichester PL, Zeuli UK (1993) Wild wheats in southern Italy. In: Damania AB (ed) Biodiversity and wheat improvement. Wiley, Chichester, pp 361–368
Quezel P, Santa S (1962) Nouvelle flore de l’Algérie et des régions désertiques méridionales. Tome I. Edition du CNRS, Paris, p 558
Rekika D, Zaharieva M, Stankova P, Xu X, Souyris I, Monneveux P (1998) Abiotic stress tolerance in Aegilops species. In: Nachit MM et al. Durum Research Network, Proceeding of the SEWANA, South Europe, West Asia and North Africa, ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria, pp 113–118
Rodriguez-Quijano M, Nieto-Taladriz MT, Carrillo JM (2000) Polymorphism of high molecular weight glutenin subunits in three species of Aegilops. Genet Resour Crop Evol 48:599–607
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Lafiandra D (2006) The high-molecular-weight subunits of glutenin. In: Wrigley C, Békés F, Bushuk W (eds) Gliadin and glutenin. The unique balance of wheat quality. AACC, St Paul, pp 143–169
Sing NK, Shepherd KW, Cornich GB (1991) A simplified SDS-PAGE procedure for separating LMW subunits of glutenin. J Cereal Sci 14:203–208
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practise of numerical classification. Freeman & Co, San Francisco, p 571
Stebbins GL (1971) Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Arnold, London, p 21
Stewart P (1974) Un nouveau climagramme pour l’Algérie et son application au barrage vert. Bull Soc Hist Nat Afrique du Nord 65:239–248
Sun X, Hu S, Qian W, Hao S, Zhang A, Wang D (2006) Characterization of HMW glutenin subunits from Aegilops searsii and identification of a novel variant HBM glutenin subunit. Theor Appl Genet 113(4):631–641
Swofford DL, Selander RB (1989) Biosys-1. A computer program for the analysis of allelic variation in population genetics and biochemical systematics. Release 1.7. Illinois Natural History Survey, Illinois, pp 43
van Slageren MW (1994) Wild Wheats: a monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae). Wageningen Agricultural University Papers 94–7, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Witcombe JR (1983) A guide to the species of Aegilops L. International Board for plant Genetic Resources. Wheat Program IBPGR, Rome, p 74
Wright S (1978) Evolution and the genetics of populations, vol 4. Variability within and among natural populations. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Zaharieva M, David J, This D, Monneveux P (1999) Analyse de la diversité génétique d’Aegilops geniculata Roth en Bulgarie. (In French, with English abstract). Cahiers Agric 8:181–188
Zaharieva M, Gaulin E, Havaux M, Acevedo E, Monneveux P (2001) Drought and heat responses in the wild wheat relative Aegilops geniculata Roth: potential interest for wheat improvement. Crop Sci 41:1321–1329
Zaharieva M, Dimov A, Stankova P, David J, Monneveux P (2003a) Morphological diversity and potential interest for wheat improvement of three Aegilops L. species from Bulgaria. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50:507–517
Zaharieva M, Suenaga K, H.M. William HM, Mujeeb-Kazi A (2003) Microsatellite markers for detection Aegilops geniculata Roth and U genome chromosomes in wheat background. Annual Wheat Newslett 49:75–78
Zhang XY, R-C Wang R, Dong YS (1996) RAPD polymorphisms in Aegilops geniculata Roth. (Ae. ovata auct. non L.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 43:429–433
Zhukovsky PM (1928) Kritiko-systematischeskii obzor vydov roda Aegilops L. (Specierum generis Aegilops L. revisio critica). Trudy Prikl Bot Genet Selekc 18:417–609 in Russian
Zohary D (1965) Colonizer species in the wheat group. In: Baker HG, Stebbins GL (eds) The genetics of colonizing species. Academic Press, New York, pp 403–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandou, H., Rodriguez-Quijano, M., Carrillo, J.M. et al. Morphological and genetic variation in Aegilops geniculata from Algeria. Plant Syst Evol 277, 85–97 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-008-0106-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-008-0106-z