Abstract
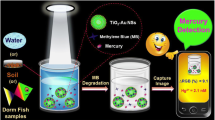
The stability of black phosphorene (BP) and its preparation and modification for develo** and applying devices have become a hot topic in the interdisciplinary field. We propose ultrasound-electrochemistry co-assisted liquid-phase exfoliation as an eco-friendly one-step method to prepare gold–silver bimetallic nanoparticles (Au−AgNPs)-decorated BP nanozyme for smartphone-based portable sensing of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) in different water sources. The structure, morphology, composition, and properties of Au−AgNPs−BP nanozyme are characterized by multiple instrumental analyses. Bimetallic salts are induced to efficiently occupy oxidative sites of BP to form highly stable Au−AgNPs−BP nanozyme and guarantee the integrity of the lamellar BP. The electrochemistry shortens the exfoliation time of the BP nanosheet and contributes to the loading efficiency of bimetallic nanoparticles on the BP nanosheet. Au−AgNPs−BP-modified screen-printed carbon electrode coupled with palm-sized smartphone-controlled wireless electrochemical analyzer as a portable wireless intelligent sensing platform was applied to the determination of 4-NP in a linear range of 0.6−10 μM with a limit of detection of 63 nM. It enables on-site determination of 4-NP content in lake water, river water, and irrigation ditch water. This work will provide a reference for an eco-friendly one-step preparation of bimetallic nanoparticle-decorated graphene-like materials as nanozymes and their smartphone-based portable sensing application outdoors.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ge Y, Camarada MB, Xu L, Qu M, Liang H, Zhao E, Li M, Wen Y (2018) A highly stable black phosphorene nanocomposite for voltammetric determination of clenbuterol. Microchim Acta 185:1
Ge Y, Li M, Zhong Y, Xu L, Lu X, Hu J, Peng Q, Bai L, Wen Y (2023) Halloysite nanotube/black phosphorene nanohybrid modified screen-printed carbon electrode as an ultra-portable electrochemical sensing platform for smartphone-capable determination of maleic hydrazide with machine learning assistance. Food Chem 406:134967
Xue T, Sheng Y, Xu J, Li Y, Lu X, Zhu Y, Duan X, Wen Y (2019) In-situ reduction of Ag+ on black phosphorene and its NH2-MWCNT nanohybrid with high stability and dispersibility as nanozyme sensor for three ATP metabolites. Biosens Bioelectron 145:111716
Qu G, **a T, Zhou W, Zhang X, Zhang H, Hu L, Shi J, Yu XF, Jiang G (2020) Property–activity relationship of black phosphorus at the nano–bio interface: from molecules to organisms. Chem Rev 120(4):2288
Du K, Lv Q, Liang Z, Liu G, Hussain S, Liu J, Qiao G (2023) Trends in the preparation and passivation techniques of black phosphorus nanostructures for optoelectronics applications: a review. ACS Applied Nano Materials 6:3159
Qin L, Zeng G, Lai C, Huang D, Xu P, Zhang C, Cheng M, Liu X, Liu S, Li B, Yi H (2018) “Gold rush” in modern science: fabrication strategies and typical advanced applications of gold nanoparticles in sensing. Coord Chem Rev 359:1
Smith BR, Gambhir SS (2017) Nanomaterials for in vivo imaging. Chem Rev 117:901
Srivastava AK, Dev A, Karmakar S (2017) Nanosensors and nanobiosensors in food and agriculture. Environ Chem Lett 16:161
Sheng Y, Zhu Y, Cerón ML, Yi Y, Liu P, Wang P, Xue T, Camarada MB, Wen Y (2021) A stable nanosilver decorated phosphorene nanozyme with phosphorus-doped porous carbon microsphere for intelligent sensing of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine. J Electroanal Chem 895:115522
Ge Y, Liu P, Chen Q, Qu M, Xu L, Liang H, Zhang X, Huang Z, Wen Y, Wang L (2023) Machine learning-guided the fabrication of nanozyme based on highly-stable violet phosphorene decorated with phosphorus-doped hierarchically porous carbon microsphere for portable intelligent sensing of mycophenolic acid in silage. Biosens Bioelectron 237:115454
Pourmadadi M, Shamsabadipour A, Aslani A, Eshaghi MM, Rahdar A, Pandey S (2023) Development of polyvinylpyrrolidone-based nanomaterials for biosensors applications: a review. Inorg Chem Commun 152:110714
Tiouitchi G, Ali MA, Benyoussef A, Hamedoun M, Lachgar A, Kara A, Ennaoui A, Mahmoud A, Boschini F, Oughaddou H, Moutaouakil AE, Kenz AE, Mounkachi O (2020) Efficient production of few-layer black phosphorus by liquid-phase exfoliation. R Soc Open Sci 10:201210
Roberto SE, Spinelli A (2020) Electrode modified with graphene quantum dots supported in chitosan for electrochemical methods and non-linear deconvolution of spectra for spectrometric methods: approaches for simultaneous determination of triclosan and methylparaben. Microchim Acta 187:12
Lu X, Jayakumar K, Wen Y, Hojjati-Najafabadi A, Duan X, Xu J (2023) Recent advances in metal-organic framework (MOF)-based agricultural sensors for metal ions: a review. Microchim Acta 191:24
Zhu X, Lin L, Wu R, Zhu Y, Sheng Y, Nie P, Liu P, Xu L, Wen Y (2021) Portable wireless intelligent sensing of ultra-trace phytoregulator α-naphthalene acetic acid using self-assembled phosphorene/Ti3C2-MXene nanohybrid with high ambient stability on laser induced porous graphene as nanozyme flexible electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 179:113062
Rao L, Zhu Y, Duan Z, Xue T, Duan X, Wen Y, Kumar AS, Zhang W, Xu J, Hojjati-Najafabadi A (2022) Lotus seedpods biochar decorated molybdenum disulfide for portable, flexible, outdoor and inexpensive sensing of hyperin. Chemosphere 301:134595
Gerent GG, Santana ER, Martins EC, Spinelli A (2021) A non-mercury electrode for the voltammetric determination of butralin in foods. Food Chem 343:128419
Baboukani AR, Khakpour I, Drozd V, Allagui A, Wang C (2019) Single-step exfoliation of black phosphorus and deposition of phosphorene via bipolar electrochemistry for capacitive energy storage application. J Mater Chem A 44:25548
Zeng D, Zhang K, Huang H, Zhang X, Wang Z, Chen S, Liu G, Wen Y, Wang P (2023) A general strategy to prepare transition metal sulfide functionalized hierarchically porous carbons with multiple enzyme-like activities for simultaneous electrochemical sensing of ATP metabolites. Chem Eng J 471:144767
Li L, Ye GJ, Ge Q, Ou X, Wu H, Feng D, Chen XH, Zhang Y (2014) Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 9:372
Wood JD, Wells SA, Jariwala D, Chen KS, Cho E, Sangwan VK, Liu X, Lauhon LJ, Marks TJ, Hersam MC (2014) Effective passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus transistors against ambient degradation. Nano Lett 14:6964
Gusmão R, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2018) Functional protection of exfoliated black phosphorus by noncovalent modification with anthraquinone. ACS Nano 12:5666
Liu H, **e Y, Liu J, Moon K-s, Lu L, Lin Z, Yuan W, Shen C, Zang X, Lin L, Tang Y, Wong CP (2020) Laser-induced and KOH-activated 3D graphene: a flexible activated electrode fabricated via direct laser writing for in-plane micro-supercapacitors. Chem Eng J 393:124672
Shen ZK, Yuan YJ, Wang P, Bai W, Pei L, Wu S, Yu ZT, Zou Z (2020) Few-layer black phosphorus nanosheets: a metal-free cocatalyst for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:17343
Donarelli M, Ottaviano L, Giancaterini L, Fioravanti G, Perrozzi F, Cantalini C (2016) Exfoliated black phosphorus gas sensing properties at room temperature. 2D Materials 3:025002
Goodman NB, Ley L, Bullett DW (1983) Valence-band structures of phosphorus allotropes. Phys Rev B 27:7440
Kang J, Wood JD, Wells SA, Lee JH, Liu X, Chen KS, Hersam MC (2015) Solvent exfoliation of electronic-grade. ACS Nano 9:3596
Li P, Chen W, Liu D, Huang H, Dan K, Hu X, Yu S, Chu PK, Yu XF (2019) Template growth of Au/Ag nanocomposites on phosphorene for sensitive SERS determination of pesticides. Nanotechnology 30:275604
Lu S, Bai L, Wen Y, Li M, Yan D, Zhang R, Chen K (2014) Water-dispersed carboxymethyl cellulose-montmorillonite-single walled carbon nanotube composite with enhanced sensing performance for simultaneous voltammetric determination of two trace phytohormones. J Solid State Electrochem 19:2023
Zhang J, Xu J, Wen Y, Wang Z, Zhang H, Ding W (2015) Voltammetric determination of phytoinhibitor maleic hydrazide using PEDOT:PSS composite electrode. J Electroanal Chem 751:65
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51962007, 31960499), the Training Project of High-level and High-skilled Leading Talents of Jiangxi Province, the Foreign Talent project of “Double Thousand Plan” of Jiangxi Province, and the Key Project for Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (2023ACB2013019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tao Chen: data curation, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing - original draft, writing – review and editing. Yu Ge: software, visualization, writing – original draft. ** Wen: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing – review and editing. Hassan Karimi-Maleh: formal analysis, software, visualization. **aoqiang Wang: data curation, resources. Zhong Huang: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, resources. Mingfang Li: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, visualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1:
(DOCX 3606 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Ge, Y., Lu, X. et al. Ultrasound-electrochemistry assisted liquid-phase co-exfoliation of phosphorene decorated by Au−Ag bimetallic nanoparticles as nanozyme for smartphone-based portable sensing of 4-nitrophenol. Microchim Acta 191, 446 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06518-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06518-7