Abstract
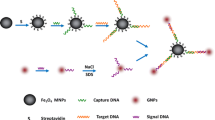
A platform was designed based on Fe3O4 and CsPbBr3@SiO2 for integrated magnetic enrichment-fluorescence detection of Salmonella typhimurium, which significantly simplifies the detection process and enhances the working efficiency. Fe3O4 served as a magnetic enrichment unit for the capture of S. typhimurium. CsPbBr3@SiO2 was employed as a fluorescence-sensing unit for quantitative signal output, where SiO2 was introduced to strengthen the stability of CsPbBr3, improve its biomodificability, and prevent lead leakage. More importantly, the SiO2 shell shows neglectable absorption or scattering towards fluorescence, making the CsPbBr3@SiO2 exhibit a high quantum yield of 74.4%. After magnetic enrichment, the decreasing rate of the fluorescence emission intensity of the CsPbBr3@SiO2 supernatant at 527 nm under excitation light at UV 365 nm showed a strong linear correlation with S. typhimurium concentration of 1 × 102~1 × 108 CFU∙mL−1, and the limit of detection (LOD) reached 12.72 CFU∙mL−1. This platform has demonstrated outstanding stability, reproducibility, and resistance to interference, which provides an alternative for convenient and quantitative detection of S. typhimurium.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Taubes G (2008) The bacteria fight back. Science 321(5887):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.321.5887.356
Havelaar AH, Kirk MD, Torgerson PR, Gibb HJ, Hald T, Lake RJ, Praet N, Bellinger DC, de Silva NR, Gargouri N, Speybroeck N, Cawthorne A, Mathers C, Stein C, Angulo FJ, Devleesschauwer B, on behalf of World Health Organization Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference G (2015) World Health Organization global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease in 2010. PLoS Med 12(12):e1001923. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001923
Sadanandan S, Ramkumar K, Pillai NP, Sreejaya MM (2023) Biorecognition elements appended gold nanoparticle biosensors for the detection of food-borne pathogens - a review. Food Control 148:109510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109510
Still WL, Tapia MD, Tennant SM, Sylla M, Touré A, Badji H, Keita AM, Sow SO, Levine MM, Kotloff KL (2020) Surveillance for invasive Salmonella disease in Bamako, Mali, from 2002 to 2018. Clin Infect Dis 71(Supplement_2):S130–S140. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa482
Fu Y, Wei J, Yao S, Zhang L, Zhang M, Zhuang X, Zhao C, Li J, Pang B (2022) Rapid qualitative and quantitative detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a single-step dual photometric/fluorometric assay. Microchim Acta 189(6):218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05312-7
Nadi ZR, Salehi TZ, Tamai IA, Foroushani AR, Sillanpaa M, Dallal MMS (2020) Evaluation of antibiotic resistance and prevalence of common Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from foodborne outbreaks. Microchem J 155:104660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104660
Silva NFD, Magalhães JMCS, Freire C, Delerue-Matos C (2018) Electrochemical biosensors for Salmonella: state of the art and challenges in food safety assessment. Biosens Bioelectron 99:667–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.019
Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM (2015) Epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory diagnosis, antimicrobial resistance, and antimicrobial management of invasive Salmonella infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 28(4):901–937. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00002-15
LaRock DL, Chaudhary A, Miller SI (2015) Salmonellae interactions with host processes. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(4):191–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3420
Majdinasab M, Hayat A, Marty JL (2018) Aptamer-based assays and aptasensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 107:60–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.07.016
Maciorowski KG, Herrera P, Jones FT, Pillai SD, Ricke SC (2006) Cultural and immunological detection methods for Salmonella spp. in animal feeds - a review. Vet Res Commun 30(2):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-006-3221-8
Kumar R, Surendran PK, Thampuran N (2008) Evaluation of culture, ELISA and PCR assays for the detection of Salmonella in seafood. Lett Appl Microbiol 46(2):221–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02286.x
Mazzotta AS (2000) D- and z-values of Salmonella in ground chicken breast meat. J Food Saf 20(4):217–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4565.2000.tb00300.x
Su Z, Dou W, Liu X, ** J, Li D, Ying Y, **e L (2022) Nano-labeled materials as detection tags for signal amplification in immunochromatographic assay. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 154:116673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116673
Draz MS, Lakshminaraasimulu NK, Krishnakumar S, Battalapalli D, Vasan A, Kanakasabapathy MK, Sreeram A, Kallakuri S, Thirumalaraju P, Li Y, Hua S, Yu XG, Kuritzkes DR, Shafiee H (2018) Motion-based immunological detection of Zika virus using Pt-nanomotors and a cellphone. ACS Nano 12(6):5709–5718. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b01515
Gug IT, Tertis M, Hosu O, Cristea C (2019) Salivary biomarkers detection: analytical and immunological methods overview. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 113:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.02.020
Gontar IP, Baranov EV, Maslakova LA, Trofimenko AS, Emelyanova OI, Paramonova OV (2016) AB0201 a new perspective of immunological detection of neurological injuries in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 75(Suppl 2):966–966. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-eular.2375
Baldofski S, Hoffmann H, Lehmann A, Breitfeld S, Garbe L-A, Schneider RJ (2016) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the anthropogenic marker isolithocholic acid in water. J Environ Manag 182:612–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.023
Konstantinou GN (2017) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In: Lin J, Alcocer M (eds) Food allergens: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, New York, NY, pp 79–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6925-8_7
He Z, Huffman J, Curtin K, Garner KL, Bowdridge EC, Li X, Nurkiewicz TR, Li P (2021) Composable microfluidic plates (cPlate): a simple and scalable fluid manipulation system for multiplexed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Anal Chem 93(3):1489–1497. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03651
Khater M, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2017) Biosensors for plant pathogen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 93:72–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.091
Huang X, Sang S, Yuan Z, Duan Q, Guo X, Zhang H, Zhao C (2021) Magnetoelastic immunosensor via antibody immobilization for the specific detection of lysozymes. ACS Sensors 6(11):3933–3939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c00802
Leonardo S, Rambla-Alegre M, Samdal IA, Miles CO, Kilcoyne J, Diogène J, O'Sullivan CK, Campàs M (2017) Immunorecognition magnetic supports for the development of an electrochemical immunoassay for azaspiracid detection in mussels. Biosens Bioelectron 92:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.015
Zhong J, Rösch EL, Viereck T, Schilling M, Ludwig F (2021) Toward rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 with functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Sensors 6(3):976–984. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02160
Liu Z, Gao Y, ** L, ** H, Xu N, Yu X, Yu S (2019) Core-shell regeneration magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers-based SERS for sibutramine rapid detection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(9):8168–8175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06120
Wang Z, Cai R, Gao Z, Yuan Y, Yue T (2020) Immunomagnetic separation: an effective pretreatment technology for isolation and enrichment in food microorganisms detection. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 19(6):3802–3824. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12656
Du M, Li J, Zhao R, Yang Y, Wang Y, Ma K, Cheng X, Wan Y, Wu X (2018) Effective pre-treatment technique based on immune-magnetic separation for rapid detection of trace levels of Salmonella in milk. Food Control 91:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.03.032
Li C, Yang Q, Wang X, Arabi M, Peng H, Li J, **ong H, Chen L (2020) Facile approach to the synthesis of molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor for the visual detection of folic acid. Food Chem 319:126575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126575
Rong Y, Ali S, Ouyang Q, Wang L, Wang B, Chen Q (2021) A turn-on upconversion fluorescence sensor for acrylamide in potato chips based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer and thiol-ene Michael addition. Food Chem 351:129215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129215
Chen C, Zhang Y, Wang X, Qiao X, Waterhouse GIN, Xu Z (2024) A core-satellite self-assembled SERS aptasensor containing a “biological-silent region” Raman tag for the accurate and ultrasensitive detection of histamine. Food Sci Human Wellness 13(2):1029–1039. https://doi.org/10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250089
Wang H, Liu Y, Zhang L, Li X, Zhao G, Song Z, Jia Y, Qiao X (2023) High throughput and noninvasive exosomal PD-L1 detection for accurate immunotherapy response prediction via Tim4-functionalized magnetic core-shell metal-organic frameworks. Anal Chem 95(49):18268–18277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04117
Li W, **ao F, Bai X, Xu H (2023) Magnetic nanoparticles for food hazard factors sensing: synthesis, modification and application. Chem Eng J 465:142816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142816
Chen J, Shao J, Sun R, Zhang W, Huang Y, Zheng J, Chi Y (2023) Anion exchanges of water-stable perovskite nanocrystals in the pure water phase and applications in detecting halide ions via a smartphone-based sensing platform. Anal Chem 95(31):11839–11848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02571
Shang Y, Sun H, Yu R, Zhang F, Liang X, Li H, Li J, Yan Z, Zeng T, Chen X, Zeng J (2023) Quantitative time-resolved visualization of catalytic degradation reactions of environmental pollutants by integrating single-drop microextraction and fluorescence sensing. Environ Sci Technol 57(30):11231–11240. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c02344
He J, Yu L, Jiang Y, Lü L, Han Z, Zhao X, Xu Z (2023) Encoding CsPbX3 perovskite quantum dots with different colors in molecularly imprinted polymers as fluorescent probes for the quantitative detection of Sudan I in food matrices. Food Chem 402:134499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134499
Rong M, Yang X, Huang L, Chi S, Zhou Y, Shen Y, Chen B, Deng X, Liu ZQ (2019) Hydrogen peroxide-assisted ultrasonic synthesis of BCNO QDs for anthrax biomarker detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(2):2336–2343. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b21786
Rong M, Ye J, Chen B, Wen Y, Deng X, Liu ZQ (2020) Ratiometric fluorescence detection of stringent ppGpp using Eu-MoS2 QDs test paper. Sensors Actuators B Chem 309:127807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127807
Ren X, Zhang D, Li C, Zhao J, Feng R, Zhang Y, Xu R, Wei Q (2024) Europium metal-organic framework with a tetraphenylethylene-based ligand: a dual-mechanism quenching immunosensor for enhanced electrochemiluminescence via the coordination trigger. Anal Chem 96(9):3898–3905. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05556
Bai C, Yao J, Meng Q, Dong Y, Chen M, Liu X, Wang X, Qiao R, Huang H, Wei B, Qu C, Miao H (2024) A near-infrared fluorescent ratiometric probe with large stokes shift for multi-mode sensing of Pb2+ and bioimaging. J Hazard Mater 469:133968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133968
Nedelcu G, Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk MI, Grotevent MJ, Kovalenko MV (2015) Fast anion-exchange in highly luminescent nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I). Nano Lett 15(8):5635–5640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02404
Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk MI, Krieg F, Caputo R, Hendon CH, Yang RX, Walsh A, Kovalenko MV (2015) Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX(3), X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett 15(6):3692–3696. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5048779
Yue Y, Xu H, Jiang L, Zhao X, Deng D (2024) Introducing specific iodine ions in perovskite-based nanocomplex to cater for versatile biomedical imaging and tumor radiotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater 13:2302721. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202302721
Park J, Jang KY, Lee SH, Kim DH, Cho SH, Lee TW (2023) Stable orthorhombic CsPbBr3 light emitters: encapsulation-assisted in situ synthesis. Chem Mater 35(16):6266–6273. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00732
Du Y, Jiang S, Han Y, Liu Q, Cui L, Zhang CY (2024) Synthesis of silica-encapsulated tetraphenylethylene with aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer for sensitively sensing microcystin-LR. Talanta 272:125752–125752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2024.125752
Zhong Q, Cao M, Hu H, Yang D, Chen M, Li P, Wu L, Zhang Q (2018) One-pot synthesis of highly stable CsPbBr3@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles. ACS Nano 12(8):8579–8587. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b04209
Guo G, Zhao T, Sun R, Song M, Liu H, Wang S, Li J, Zeng J (2023) Au-Fe3O4 dumbbell-like nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay for colorimetric and photothermal dual-mode detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Chin Chem Lett 35(6):109198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109198
Dehghani Z, Nguyen T, Golabi M, Hosseini M, Rezayan AH, Mohammadnejad J, Wolff A, Vinayaka AC (2021) Magnetic beads modified with Pt/Pd nanoparticle and aptamer as a catalytic nano-bioprobe in combination with loop mediated isothermal amplification for the on-site detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food and fecal samples. Food Control 121:107664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107664
Gao L, Ge Y, **e J, Li Y, Zhang H, Du S (2024) A gas-driven capillary based on the synergy of the catalytic and photothermal effect of PB@Au for Salmonella typhimurium detection. Talanta 269:125455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125455
Ma X, Lin X, Xu X, Wang Z (2021) Fabrication of gold/silver nanodimer SERS probes for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Microchim Acta 188(6):202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04791-4
Liu Y, Jiang D, Wang S, Cai G, Xue L, Li Y, Liao M, Lin J (2022) A microfluidic biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on magnetic separation, enzymatic catalysis and electrochemical impedance analysis. Chin Chem Lett 33(6):3156–3160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.10.064
Yuan P, Deng Z, Qiu P, Yin Z, Bai Y, Su Z, He J (2023) Bimetallic metal-organic framework nanorods with peroxidase mimicking activity for selective colorimetric detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food. Food Control 144:109357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109357
Zhuang QQ, He S-B, Jiang YC, Huang KY, Xu YY, Peng HP, Deng HH, Chen W (2022) Immunofluorescent-aggregation assay based on anti-Salmonella typhimurium IgG-AuNCs, for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Microchim Acta 189(4):160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05263-z
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Scientific Foundation of Shandong (nos. ZR2023MC039, ZR2020ZD13 and ZR2022JQ07), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. 21CX06014A), and the Taishan Scholarship of Shandong Province (no. tsqn202211080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was approved by all authors for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research did not involve human or animal samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 34.8 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Y., Wang, J., **a, H. et al. A highly sensitive point-of-care detection platform for Salmonella typhimurium by integrating magnetic enrichment and fluorescent CsPbBr3@SiO2. Microchim Acta 191, 303 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06361-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06361-w