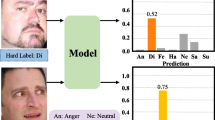
Abstract
Facial expression intensity estimation has promising applications in health care and affective computing, such as monitoring patients’ pain feelings. However, labeling facial expression intensity is a specialized and time-consuming task. Ordinal regression (OR)-based methods address this issue to some extent by estimating the relative intensity but failing to estimate the absolute intensity due to lack of exploring useful information from noisy labels caused by manual and automatic labeling biases. Inspired by label distribution learning (LDL) to resist the noisy labels, this paper introduces the label-distribution-learning-enhanced OR (LDL-EOR) approach for facial expression intensity estimation. This design aims to utilize LDL to improve the accuracy of absolute intensity estimation while kee** the cost of manual labeling low. The label distribution is converted into a continuous intensity value by calculating the mathematical expectation, which makes the prediction results meet both relative and absolute intensity constraints. Ensuring the feasibility of LDL-EOR in different supervised settings, this paper presents a unified label distribution generation framework to automatically relabel training data frame by frame. The generated soft labels are used to supervise the LDL-EOR model and enhance its robustness to the noise existing in the original labels. Numerous experiments were conducted on three public expression datasets (CK+, BU-4DFE, and PAIN) to validate the superiority of LDL-EOR relative to other state-of-the-art approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in our paper (CK+, BU-4DFE, and PAIN) are publicly available.
References
Yang, P., Liu, Q., Metaxas, D.N.: Rankboost with l1 regularization for facial expression recognition and intensity estimation. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1018–1025 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459371
Rudovic, O., Pavlovic, V., Pantic, M.: Multi-output laplacian dynamic ordinal regression for facial expression recognition and intensity estimation, pp. 2634–2641 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247983
Sabri, M., Kurita, T.: Facial expression intensity estimation using siamese and triplet networks. Neurocomputing 313, 143–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.054
Saha, C., Ghosh, K.: Estimation of facial expression intensity from a sequence of binary face images, pp. 1–6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIIP.2011.6108935
Ming, Z., Bugeau, A., Rouas, J.-L., Shochi, T.: Facial action units intensity estimation by the fusion of features with multi-kernel support vector machine. In: 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), vol. 06, pp. 1–6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2015.7284870
Batista, J.C., Bellon, O.R., Silva, L.: Landmark-free smile intensity estimation. In: Workshop Conf. Graphics (2016)
Lee, K.K., Xu, Y.: Real-time estimation of facial expression intensity. In: 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.03CH37422), vol. 2, pp. 2567–25722 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2003.1241979
Kamarol, S.K.A., Jaward, M.H., Kälviäinen, H., Parkkinen, J., Parthiban, R.: Joint facial expression recognition and intensity estimation based on weighted votes of image sequences. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 92, 25–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.04.003
Xue, M., Duan, X., Liu, W., Ren, Y.: A semantic facial expression intensity descriptor based on information granules. Inf. Sci. 528, 113–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.04.012
Lien, J.J.-J., Kanade, T., Cohn, J.F., Li, C.-C.: Subtly different facial expression recognition and expression intensity estimation. In: Proceedings. 1998 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Cat. No.98CB36231), pp. 853–859 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.1998.698704
Liao, C.-T., Chuang, H.-J., Lai, S.-H.: Learning expression kernels for facial expression intensity estimation. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2217–2220 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6288354
Li, J., Cheng, K., Wang, S., Morstatter, F., Trevino, R.P., Tang, J., Liu, H.: Feature selection: a data perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3136625
Nomiya, H., Sakaue, S., Hochin, T.: Recognition and intensity estimation of facial expression using ensemble classifiers. Int. J. Network. Distrib. Comput. 4, 203–211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2991/ijndc.2016.4.4.1
Mohammadi, M.R., Fatemizadeh, E., Mahoor, M.H.: Intensity estimation of spontaneous facial action units based on their sparsity properties. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(3), 817–826 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2416317
Zhang, Y., Wu, B., Dong, W., Li, Z., Liu, W., Hu, B.-G., Ji, Q.: Joint representation and estimator learning for facial action unit intensity estimation. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3452–3461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00357
Lu, G., Zhang, W.: Happiness intensity estimation for a group of people in images using convolutional neural networks. In: 2019 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering (EITCE), pp. 1707–1710 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/EITCE47263.2019.9094832
Tavakolian, M., Hadid, A.: A spatiotemporal convolutional neural network for automatic pain intensity estimation from facial dynamics. Int. J. Comput. Vision (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01191-3
Ntinou, I., Sanchez, E., Bulat, A., Valstar, M., Tzimiropoulos, G.: A transfer learning approach to heatmap regression for action unit intensity estimation. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 14(1), 436–450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2021.3061605
Fan, Y., Lam, J., Li, V.: Facial action unit intensity estimation via semantic correspondence learning with dynamic graph convolution. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 34(07), 12701–12708 (2020)
Batista, J.C., Albiero, V., Bellon, O.R.P., Silva, L.: Aumpnet: Simultaneous action units detection and intensity estimation on multipose facial images using a single convolutional neural network. In: 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), pp. 866–871 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2017.111
Tavakolian, M., Bordallo Lopez, M., Liu, L.: Self-supervised pain intensity estimation from facial videos via statistical spatiotemporal distillation. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 140, 26–33 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.09.012
Song, X., Shi, T., Feng, Z., Song, M., Lin, J., Lin, C., Fan, C., Yuan, Y.: Unsupervised learning facial parameter regressor for action unit intensity estimation via differentiable renderer. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3394171.3413955
Zhao, R., Gan, Q., Wang, S., Ji, Q.: Facial expression intensity estimation using ordinal information. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3466–3474 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.377
Zhang, Y., Dong, W., Hu, B.-G., Ji, Q.: Weakly-supervised deep convolutional neural network learning for facial action unit intensity estimation. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2314–2323 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00246
Geng, X.: Label distribution learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 28(7), 1734–1748 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2545658
Gao, B.-B., **ng, C., **e, C.-W., Wu, J., Geng, X.: Deep label distribution learning with label ambiguity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(6), 2825–2838 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2689998
Díaz, R., Marathe, A.: Soft labels for ordinal regression. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4733–4742 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00487
Lucey, P., Cohn, J.F., Kanade, T., Saragih, J., Ambadar, Z., Matthews, I.: The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition - Workshops, pp. 94–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543262
Zhang, X., Yin, L., Cohn, J.F., Canavan, S., Reale, M., Horowitz, A., Liu, P.: A high-resolution spontaneous 3d dynamic facial expression database. In: 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2013.6553788
Lucey, P., Cohn, J.F., Prkachin, K.M., Solomon, P.E., Matthews, I.: Painful data: The unbc-mcmaster shoulder pain expression archive database. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), pp. 57–64 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2011.5771462
Prkachin, K.M., Solomon, P.E.: The structure, reliability and validity of pain expression: evidence from patients with shoulder pain. Pain 139(2), 267–274 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.04.010
Shrout, P.E., Fleiss, J.L.: Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 86(2), 420–8 (1979)
Drucker, H., Burges, C.J.C., Kaufman, L., Smola, A., Vapnik, V.: Support vector regression machines. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 155–161 (1996)
Chu, W., Keerthi, S.S.: New approaches to support vector ordinal regression. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 145–152 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1102351.1102370
Xu, R., Han, J., Chen, J.: Ordinal information based facial expression intensity estimation for emotional interaction: a novel semi-supervised deep learning approach. Computing 1–18 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62377018 and the Research Funds of CCNU from the Colleges’ Basic Research and Operation of MOE, under Grant No. CCNU22JC010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RX and JC: proposed the conceptualization and methodology, RX and ZW: wrote the main manuscript and prepared the figures, ZW and LZ: conducted the experiments, and JC: revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by R. Huang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R., Wang, Z., Chen, J. et al. Facial expression intensity estimation using label-distribution-learning-enhanced ordinal regression. Multimedia Systems 30, 13 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01219-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01219-2