Abstract
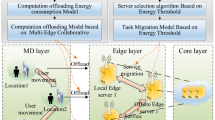
The combination of idle computing resources in mobile devices and the computing capacity of mobile edge servers enables all available devices in an edge network to complete all computing tasks in coordination to effectively improve the computing capacity of the edge network. This is a research hotspot for 5G technology applications and integrating collaborative computing techniques into edge computing. Previous research has focused on the minimum energy consumption and/or delay to determine the formulation of the computational offloading strategy but neglected the cost required for the computation of collaborative devices (mobile devices, mobile edge servers, etc.); therefore, we propose a cost-based collaborative computation offloading model. In this model, when a task requests these devices’ assistance in computing, it needs to pay the corresponding calculation cost; and on this basis, the task is offloaded and computed. In addition, for the model, we propose an adaptive neighborhood search based on simulated annealing algorithm (ANSSA) to jointly optimize the offloading decision and resource allocation with the goal of minimizing the sum of both the energy consumption and calculation cost. The adaptive mechanism enables different operators to update the probability of selection according to historical experience and environmental perception, which makes the individual evolution have certain autonomy. A large number of experiments conducted on different scales of mobile user instances show that the ANSSA can obtain satisfactory time performance with guaranteed solution quality. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the mobile edge computing (MEC) offloading system. It is of great significance to strike a balance between maintaining the life cycle of smart mobile devices and breaking the performance bottleneck of MEC servers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Abbas N, Zhang Y, Taherkordi A, Skeie T (2017) Mobile edge computing: a survey. IEEE Intern Things J 5(1):450–465
Cao X, Wang F, Xu J, Zhang R, Cui S (2018) Joint computation and communication cooperation for energy-efficient mobile edge computing. IEEE Intern Things J 6(3):4188–4200
Chen M, Hao Y (2018) Task offloading for mobile edge computing in software defined ultra-dense network. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 36(3):587–597
Gumaei A, Al-Rakhami M, AlSalman H, Rahman SMM, Alamri A (2020) DL-HAR: deep learning-based human activity recognition framework for edge computing. CMC Comput Mater Contin 65(2):1033–1057
Guo J, Song Z, Cui Y, Liu Z, Ji Y (2017) Energy-efficient resource allocation for multi-user mobile edge computing. In: GLOBECOM 2017-2017 IEEE global communications conference, IEEE, pp 1–7
Huang PQ, Wang Y, Wang K, Liu ZZ (2019) A bilevel optimization approach for joint offloading decision and resource allocation in cooperative mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2916728
Liu M, Liu Y (2017) Price-based distributed offloading for mobile-edge computing with computation capacity constraints. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett 7(3):420–423
Liu P, Ren H, Shi X, Li Y, Cai Z, Liu F, Zeng H (2020) Motransframe: model transfer framework for CNNs on low-resource edge computing node. CMC Comput Mater Contin 65(3):2321–2334
Mao Y, Zhang J, Letaief KB (2016) Dynamic computation offloading for mobile-edge computing with energy harvesting devices. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 34(12):3590–3605
Pu L, Chen X, Xu J, Fu X (2016) D2d fogging: an energy-efficient and incentive-aware task offloading framework via network-assisted d2d collaboration. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 34(12):3887–3901
Qasim A, Kazmi SAR (2019) Formal modelling of real-time self-adaptive multi-agent systems. Intell Autom Soft Comput 25(1):49–63
Qian C, Li X, Sun N, Tian Y (2020) Data security defense and algorithm for edge computing based on mean field game. J Cybersecur 2(2):97
Sahni LY, Cao J (2021) Multi-hop multi-task partial computation offloading in collaborative edge computing. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 32(5):1133–1145
Ti NT, Le LB (2017) Computation offloading leveraging computing resources from edge cloud and mobile peers. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), IEEE, pp 1–6
Tran TX, Pompili D (2018) Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(1):856–868
Wang J, Yu Sj (2011) Blind detection based on simulated annealing chaotic particle swarm optimization. Comput Technol Dev 21(1):35–37
Wei F, Chen S, Zou W (2018) A greedy algorithm for task offloading in mobile edge computing system. China Commun 15(11):149–157
Wei X, Liu J, Wang Y, Tang C, Hu Y (2021) Wireless edge caching based on content similarity in dynamic environments. J Syst Archit 115:102000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2021.102000
Xue Y, Tang T, Pang W, Liu AX (2020) Self-adaptive parameter and strategy based particle swarm optimization for large-scale feature selection problems with multiple classifiers. Appl Soft Comput 88:106031
Zhang K, Mao Y, Leng S, Zhao Q, Li L, Peng X, Pan L, Maharjan S, Zhang Y (2016) Energy-efficient offloading for mobile edge computing in 5g heterogeneous networks. IEEE Access 4:5896–5907
Zheng H, Hu Xb, Zheng Mm, Liu Rj (2013) An improved hybrid algorithm based on particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing and its application. Comput Technol Dev 23(7):26–30
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This paper was supported in part by Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2020M-671552, in part by Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds under Grant 2019K223, in part by NUPTSF (NY220060), in part by the Opening Project of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Data Science and Smart Software (No. 2020DS301), in part by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China under Grant BK20191381, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61772286, Grant 61771258 and Grant 61876089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to this research equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Deng, T., Liu, Y. et al. Optimization of cooperative offloading model with cost consideration in mobile edge computing. Soft Comput 27, 8233–8243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07733-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07733-1