Abstract
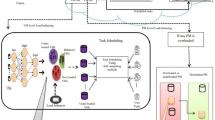
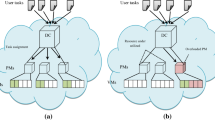
In today’s world, most of the applications run with the service of cloud computing, which proceeds the process using the internet. In the case of cloud computing, based on customer needs, they may increase or decrease resource utilization. Virtualization is the process of multiplexing the resources from physical machines to virtual machines. However, it is challenging to prevent overloading for each physical machine of an automatic resources management system which affects virtualization to allocate the resources dynamically. To overcome these concerns, a new algorithm is proposed in this work, which can predict the future load precisely in the physical machine and decide which may be overloaded next. Then, the necessary action is taken to prevent overload in the system. In this work, the prediction of loads for allocating future resources is presented, and the dynamic scheduling and resource allocation for the predicted tasks are performed using IFPA. The difference of Gaussian-based adaptive least mean square filter is employed for predicting the loads function points which are used to estimate the complexity and cost rate. Also, a soft computing technique (improved flower pollination algorithm) is employed for the effective resource allocation strategy. The performance of the approach is intended and compared with other conventional works. The results proved that the work has better accuracy in load prediction and provide a way to allocate the resource precisely. At the same time, the traffic at the physical machines is significantly controlled.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 December 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07757-7
References
Armbrust M, Stoica I, Zaharia M, Fox A, Griffith R, Joseph AD, Katz R, Konwinski A, Lee G, Patterson D, Rabkin A (2010) A view of cloud computing. Commun ACM 53(4):50
Calyam P, Rajagopalan S, Seetharam S, Selvadhurai A, Salah K, Ramnath R (2014) VDC-analyst: design and verification of virtual desktop cloud resource allocations. Comput Netw 68:110–122
Caron E, Desprez F, Muresan A (2011) Pattern matching based forecasting of non-periodic repetitive behavior for cloudclients. J Grid Comput 9(1):49–64
Davidson MW, Abramowitz M (2006) Molecular expressions microscopy primer: digital image processing-difference of Gaussians edge enhancement algorithm. Olympus America Inc., and Florida State University
Di S, Wang C-L (2013) Error-tolerant resource allocation and payment minimization for a cloud system. Parallel Distrib Syst IEEE Trans 24(6):1097–1106
Function Point http://www.codeproject.com/KB/architecture/Calculate_Function_Point
Google Whitepaper (2011) Google’s green data centers: network POP case study. Google.http://static.googleusercontent.com/external_content/untrusted_dlcp/www.google.com/en/us/corporate/datacenter/dc-best-practices-google.pdf
Islam S, Keung J, Lee K, Liu A (2012) Empirical prediction models for adaptive resource provisioning in the cloud. Fut Gen Comput Syst 28(1):155–162
Jalote P (1997) An integrated approach to software engineering, 3rd edn. Metrics-Function Points. Springer, New York, pp 121–125
Kim H, Kim W, Kim Y (2011) A pattern-based prediction model for dynamic resource provisioning in the cloud environment. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems 5(10):1712–1732
Lian Z, Er MJ, Li J (2011) A Novel Face Recognition Approach under Illumination Variations Based on Local Binary Pattern. In: 14th International conference on computer analysis of images and patterns, vol 6855, pp 89–96
Mell P, Grance T (2009) Definition of cloud computing. Technical report SP 800–145, National Institute of Standard and Technology (NIST), Gaithersburg, MD
Morshedlou H, Meybodi MR (2014) Decreasing impact of SLA violations: a proactive resource allocation approach for cloud computing environments. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 2(2):156–167
Nathuji R, Kansal A, Ghaffarkhah A (2010) Q-Clouds: managing performance interference effects for QoS-aware clouds. In: 5th European conference on a computer system (EuroSys’10), pp 237–250
Oehoa EM (1996) Clustered microcalcification detection using the optimized difference of Gaussians, M.Sc Thesis, Air Force Institute of Technology
Qureshi SR (2014) Cache based cloud architecture for optimization of resource allocation and data distribution. In: Satapathy SC, Avadhani PS, Udgata SK, Lakshminarayana S (eds) ICT and criticalinfrastructure: proceedings of the 48th Annual Convention of Computer Society of India, vol 1, 248. Springer, Berlin, pp 535–542
Rygielski P, Tomczak J (2011) Context change detection for resource allocation in service-oriented systems. In: König A, Dengel A, Hinkelmann K, Kise K, Howlett R, Jain L (eds) Knowledge-based and intelligent information and engineering systems, vol 6882. Springer, Berlin, pp 591–600
Sood SK (2016) Function points-based resource prediction in cloud computing. Concurr Comput: Pract Exp 28(10):2781–2794
Tsai J-T, Fang J-C, Chou J-H (2013) Optimized task scheduling and resource allocation INA cloud computing environment using an improved differential evolution algorithm. Comput Oper Res 40(12):3045–3055
Vakilinia S, Heidarpour B, Cheriet M (2016) Energy-efficient resource allocation in cloud computing environments. IEEE Access 4:8544–8557
Varalakshmi P, Ramaswamy A, Balasubramanian A, Vijaykumar P (2011) An optimal workflow-based scheduling and resource allocation in the cloud. In: Abraham A, Mauri JL, Buford J, Suzuki J, Thampi S (eds) Advances in computing and communications. Springer, Berlin, pp 411–420
Wang L, Kunze M, Tao J, Laszewski G (2011) Towards building a cloud for scientific applications. Adv Eng Softw 42(9):714–722
Wang L, Chen D, Zhao J, Tao J (2012) Resource management of distributed virtual machines. IJAHUC 10(2):96–111
Yang XS (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In: International conference on unconventional computing and natural computation. Springer, Berlin, pp 240–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Humans and animals rights
Humans and animals are not involved in this research work.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07757-7"
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Reshmi, R., Saravanan, D.S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Load prediction using (DoG–ALMS) for resource allocation based on IFP soft computing approach in cloud computing. Soft Comput 24, 15307–15315 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04864-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04864-1