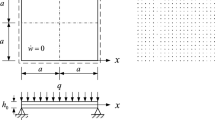
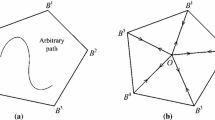
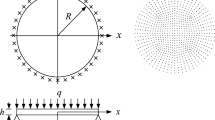
Abstract
In this paper, a novel numerical solution procedure is developed for the upper bound shakedown analysis of elastic-perfectly plastic structures. The nodal natural element method (nodal-NEM) combines the advantages of the NEM and the stabilized conforming nodal integration scheme, and is used to discretize the established mathematical programming formulation of upper bound shakedown analysis based on Koiter’s theorem. In this formulation, the displacement field is approximated by using the Sibson interpolation and the difficulty caused by the time integration is solved by König’s technique. Meanwhile, the nonlinear and non-differentiable characteristic of objective function is overcome by distinguishing non-plastic areas from plastic areas and modifying associated constraint conditions and goal function at each iteration step. Finally, the objective function subjected to several equality constraints is linearized and the upper bound shakedown load multiplier is obtained. This direct iterative process can ensure the shakedown load to monotonically converge to the upper bound of true solution. Several typical numerical examples confirm the efficiency and accuracy of the proposed method.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu BY, Liu XS (1985) Plastic limit analysis of structures. China Architecture and Building Press, Bei**g
Chen G, Liu YH (2006) Numerical theories and engineering methods for structural limit and Shakedown analyses. Science Press, Bei**g
Melan E (1938) Zur Plastizitä t des räumlichen Kontinuums. Ing-Arch 9:115–126
Koiter WT (1956) A new general theorem on shakedown of elastic-plasitc structures. Proc Konink Ned Akad Wet B 59:24–34
Kamenjarzh J, Merzljakov A (1994) On kinematic method in shakedown theory. I: duality of extremum problems. Int J Plast 10(4):363–380
Kamenjarzh J, Merzljakov A (1994) On kinematic method in shakedown theory. II: modified kinematic method. Int J Plast 10(4):381–392
Khoi VD, Yan AM, Hung ND (2004) A dual form for discretized kinematic formulation in shakedown analysis. Int J Solids Struct 41(1):267–277
Khoi VD, Yan AM, Hung ND (2004) A primal-dual algorithm for shakedown analysis of structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(42–44):4663–4674
Tran TN, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) An edge-based smoothed finite element method for primal-dual shakedown analysis of structures. Int J Numer Meth Eng 82(7):917–938
Tran TN (2011) A dual algorithm for shakedown analysis of plate bending. Int J Numer Meth Eng 86(7):862–875
Stein E, Zhang GB, Konig JA (1992) Shakedown with nonlinear strain-hardening including structural computation using finite-element method. Int J Plast 8(1):1–31
Zhang YG (1995) An iteration algorithm for kinematic shakedown analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 127(1–4):217–226
Hachemi A, Weichert D (1998) Numerical shakedown analysis of damaged structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 160:57–70
Yan AM, Hung ND (2001) Kinematical shakedown analysis with temperature-dependent yield stress. Int J Numer Meth Eng 50(5):1145–1168
Maier G, Pan LG, Perego U (1993) Geometric effects on shakedown and ratchetting of axisymmetric cylindrical shells subjected to variable thermal loading. Eng Struct 15:453–465
Borino G, Polizzotto C (1996) Dynamic shakedown of structures with variable appended masses and subjected to repeated excitations. Int J Plast 12(2):215–228
Tran TN, Kreissig R, Staat M (2009) Probabilistic limit and shakedown analysis of thin plates and shells. Struct Saf 31(1):1–18
Carvelli V (2004) Shakedown analysis of unidirectional fiber reinforced metal matrix composites. Comput Mater Sci 31(1–2):24–32
Li HX, Yu HS (2006) A non-linear programming approach to kinematic shakedown analysis of composite materials. Int J Numer Meth Eng 66(1):117–146
Li HX, Yu HS (2006) A nonlinear programming approach to kinematic shakedown analysis of frictional materials. Int J Solids Struct 43(21):6594–6614
Feng XQ, Liu XS (1997) On shakedown of three-dimensional elastoplastic strain-hardening structures. Int J Plast 12(10):1241–1256
Feng XQ, Sun QP (2007) Shakedown analysis of shape memory alloy structures. Int J Plast 23(2):183–206
Carvelli V, Cen ZZ, Liu YH, Maier G (1999) Shakedown analysis of defective pressure vessels by a kinematic approach. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):751–764
Chen HF, Ure J, Li TB, Chen WH, Mackenzie D (2011) Shakedown and limit analysis of \(90^{\circ }\) pipe bends under internal pressure, cyclic in-plane bending and cyclic thermal loading. Trans ASME J Press Vessel Technol 88(5–7):213–222
Gross-Wedge J (1997) On the numerical assessment of the safety factor of elastic-plastic structures under variable loading. Int J Mech Sci 39(4):417–433
Shiau SH (2001) Numerical methods for shakedown analysis of pavements under moving surface loads. PhD thesis, University of Newcastle, NSW, Australia
Konig JA, Maier G (1981) Shakedown analysis of elastoplastic structures: a review of recent developments. Nucl Eng Des 66(1):81–95
Panzeca T (1992) Shakedown and limit analysis by the boundary integral equation method. Eur J Mech A-Solids 11(5):685–699
Zhang XF, Liu YH, Cen ZZ (2004) Boundary element methods for lower bound limit and shakedown analysis. Eng Anal Boundary Elem 28(8):905–917
Liu YH, Zhang XF, Cen ZZ (2005) Lower bound shakedown analysis by the symmetric Galerkin boundary element method. Int J Plast 21(1):21–42
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element free Galerkin method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 37(2):229–256
Liu WK, Jun S, Zhang YF (1995) Reproducing kernel particle method. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 20(8–9):1081–1106
Liszka TJ, Duarte CAM, Tworzydlo WW (1996) hp-meshless cloud method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 139(1–4):263–288
Atluri SN, Zhu T (1998) A new meshless local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) approach in computational mechanics. Comput Mech 22(2):117–127
Sukumar N, Moran B, Belytschko T (1998) The natural element method in solid mechanics. Int J Numer Meth Eng 43(5):839–887
Zhang XG, Liu XH, Song KZ, Lu MW (2001) Least-squares collocation meshless method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 51(9):1089– 1100
Liu GR, Wang JG (2002) A point interpolation meshless method based on radial basis functions. Int J Numer Meth Eng 54(11):1623–1648
Gu L (2003) Moving Kriging interpolation and element free Galerkin method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 56(1):1–11
Kim DW, Yoon YC, Liu WK, Belytschko T (2007) Extrinsic meshfree approximation using asymptotic expansion for interfacial discontinuity of derivative. J Comput Phys 221(1):370–394
Bessa MA, Foster JT, Belytschko T, Liu WK (2013) A meshfree unification: reproducing kernel peridynamics. Comput Mech. doi:10.1007/s00466-013-0969-x
Yoon YC, Song JH (2013) Extended particle difference method for weak and strong discontinuity problems: part I. Derivation of the extended particle derivative approximation for the representation of weak and strong discontinuities. Comput Mech. doi:10.1007/s00466-013-0950-8
Yoon YC, Song JH (2013) Extended particle difference method for weak and strong discontinuity problems: part II. Formulations and applications for various interfacial singularity problems. Comput Mech. doi:10.1007/s00466-013-0951-7
Chen SS, Liu YH, Cen ZZ (2008) Lower bound shakedown analysis by using the element free Galerkin method and nonlinear programming. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197:3911–3921
Chen SS, Liu YH, Li J, Cen ZZ (2010) Performance of the MLPG method for static shakedown analysis for bounded kinematic hardening structures. Eur J Mech A/Solids 30(2):183–194
Beissel S, Belytschko T (1996) Nodal integration of the element-free Galerkin method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 139(1–4):49–74
Chen JS, Wu CT, Yoon S, You Y (2001) A stabilized conforming nodal integration for Galerkin mesh-free methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 50(2):435–466
Chen JS, Yoon S, Wu CT (2002) Non-linear version of stabilized conforming nodal integration for Galerkin mesh-free methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 53(12):2587–2615
Chen JS, Wu CT, Belytschko T (2000) Regularization of material instabilities by meshfree approximations with intrinsic length scales. Int J Numer Meth Eng 47(7):1303–1322
Wang D, Chen JS (2004) Locking-free stabilized conforming nodal integration for Mindlin–Reissner plate. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(12–14):1065–1083
Wang D, Chen JS (2006) A locking-free meshfree curved beam formulation with the stabilized conforming nodal integration. Comput Mech 39(1):83–90
Wang D, Chen JS (2008) A Hermite reproducing kernel approximation for thin plate analysis with sub-domain stabilized conforming integration. Int J Numer Meth Eng 74(3):368–390
Wang D, Lin Z (2011) Dispersion and transient analyses of Hermite reproducing kernel Galerkin meshfree method with sub-domain stabilized conforming integration for thin beam and plate structures. Comput Mech 48(1):47–63
Yoo JW, Moran B, Chen JS (2004) Stabilized conforming nodal integration in the natural-element method. Int J Numer Meth Eng 60:861–890
Puso MA, Chen JS, Zywicz E, Elmer W (2008) Meshfree and finite element nodal integration methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 74:416–446
Sibson R (1980) Vector identity for the dirichlet tessellation. Math Proc Camb Philos Soc 87:151–155
Braun J, Sambridge M (1995) A numerical method for solving partial differential equations on highly irregular evolving grids. Nature 376:655–660
Sukumar N, Moran B, Semenov AY, Belikov VV (2001) Natural neighbour Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 50(1):1–27
Cueto E, Sukumar N, Calvo B, Martinez MA, Cegonino J, Doblare M (2003) Overview and recent advances in natural neighbour Galerkin methods. Arch Comput Methods Eng 10(4):307–384
Gonzalez D, Cueto E, Doblare M (2004) Volumetric locking in natural neighbour Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 61(4):611–632
Thiessen AH (1911) Precipitation averages for large areas. Mon Weather Rep 39:1082–1084
Belikov VV, Ivanov VD, Kontorovich VK, Korytnik SA (1997) The non-Sibsonian interpolation: a new method of interpolation of the values of a function on an arbitrary set of points. Comput Math Math Phys 37(1):9–15
Hiyoshi H, Sugihara K (1999) Two generalizations of an interpolant based on Voronoi diagrams. Int J Shape Model 5(2):219–231
Alfaro I, Yvonnet J, Chinesta F, Cueto E (2007) A study on the performance of natural neighbour-based Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 71(12):1436–1465
Cueto E, Doblare M, Gracia L (2000) Imposing essential boundary conditions in the natural element method by means of density-scaled a-shapes. Int J Numer Meth Eng 49:519–546
Zhou ST, Liu YH (2012) Upper-bound limit analysis based on the natural element method. Acta Mech Sin 28(5):1398–1415
Himmelblau DM (1972) Appl Nonlinear Progr. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Belytschko T (1972) Plane stress shakedown analysis by finite elements. Int J Mech Sci 14(9):619–625
Corradi L, Zavelani A (1974) A linear programming approach to shakedown analysis of structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 3(1):37–53
Nguyen DH, Palgen L (1980) Shakedown analysis by displacement method and equilibrium finite elements. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 61:34–40
Genna F (1988) A nonlinear inequality, finite element approach to the direct computation of shakedown load safety factors. Int J Mech Sci 30(10):769–789
Zouain N, Borges L, Silveira JL (2002) An algorithm for shakedown analysis with nonlinear yield functions. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191(23–24):2463–2481
Garcea G, Armentano G, Petrolo S, Casciaro R (2005) Finite element shakedown analysis of two-dimensional structures. Int J Numer Meth Eng 63(8):1174–1202
Tin-Loi F, Ngo NS (2007) Performance of a p-adaptive finite element method for shakedown analysis. Int J Mech Sci 49(10):1168–1178
Zhang TG, Raad L (2002) An eigen-mode method in kinematic shakedown analysis. Int J Plast 18(1):71–90
Krabbenhoft K, Lyamin AV, Sloan SW (2007) Bounds to shakedown loads for a class of deviatoric plasticity models. Comput Mech 39(6):879–888
Chen SS (2009) Lower-bound limit and Shakedown analysis based on meshless methods. PhD thesis, Tsinghua University, Bei**g, People’s Republic of China
Vu DK (2001) Dual limit and shakedown analysis of structures, dissertation. Universite de Liege, Belgium
Acknowledgments
S. Zhou is supported by the Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M540934). Y. Liu is supported by the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (11325211). D. Wang is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11222221). K. Wang is supported by the Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (J13LG51).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Liu, Y., Wang, D. et al. Upper bound shakedown analysis with the nodal natural element method. Comput Mech 54, 1111–1128 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-014-1043-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-014-1043-z