Abstract
Purpose
As a type of cancer with the highest morbidity and mortality, lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) has a very poor prognosis. Long-non-coding RNA (lncRNA) has recently attracted attentions because it can play the role of competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to inhibit microRNA (miRNA) functions. In this study, we aimed to find prognosis-related lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs and construct a prognosis-related ceRNA network.
Methods
The original LUSC RNA-sequencing data and miRNA profiles data were downloaded from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database. Differentially expressed lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs were then identified between patients with lymph node metastasis and no lymph node metastasis. Univariate Cox regression analysis was performed to find the survival-associated lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs. Subsequently, prognostic-related ceRNA network was established. By multivariate Cox regression analysis, three lncRNA signatures and three mRNA signatures were developed and used for predicting LUSC patients’ survival.
Results
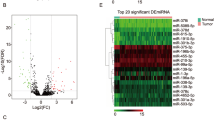
A total of 224 lncRNAs, 160 miRNAs, 913 mRNAs were identified between samples with lymph node metastasis and no lymph node metastasis. Univariate Cox regression analysis showed that, among them, 28 lncRNAs, 8 miRNAs, 105 mRNAs were significantly associated with patients’ overall survival time. Further pathway and enrichment analysis suggested that these mRNAs were associated with the regulation of transmembrane transport, regulation of blood circulation, plasma lipoprotein particle organization. Then we constructed a survival-related ceRNA network including 9 lncRNAs, 8 miRNAs and 23 mRNAs. Additionally, a multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that three lncRNAs (AL161431.1, LINC02389, APCDD1L.DT) and three mRNAs (KLK6, SLITRK5, CCDC177) had a significant prognostic value. Risk score indicated that lncRNA signature and mRNA signature could independently predict overall survival in LUSC patients.
Conclusion
The current study provided a better understanding of the ceRNA network in the progression of LUSC and laid a theoretical foundation for LUSC prognosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Chen J et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder cancer. Mol Cancer 18:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0947-9
Chen W, Zhuang X, Qi R, Qiao T (2019) MiR-302a-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma by targeting ITGA6. Am J Transl Res 11:4348–4357
Choi M et al (2017) Mutation profiles in early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma with clinical follow-up and correlation with markers of immune function. Ann Oncol 28:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw437
Das MK, Evensen HSF, Furu K, Haugen TB (2019) miRNA-302s may act as oncogenes in human testicular germ cell tumours. Sci Rep 9:9189–9189. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45573-6
Dong W et al (2019) Circular RNA ACVR2A suppresses bladder cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through miR-626/EYA4 axis. Mol cancer 18:95–95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1025-z
Galupa R, Heard E (2015) X-chromosome inactivation: new insights into cis and trans regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 31:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2015.04.002
Ji ZC, Han SH, **ng YF (2018) Overexpression of miR-3196 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis through targeting ERBB3 in breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:8383–8390. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16536
Jiang Z, Zhang J, Chen F, Sun Y (2019) MiR-148b suppressed non-small cell lung cancer progression via inhibiting ALCAM through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13285
Ju Q et al (2019) Identification of a miRNA-mRNA network associated with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett 18:1179–1188. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10460
Kamil M et al (2019) High filamin-C expression predicts enhanced invasiveness and poor outcome in glioblastoma multiforme. Br J Cancer 120:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0413-x
Kim J et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat Genet 50:1705–1715. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0252-3
Kopp F, Mendell JT (2018) Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 172:393–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011
Li Y, Huo J, Pan X, Wang C, Ma X (2018) MicroRNA 302b–3p/302c-3p/302d-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes apoptosis in human endometrial carcinoma cells. Onco Targets Ther 11:1275–1284. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154517
Liu N et al (2019) FAM163A, a positive regulator of ERK signaling pathway, interacts with 14–3-3β and promotes cell proliferation in squamous cell lung carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 12:6393–6406. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S214731
Liu Y, **ao N, Xu SF (2017) Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA LINC00261 is a prognostic marker for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a preliminary study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:5691–5695. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201712_14014
Luk ST et al (2019) Deficiency in embryonic stem cell marker REX1 activates MKK6-dependent p38 MAPK signaling to drive hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31020
Luo H et al (2019) HOTTIP lncRNA promotes hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal leading to AML-like disease in mice. Cancer Cell 36:645–659.e648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.10.011
Ming Z, Pang Y, Liu J (2019) Mechanical deformation mediated transmembrane transport. Macromol Rapid Commun. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201900518
Nibbe RK, Chowdhury SA, Koyutürk M, Ewing R, Chance MR (2011) Protein-protein interaction networks and subnetworks in the biology of disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 3:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.121
Ning P et al (2018) Integrated genomic analyses of lung squamous cell carcinoma for identification of a possible competitive endogenous RNA network by means of TCGA datasets. PeerJ 6:e4254–e4254. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4254
Park HJ et al (2018) 3' UTR shortening represses tumor-suppressor genes in trans by disrupting ceRNA crosstalk. Nat Genet 50:783–789. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0118-8
Pepe F, Visone R, Veronese A (2018) The glucose-regulated MiR-483–3p influences key signaling pathways in cancer. Cancers 10:181. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060181
Qi L, Zhang T, Yao Y, Zhuang J, Liu C, Liu R, Sun C (2019) Identification of lncRNAs associated with lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis in the competitive endogenous RNA network. PeerJ 7:e7727. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7727
Qian T et al (2019) PINCH-1 interacts with myoferlin to promote breast cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-1135-5
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Shahabi S et al (2019) LINC00261 is an epigenetically regulated tumor suppressor essential for activation of the DNA damage response. Cancer Res 79:3050–3062. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2034
Shain AH et al (2018) Genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals incremental disruption of key signaling pathways during melanoma evolution. Cancer Cell 34:45–55.e44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.06.005
Shannon P et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Shi J, Ma H, Wang H, Zhu W, Jiang S, Dou R, Yan B (2019) Overexpression of LINC00261 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells progression by interacting with miR-522–3p and suppressing Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem 120:18378–18387. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29149
Sun Y, Xu C, Wu Q, Zhang L, Wang P (2019) Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-204/EphA7 axis. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29548
Sun Y et al (2017) A long non-coding RNA HOTTIP expression is associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in small cell lung cancer patients. Mol Cancer 16:162–162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0729-1
Tanabe K et al (2017) Filamin C promotes lymphatic invasion and lymphatic metastasis and increases cell motility by regulating Rho GTPase in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:6353–6363. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14087
Tay Y et al (2011) Coding-independent regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by competing endogenous mRNAs. Cell 147:344–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.029
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Thomson DW, Dinger ME (2016) Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet 17:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.20
Wang C et al (2015) Elevated miR-483–3p expression is an early event and indicates poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:9447–9456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3690-x
Wang F et al (2014) Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. Hepatology 60:1278–1290. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27239
Wang Q et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes renal cell carcinoma progression through the regulation of the miR-615/IGF-2 pathway. Int J Oncol 53:2278–2288. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4539
Wang Z et al (2019) Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00261 acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer via regulating miR-105/FHL1 Axis. J Cancer 10:6414–6421. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.32251
Wong C-M, Tsang FH-C, Ng IO-L (2018) Non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular functions and pathological implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.169
Wu Y et al (2019a) Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 promotes cell proliferation and migration through sponging miR-4465 in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 23:5025–5036. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14359
Wu Y et al (2019b) A LTR retrotransposon-derived long non-coding RNA lncMER52A promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by binding p120-catenin. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2115
Xue D et al (2019) Circ-AKT3 inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering miR-296–3p/E-cadherin signals. Mol Cancer 18:151–151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1072-5
Yang J et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA LCAT1 functions as a ceRNA to regulate RAC1 function by sponging miR-4715–5p in lung cancer. Mol Cancer 18:171
Ye J et al (2019) Integrated analysis of a competing endogenous RNA network reveals key long noncoding RNAs as potential prognostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 120:13810–13825. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28655
Yue C, Ren Y, Ge H, Liang C, Xu Y, Li G, Wu J (2019) Comprehensive analysis of potential prognostic genes for the construction of a competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 12:561–576. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S188913
Zhang YQ, Zhang JJ, Song HJ, Li DW (2017) Overexpression of CST4 promotes gastric cancer aggressiveness by activating the ELFN2 signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res 7:2290–2304
Zhao R et al (2018) Exosomal long noncoding RNA HOTTIP as potential novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker test for gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 17:68–68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0817-x
Zhou B, Guo W, Sun C, Zhang B, Zheng F (2018) Linc00462 promotes pancreatic cancer invasiveness through the miR-665/TGFBR1-TGFBR2/SMAD2/3 pathway. Cell Death Dis 9:706–706. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0724-5
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank all participants involved in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by The National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Grant No. 81802415 to YZ), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2018PH025 to YZ), The Doctoral Scientific Fund Project of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University (Grant No. 2796 to QJ), Clinical Medicine + X Project, Medical College, Qingdao University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QJ and YZ designed and supervised the study. SM, XL and HZ analyzed the data and wrote the original draft. SZ, YY, SY edited draft. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, Q., Zhao, Yj., Ma, S. et al. Genome-wide analysis of prognostic-related lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs forming a competing endogenous RNA network in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1711–1723 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03224-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03224-8