Abstract
Background
To compared pemetrexed-based doublet with single-agent pemetrexed as second-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Methods
We systematically searched for randomized clinical trials that compared pemetrexed-based doublet with single-agent pemetrexed in patients with histologically proven non-small-cell lung cancer. The primary end point was overall survival. Secondary end points were progression-free survival, overall response rate and grade 3 or 4 toxicity. Data were extracted from the studies by 2 independent reviewers. The meta-analysis was performed by Stata version 10.0 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, Texas, USA).
Results
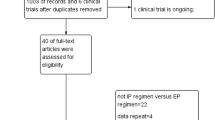
Five randomized clinical trials (totally 1,186 patients) were eligible. Meta-analysis showed that there was significant improvement in PFS (HR 0.82, 95% CI 0.71–0.95, P = 0.007) and overall response rate (OR 2.39, 95% CI 1.58–3.62, P = 0.000) in pemetrexed-based doublet group, compared with pemetrexed alone, though the pooled HR for overall survival (HR 0.89, 95% CI 0.76–1.04; P = 0.129) showed no significant difference between the two groups. However, there were more incidences of grade 3 or 4 neutropenia (OR 2.3, 95% CI 1.4–3.77, P = 0.001), thrombocytopenia (OR 6.41, 95% CI 2.57–16.0, P = 0.000), and leucopenia (OR 2.45, 95% CI 1.13–5.34, P = 0.024) in pemetrexed-based doublet group. With regard to the risk of grade 3 or 4 anemia (OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.17–2.91, P = 0.629) and fatigue (OR 1.47, 95% CI 0.92–2.35, P = 0.104), there was no significant difference between the two groups.
Conclusion
Pemetrexed-based doublet therapy didn’t gain any benefit in survival but significantly improved PFS and better ORR compared with single-agent pemetrexed as second-line therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. However, more incidences of grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and leucopenia were observed in pemetrexed-based doublet group.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrieta O, Villarreal-Garza C, Pachuca D et al (2011) High response of second-line chemotherapy with pemetrexed or gemcitabine combined with carboplatin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer experiencing progression following 6 months after concluding platinum-based chemotherapy. Med Oncol 8:300–306
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Chiappori A, Bepler G, Barlesi F et al (2010) Phase II, double-blinded, randomized study of enzastaurin plus pemetrexed as second-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:369–375
de Boer RH, Arrieta Ó, Yang CH et al (2011) Vandetanib plus pemetrexed for the second-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 29:1067–1074
Di Maio M, Chiodini P, Georgoulias V et al (2009) Meta-analysis of single-agent chemotherapy compared with combination chemotherapy as second-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:1836–1843
Favaretto A, Pasello G, Magro C et al (2009) Second and third line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 71:117–126
Felip E, Rosell R, Pampaloni G (2008) Pemetrexed as second-line therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ther Clin Risk Manag 4:579–585
Hanauske AR, Eismann U, Oberschmidt O et al (2007) In vitro chemosensitivity of freshly explanted tumor cells to pemetrexed is correlated with target gene expression. Invest New Drugs 25:417–423
Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV et al (2004) Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 22:1589–1597
Ho C, Davies AM, Lara PN Jr et al (2006) Second-line treatment for advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer: current and future options. Clinic Lung Cancer 7:S118–S125
Marinis F, Grossib F (2008) Clinical evidence for second- and third-line treatment options in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 13:14–20
Moher D, Pham B, Jones A et al (1998) Does quality of reports of randomized trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 352:609–613
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Qi WX, Shen Z, Yao Y (2011) Meta-analysis of docetaxel-based doublet versus docetaxel alone as second-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1678-9
Russo FBA, Pampaloni G (2008) Pemetrexed single agent chemotherapy in previously treated patients with local advanced or metastatic non small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 8:216–223
Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J et al (2008) Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:3543–3551
Scagliotti G, Hanna N, Fossella F et al (2009) The differential efficacy of pemetrexed according to NSCLC histology: a review of two phase III studies. Oncologist 14:253–263
Scagliotti GV, Germonpré P, Bosquée L et al (2010) A randomized phase II study of bortezomib and pemetrexed, in combination or alone, in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 68:420–426
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP et al (2002) Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346:92–98
Schiller JH, von Pawel J, Schütt P et al (2010) Pemetrexed with or without matuzumab as second-line treatment for patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:1977–1985
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T (2005) National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Smit EF, Burgers SA, Biesma B et al (2009) Randomized phase II and pharmacogenetic study of pemetrexed compared with pemetrexed plus carboplatin in pretreated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:2038–2045
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Yusuf S, Peto R, Jones DR, Collins R et al (1985) Beta blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 27:335–371
Zintzaras E, Ioannidis JP (2005) Heterogeneity testing in meta-analysis of genome searches. Genet Epidemiol 28:123–137
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, WX., Tang, LN., He, AN. et al. Effectiveness and safety of pemetrexed-based doublet versus pemetrexed alone as second-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 745–751 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1155-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1155-9