Abstract
Purpose
Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance have been linked to increased risk of occurrence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recently, retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) was clarified as a specific serological marker of insulin resistance. The aim of this study was to determine whether serum RBP4 could be used as a potential marker for predicting prognosis in patients with HCC after curative resection.
Methods
Western immunoblotting and Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were used to measure the RBP4 expression in cell lines, supernatant, and serum. Serum RBP4 levels were compared with clinicopathological features and outcomes of patients with HCC. Furthermore, we investigated the impact of serum RBP4 level, serum C-peptide level, and HOMA-IR on overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) of patients with HCC in the training cohort (156 patients with HCC), and then were validated in the validation cohort (105 patients with HCC).
Results
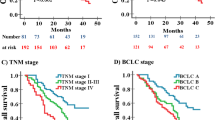
RBP4 protein overexpressed in HCC cell lines compared with normal liver cell line (P < 0.001) and correlated with metastatic potential. Serum RBP4 levels were associated with OS [hazard ratio (HR) = 2.208, P < 0.001] and DFS (HR = 1.878, P = 0.029) of patients with HCC. By multivariate analysis, the serum RBP4 level was identified as an independent factor for OS (HR = 2.170, P = 0.004) and DFS (HR = 1.769, P = 0.037) of patients with HCC. The prognostic value of serum RBP4 level was confirmed in the validation cohort.
Conclusions
The serum RBP4 level is potential to be a useful prognostic factor for HCC after curative resection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce WR, Giacca A, Medline A (2000) Possible mechanisms relating diet and risk of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9:1271–1279
Chung YW, Han DS, Park KH, Eun CS, Yoo KS, Park CK (2004) Insulin therapy and colorectal cancer risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Gastroenterology 127:1044–1050
Deng ZB, Poliakov A, Hardy RW, Clements R, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang J, **ang X, Zhang S, Zhuang X, Shah SV, Sun D, Michalek S, Grizzle WE, Garvey T, Mobley J, Zhang HG (2009) Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 58:2498–2505
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Madarnas Y, Hartwick W, Hoffman B, Hood N (2002) Fasting insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol 20:42–51
Graham TE, Yang Q, Blüher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi TP, Henry RR, Wason CJ, Oberbach A, Jansson PA, Smith U, Kahn BB (2005) Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med 354:2552–2563
Janke J, Engeli S, Boschmann M, Adams F, Bohnke J, Luft FC, Sharma AM, Jordan J (2004) Retinol-binding protein 4 in human obesity. Diabetes 55:2805–2810
Kaaks R, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, Lukanova A, Biessy C, Dechaud H, Rinaldi S, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Shore RE, Riboli E (2000) Serum C-peptide, IGF-I, IGFBPs, and colorectal cancer risk in women. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1592–1600
Kinoshita M, Miyata M (2002) Underexpression of mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma focusing on eight loci. Hepatology 36:433–438
Li LD, Zhang SW, Lu FZ (1997) Research on characteristics of mortality spectrum and type composition of malignant tumors in China. Chin J Oncol 19:323–328 (in Chinese)
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL, Liu YK, Tang ZY (2004) Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:460–468
Li D, Yeung SC, Hassan MM, Konopleva M, Abbruzzese JL (2009) Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 137:482–488
Miuma S, Ichikawa T, Taura N, Shibata H, Takeshita S, Akiyama M, Motoyoshi Y, Ozawa E, Fujimoto M, Kawashimo H, Miyaaki H, Eguchi K, Nakao K (2009) The level of fasting serum insulin, but not adiponectin, is associated with the prognosis of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 22:1415–1424
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Pasanisi P, Berrino F, De Petris M, Venturelli E, Mastroianni A, Panico S (2006) Metabolic syndrome as a prognostic factor for breast cancer recurrences. Int J Cancer 119:236–238
Petta S, Cammà C, Di Marco V, Alessi N, Barbaria F, Cabibi D, Caldarella R, Ciminnisi S, Licata A, Massenti MF, Mazzola A, Tarantino G, Marchesini G, Craxì A (2008) Retinol-binding protein 4: a new marker of virus-induced steatosis in patients infected with HCV genotype 1. Hepatology 48:28–37
Poon RT, Ng IO, Lau C, Yu WC, Yang ZF, Fan ST, Wong J (2002) Tumor microvessel density as a predictor of recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. J Clin Oncol 20:1775–1785
Stefan N, Hennige AM, Staiger H, Machann J, Schick F, Schleicher E, Fritsche A, Häring HU (2007) High circulating retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with elevated liver fat but not with total, subcutaneous, visceral, or intramyocellular fat in humans. Diabetes Care 30:1173–1178
Sun FX, Tang ZY, Lui KD, Ye SL, Xue Q, Gao DM, Ma ZC (1996) Establishment of a metastatic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice via orthotopic implantation of histologically intact tissues. Int J Cancer 66:239–243
Sun HC, Zhang W, Qin LX, Zhang BH, Ye QH, Wang L, Ren N, Zhuang PY, Zhu XD, Fan J, Tang ZY (2007) Positive serum hepatitis B e antigen is associated with higher risk of early recurrence and poorer survival in patients after curative resection of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 47:684–690
Tang ZY (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma surgery–review of the past and prospects for the 21st century. J Surg Oncol 91:95–96
Tian J, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Lin ZY, Chen J, Xue Q (1999) New human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line with highly metastatic potential (MHCC97) and its expression of the factors associated with metastasis. Br J Cancer 81:814–821
Van Dam RM, Hu FB (2007) Lipocalins and insulin resistance: etiological role of retinol-binding protein 4 and lipocalin-2? Clin Chem 53:5–7
Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Chan AT, Ng K, Chan JA, Wu K, Pollak MN, Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS (2009) Insulin, the insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Ocol 27:176–185
Yagmur E, Weiskirchen R, Gressner AM, Trautwein C, Tacke F (2007) Insulin resistance in liver cirrhosis is not associated with circulating retinol-binding protein 4. Diabetes Care 30:1168–1172
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L, Kahn BB (2005) Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436:356–362
Yao-Borengasser A, Varma V, Bodles AM, Rasouli N, Phanavanh B, Lee MJ, Starks T, Kern LM, Spencer HJ 3rd, Rashidi AA, McGehee RE Jr, Fried SK, Kern PA (2007) Retinol binding protein 4 expression in humans: relationship to insulin resistance, inflammation, and response to pioglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2590–2597
Zhu XD, Zhang JB, Zhuang PY, Zhu HG, Zhang W, **ong YQ, Wu WZ, Wang L, Tang ZY, Sun HC (2008) High expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in peritumoral liver tissue is associated with poor survival after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:2707–2716
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly supported by National Natural Science Funds of China (No. 30973499); National Natural Science Funds of China (No. 30801102); National S&T Major Project (No. 2008ZX10002-026); Dawn Program of Shanghai Education Commission (No. 07SG04).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
D.-D. Wang, Y.-M. Zhao, G. Ren, F. Wang, and Z.-G. **a contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2010_927_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. S1 In training cohort, Stratified survival curve were drawn according to absence or presence of liver cirrhosis (A-D) and TNM stage (E-H) to further investigate the prognostic value of serum RBP4 in HCC patients (TIFF 1048 kb)
432_2010_927_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. S2 With the cutoff used in training cohort, prognostic significance of serum RBP4 level for OS (A) and DFS (B) were confirmed in the validation cohort (TIFF 262 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, DD., Zhao, YM., Wang, L. et al. Preoperative serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 651–658 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0927-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0927-3