Abstract
Main conclusion
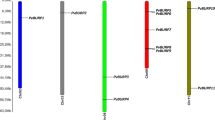
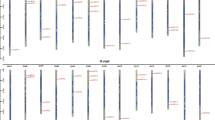
Genome-wide identification reveals 55 PvuGRAS genes belonging to 16 subfamilies and their gene structures and evolutionary relationships were characterized. Expression analyses highlight their prominence in plant growth, development and abiotic stress responses.
Abstract
GRAS proteins comprise a plant-specific transcription factor family involved in multiple growth regulatory pathways and environmental cues including abiotic/biotic stresses. Despite its crucial importance, characterization of this gene family is still elusive in common bean. A systematic genome-wide scan identified 55 PvuGRAS genes unevenly anchored to the 11 common bean chromosomes. Segmental duplication appeared to be the key driving force behind expansion of this gene family that underwent purifying selection during evolution. Computational investigation unraveled their intronless organization and identified similar motif composition within the same subfamily. Phylogenetic analyses clustered the PvuGRAS proteins into 16 phylogenetic clades and established extensive orthologous relationships with Arabidopsis and rice. Analysis of the upstream promoter region uncovered cis-elements responsive to growth, development, and abiotic stresses that may account for their differential expression. The identified SSRs could serve as putative molecular markers facilitating future breeding programs. 37 PvuGRAS transcripts were post-transcriptionally regulated by different miRNA families, miR171 being the major player preferentially targeting members of the HAM subfamily. Global expression profile based on RNA-seq data indicates a clade specific expression pattern in various tissues and developmental stages. Additionally, nine PvuGRAS genes were chosen for further qPCR analyses under drought, salt, and cold stress suggesting their involvement in acclimation to environmental stimuli. Combined, the present results significantly contribute to the current understanding of the complexity and biological function of the PvuGRAS gene family. The resources generated will provide a solid foundation in future endeavors for genetic improvement in common bean.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- TFBS:
-
Transcription factor binding site
References
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Bolle C (2004) The role of GRAS proteins in plant signal transduction and development. Planta 218:683–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1203-z
Bolle C (2016) Structure and evolution of plant GRAS family proteins. In: Gonzalez DH (ed) Plant transcription factors. Evolutionary, structural and functional aspects. Academic Press, New York, pp 153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800854-6.00010-5
Bolle C, Koncz C, Chua NH (2000) PAT1, a new member of the GRAS family, is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction. Genes Dev 14:1269–1278. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.14.10.1269
Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 252:55–128. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024146710611
Cenci A, Rouard M (2017) Evolutionary analyses of GRAS transcription factors in angiosperms. Front Plant Sci 8:273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00273
Chen K, Li H, Chen Y, Zheng Q, Li B, Li Z (2015) TaSCL14, a novel wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) GRAS gene, regulates plant growth, photosynthesis, tolerance to photooxidative stress, and senescence. J Genet Genom 42:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2014.11.002
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, **a R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Cui H (2012) Killing two birds with one stone: transcriptional regulators coordinate development and stress responses in plants. Plant Signal Behav 7:701–703. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.20283
Cui H, Levesque MP, Vernoux T, Jung JW, Paquette AJ, Gallagher KL, Wang JY, Blilou I, Scheres B, Benfey PN (2007) An evolutionarily conserved mechanism delimiting SHR movement defines a single layer of endodermis in plants. Science 316:421–425. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1139531
Dai X, Zhao PX (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155-159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr319
David-Schwartz R, Borovsky Y, Zemach H, Paran I (2013) CaHAM is autoregulated and regulates CaSTM expression and is required for shoot apical meristem organization in pepper. Plant Sci 203:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.12.011
Delaux PM, Radhakrishnan GV, Jayaraman D, Cheema J, Malbreil M, Volkening JD, Sekimoto H, Nishiyama T, Melkonian M, Pokorny L, Rothfels CJ (2015) Algal ancestor of land plants was preadapted for symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:13390–13395. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515426112
Di Laurenzio L, Wysocka-Diller J, Malamy JE, Pysh L, Helariutta Y, Freshour G, Hahn MG, Feldmann KA, Benfey PN (1996) The SCARECROW gene regulates an asymmetric cell division that is essential for generating the radial organization of the Arabidopsis root. Cell 86:423–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80115-4
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195
Fan S, Zhang D, Gao C, Zhao M, Wu H, Li Y, Shen Y, Han M (2017) Identification, classification, and expression analysis of GRAS gene family in Malus domestica. Front Physiol 8:253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00253
Fode B, Siemsen T, Thurow C, Weigel R, Gatz C (2008) The Arabidopsis GRAS protein SCL14 interacts with class II TGA transcription factors and is essential for the activation of stress-inducible promoters. Plant Cell 20:3122–3135. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058974
Gao TW, Zhang WW, Song AP, An C, **n JJ, Jiang JF, Guan ZY, Chen FD, Chen SM (2018) Phylogenetic and transcriptional analysis of chrysanthemum GRAS transcription factors. Biol Plant 62:711–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0816-1
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Springer protocols handbooks. Humana Press, pp 571–607. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-890-0:571
Griffiths J, Murase K, Rieu I, Zentella R, Zhang ZL, Powers SJ, Gong F, Phillips AL, Hedden P, Sun TP, Thomas SG (2006) Genetic characterization and functional analysis of the GID1 gibberellin receptors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:3399–3414. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.047415
Grimplet J, Agudelo-Romero P, Teixeira RT, Martinez-Zapater JM, Fortes AM (2016) Structural and functional analysis of the GRAS gene family in grapevine indicates a role of GRAS proteins in the control of development and stress responses. Front Plant Sci 7:353. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00353
Grosche C, Genau AC, Rensing SA (2018) Evolution of the symbiosis-specific gras regulatory network in bryophytes. Front Plant Sci 9:1621. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01621
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC (2007) GSDS: a gene structure display server. Hereditas 29:1023–1026. https://doi.org/10.1360/yc-007-1023
Guo Y, Wu H, Li X, Li Q, Zhao X, Duan X, An Y, Lv W, An H (2017) Identification and expression of GRAS family genes in maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 12:e0185418. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185418
Guo P, Wen J, Yang J, Ke Y, Wang M, Liu M, Ran F, Wu Y, Li P, Li J, Du H (2019) Genome-wide survey and expression analyses of the GRAS gene family in Brassica napus reveals their roles in root development and stress response. Planta 250:1051–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03199-y
Hakoshima T (2018) Structural basis of the specific interactions of GRAS family proteins. FEBS Lett 592:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12987
Heck C, Kuhn H, Heidt S, Walter S, Rieger N, Requena N (2016) Symbiotic fungi control plant root cortex development through the novel GRAS transcription factor MIG1. Curr Biol 226(20):2770–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.07.059
Helariutta Y, Fukaki H, Wysocka-Diller J, Nakajima K, Jung J, Sena G, Hauser MT, Benfey PN (2000) The SHORT-ROOT gene controls radial patterning of the Arabidopsis root through radial signaling. Cell 101:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80865-X
Hirsch S, Oldroyd GE (2009) GRAS-domain transcription factors that regulate plant development. Plant Signal Behav 4:698–700. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.4.8.9176
Hirsch S, Kim J, Muñoz A, Heckmann AB, Downie JA, Oldroyd GE (2009) GRAS proteins form a DNA binding complex to induce gene expression during nodulation signaling in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 21:545–557. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064501
Hou X, Lee LY, **a K, Yan Y, Yu H (2010) DELLAs modulate jasmonate signaling via competitive binding to JAZs. Dev Cell 19:884–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.024
Huang W, **an Z, Kang X, Tang N, Li Z (2015) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of GRAS gene family in tomato. BMC Plant Biol 15:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0590-6
Huang W, Peng S, **an Z, Lin D, Hu G, Yang L, Ren M, Li Z (2017) Overexpression of a tomato miR171 target gene SlGRAS24 impacts multiple agronomical traits via regulating gibberellin and auxin homeostasis. Plant Biotechnol J 15:472–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12646
Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Sato Y, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2002) The gibberellin signaling pathway is regulated by the appearance and disappearance of SLENDER RICE1 in nuclei. Plant Cell 14:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010319
Kaló P, Gleason C, Edwards A, Marsh J, Mitra RM, Hirsch S, Jakab J, Sims S, Long SR, Rogers J, Kiss GB (2005) Nodulation signaling in legumes requires NSP2, a member of the GRAS family of transcriptional regulators. Science 308:1786–1789. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1110951
Koizumi K, Gallagher KL (2013) Identification of SHRUBBY, a SHORT-ROOT and SCARECROW interacting protein that controls root growth and radial patterning. Development 140:1292–12300. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.090761
Kundu A, Patel A, Pal A (2013) Defining reference genes for qPCR normalization to study biotic and abiotic stress responses in Vigna mungo. Plant Cell Rep 32(10):1647–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1478-2
Kundu A, Paul S, Dey A, Pal A (2017) High throughput sequencing reveals modulation of microRNAs in Vigna mungo upon Mungbean Yellow Mosaic India Virus inoculation highlighting stress regulation. Plant Sci 257:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.01.016
Kundu A, Singh PK, Dey A et al (2019) Complex molecular mechanisms underlying MYMIV-resistance in Vigna mungo revealed by comparative transcriptome profiling. Sci Rep 9:8858. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45383-w
Lee MH, Kim B, Song SK, Heo JO, Yu NI, Lee SA, Kim M, Kim DG, Sohn SO, Lim CE, Chang KS (2008) Large-scale analysis of the GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 67:659–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9345-1
Lee TH, Tang H, Wang X, Paterson AH (2013) PGDD: a database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D1152–D1158. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1104
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic I, Bork P (2019) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W256–W259. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz239
Li L, Stoeckert CJ, Roos DS (2003a) OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res 13:2178–2189. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1224503
Li X, Qian Q, Fu Z, Wang Y, **ong G, Zeng D, Wang X, Liu X, Teng S, Hiroshi F, Yuan M (2003b) Control of tillering in rice. Nature 422:618–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01518
Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Shi C (2010) Identification and characterization of dwarf 62, a loss-of-function mutation in DLT/OsGRAS-32 affecting gibberellin metabolism in rice. Planta 232:1383–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1263-1
Liu X, Widmer A (2014) Genome-wide comparative analysis of the GRAS gene family in Populus, Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:1129–1145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0721-5
Liu B, Sun Y, Xue J, Jia X, Li R (2018) Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of GRAS gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). PeerJ 6:e4796. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4796
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu J, Wang T, Xu Z, Sun L, Zhang Q (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Prunus mume. Mol Genet Genom 290:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0918-1
Ma HS, Liang D, Shuai P, **a XL, Yin WL (2010) The salt-and drought-inducible poplar GRAS protein SCL7 confers salt and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 61:4011–4019. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq217
Ma W, Noble WS, Bailey TL (2014) Motif-based analysis of large nucleotide data sets using MEME-ChIP. Nat Protoc 9(6):1428–1450. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.083
Morohashi K, Minami M, Takase H, Hotta Y, Hiratsuka K (2003) Isolation and characterization of a novel GRAS gene that regulates meiosis-associated gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:20865–20873. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301712200
Niu Y, Zhao T, Xu X, Li J (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of GRAS transcription factors in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). PeerJ 5:e3955. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3955
Peng J, Carol P, Richards DE, King KE, Cowling RJ, Murphy GP, Harberd NP (1997) The Arabidopsis GAI gene defines a signaling pathway that negatively regulates gibberellin responses. Genes Dev 11:3194–3205. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.23.3194
Pysh LD, Wysocka Diller JW, Camilleri C, Bouchez D, Benfey PN (1999) The GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis: sequence characterization and basic expression analysis of the SCARECROW-LIKE genes. Plant J 18:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00431.x
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Shu S, Song Q, Chavarro C, Torres-Torres M (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46:707–713. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3008
Schumacher K, Schmitt T, Rossberg M, Schmitz G, Theres K (1999) The Lateral suppressor (Ls) gene of tomato encodes a new member of the VHIID protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.1.290
Shan Z, Luo X, Wu M, Wei L, Fan Z, Zhu Y (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression of GRAS gene family members in cassava. BMC Plant Biol 20:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2242-8
Sidhu NS, Pruthi G, Singh S, Bishnoi R, Singla D (2020) Genome-wide identification and analysis of GRAS transcription factors in the bottle gourd genome. Sci Rep 10:14338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71240-2
Song XM, Liu TK, Duan WK, Ma QH, Ren J, Wang Z, Li Y, Hou XL (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Genomics 103:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.12.004
Song L, Tao L, Cui H, Ling L, Guo C (2017) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the GRAS family proteins in Medicago truncatula. Acta Physiol Plant 39:93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2393-x
Stuurman J, Jäggi F, Kuhlemeier C (2002) Shoot meristem maintenance is controlled by a GRAS-gene mediated signal from differentiating cells. Genes Dev 16:2213–2218. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.230702
Sun TP, Gubler F (2004) Molecular mechanism of gibberellin signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:197–223. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141753
Sun X, Xue B, Jones WT, Rikkerink E, Dunker AK, Uversky VN (2011) A functionally required unfoldome from the plant kingdom: intrinsically disordered N-terminal domains of GRAS proteins are involved in molecular recognition during plant development. Plant Mol Biol 77(3):205–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9803-z
Sun X, Rikkerink EH, Jones WT, Uversky VN (2013) Multifarious roles of intrinsic disorder in proteins illustrate its broad impact on plant biology. Plant Cell 25:38–55. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.106062
Suyama M, Torrents D, Bork P (2006) PAL2NAL: robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W609–W612. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl315
Tian C, Wan P, Sun S, Li J, Chen M (2004) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 54:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000038256.89809.57
To VT, Shi Q, Zhang Y, Shi J, Shen C, Zhang D, Cai W (2020) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Genes 11:553. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050553
Torres-Galea P, Hirtreiter B, Bolle C (2013) Two GRAS proteins, SCARECROW-LIKE21 and PHYTOCHROME A SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION1, function cooperatively in phytochrome A signal transduction. Plant Physiol 161:291–304. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.206607
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: toward genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wang Y, Shi S, Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Yang J, Tang X (2016) Genome-wide identification and characterization of GRAS transcription factors in sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). PeerJ 31(4):e2388. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2388
Wang YX, Liu ZW, Wu ZJ, Li H, Wang WL, Cui X, Zhuang J (2018) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of GRAS family transcription factors in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci Rep 8:3949. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22275-z
Wang L, Ding X, Gao Y, Yang S (2020) Genome-wide identification and characterization of GRAS genes in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Plant Biol 20:415. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02636-5
Xu K, Chen SJ, Li TF, Ma XS, Liang XH, Ding XF et al (2015) OsGRAS23, a rice GRAS transcription factor gene, is involved in drought stress response through regulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 15:141. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0532-3
Xu W, Chen Z, Ahmed N, Han B, Cui Q, Liu A (2016) Genome-wide identification, evolutionary analysis, and stress responses of the GRAS gene family in castor beans. Int J Mol Sci 17:1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071004
Zhang ZL, Ogawa M, Fleet CM, Zentella R, Hu J, Heo JO, Lim J, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S, Sun TP (2011) Scarecrow-like 3 promotes gibberellin signaling by antagonizing master growth repressor DELLA in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2160–2165. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1012232108
Zhang D, Iyer LM, Aravind L (2012) Bacterial GRAS domain proteins throw new light on gibberellic acid response mechanisms. Bioinformatics 28:2407–2411. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts464
Zhang H, Cao Y, Shang C, Li J, Wang J, Wu Z, Ma L, Qi T, Fu C, Bai Z, Hu B (2017) Genome-wide characterization of GRAS family genes in Medicago truncatula reveals their evolutionary dynamics and functional diversification. PLoS ONE 12:e0185439. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185439
Zhang B, Liu J, Yang ZE, Chen EY, Zhang CJ, Zhang XY, Li FG (2018) Genome-wide analysis of GRAS transcription factor gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genom 19:348. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4722-x
Zhang H, Mi L, Xu L, Yu C, Li C, Chen C (2019) Genome-wide identification, characterization, interaction network and expression profile of GRAS gene family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Sci Rep 9:2156. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38185-z
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Principal, Ramakishna Mission Vivekananda Centenary College, Rahara, Kolkata (India) for providing necessary infrastructure. The financial requirements were borne by the authors and no additional funding was received from any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: AK, PL, and SB; performed the experiments: PL, SB, AC, and AK; analyzed the data: PL, SB, AC, and AK; wrote the paper: SB and AK; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laskar, P., Bhattacharya, S., Chaudhuri, A. et al. Exploring the GRAS gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): characterization, evolutionary relationships, and expression analyses in response to abiotic stresses. Planta 254, 84 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03725-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03725-x