Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to examine the impact of supra-maximal interval training (SMIT) and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on cardiac auto-regulation response.
Methods
Physically active young adults volunteered to participate in the study with a randomized cross-over counterbalanced design (N = 12). HIIT sessions consisted of 20 bouts of 10 s of exercise followed by 50 s of recovery, totaling 20 min at two different intensities; “all-out (SMIT)” vs. “115–130% Wmax (HIIT)”. The cardiac auto-regulation included heart rate variability (HRV) and vascular function. HRV and vascular function were measured at baseline and five different time points after acute exercise.
Results
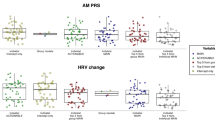
The SMIT was higher in workload (31%), peak heart rate (28%), and rate of perceived exertion (40%) compared with HIIT (all p < 0.001). The R-R interval, NN50, and pNN50 measured until 60 min after acute exercise was higher in the HIIT compared with SMIT (all p < 0.05). The SMIT elicited a greater shift in ln LF/HF ratio immediately after acute exercise (3802%, p < 0.01) and induced a decrease in bilateral ba-PWV at the time point 5 min after acute exercise, persisting until 65 min after (p < 0.05). Yet, HIIT showed no change over time in the frequency domain of HRV and blood vascular tone after cessation of acute exercise.
Conclusion
Our findings confirmed that SMIT is a more potent modulator of the autonomic nervous system compared with HIIT. Further study is needed to monitor through complete recovery to baseline, to understand acute cardiac auto-regulation response after cessation of various exercise intensities identical interval training protocol.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data that support the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HIIT:
-
High-intensity interval training
- SMIT:
-
Supra-maximal intensity interval training
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- Kp:
-
Kiloponds
- ECG:
-
Electro-cardiograph
- SDNN:
-
Standard deviation of the NN intervals
- rMSSD:
-
Root mean square of the successive R-R interval differences
- NN50:
-
Number of pairs of successive normal to normal (NN) intervals that differ by more than 50 ms
- pNN50:
-
Proportion of NN50 divided by the total number of NN intervals
- LF:
-
Low-frequency
- HF:
-
High-frequency
- ba-PWV:
-
Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- RPE:
-
Rating of perceived exertion
References
Abreu RM, Rehder-Santos P, Simões RP, Catai AM (2019) Can high-intensity interval training change cardiac autonomic control? A systematic review. Braz J Phys Ther 23(4):279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjpt.2018.09.010
Alansare A, Alford K, Lee S, Church T, Jung HC (2018) The effects of high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on heart rate variability in physically inactive adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071508
Batacan RB Jr, Duncan MJ, Dalbo VJ, Tucker PS, Fenning AS (2017) Effects of high-intensity interval training on cardiometabolic health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention studies. Br J Sports Med 51(6):494–503. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-095841
Besnier F, Labrunée M, Richard L, Faggianelli F, Kerros H, Soukarié L, Bousquet M, Garcia JL, Pathak A, Gales C, Guiraud T, Sénard JM (2019) Short-term effects of a 3-week interval training program on heart rate variability in chronic heart failure. A randomised controlled trial. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 62(5):321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rehab.2019.06.013
Boff W, da Silva AM, Farinha JB, Rodrigues-Krause J, Reischak-Oliveira A, Tschiedel B, Puñales M, Bertoluci MC (2019) Superior effects of high-intensity interval vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on endothelial function and cardiorespiratory fitness in patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Front Physiol 10:450. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00450
Brockmann L, Hunt KJ (2023) Heart rate variability changes with respect to time and exercise intensity during heart-rate-controlled steady-state treadmill running. Sci Rep 13(1):8515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35717-0
Buchheit M, Laursen PB (2013) High-intensity interval training, solutions to the programming puzzle: part I: cardiopulmonary emphasis. Sports Med 43(5):313–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0029-x
Campbell WW, Kraus WE, Powell KE, Haskell WL, Janz KF, Jakicic JM, Troiano RP, Sprow K, Torres A, Piercy KL, Bartlett DB (2019) High-intensity interval training for cardiometabolic disease prevention. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51(6):1220–1226. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000001934
Cassidy S, Thoma C, Hallsworth K, Parikh J, Hollingsworth KG, Taylor R, Jakovljevic DG, Trenell MI (2016) High intensity intermittent exercise improves cardiac structure and function and reduces liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 59(1):56–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3741-2
Chen CY, Bonham AC (2010) Postexercise hypotension: central mechanisms. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 38(3):122–127. https://doi.org/10.1097/JES.0b013e3181e372b5
Chorepsima S, Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris A, Moyssakis I, Protogerou A, Kokkinos A, Sfikakis PP, Tentolouris N (2017) Pulse wave velocity and cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord 17(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-017-0178-2
Cicioni-Kolsky D, Lorenzen C, Williams MD, Kemp JG (2013) Endurance and sprint benefits of high-intensity and supramaximal interval training. Eur J Sport Sci 13(3):304–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2011.606844
Cipryan L (2018) The effect of fitness level on cardiac autonomic regulation, IL-6, total antioxidant capacity, and muscle damage responses to a single bout of high-intensity interval training. J Sport Health Sci 7(3):363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2016.11.001
Cipryan L, Vala R (2015) Cardiac autonomic regulation after continuous and intermittent maximal exercise interventions. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 55(5):495–505
Couto GK, Paula SM, Gomes-Santos IL, Negrão CE, Rossoni LV (2018) Exercise training induces eNOS coupling and restores relaxation in coronary arteries of heart failure rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314(4):H878-h887. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00624.2017
Dawson EA, Cable NT, Green DJ, Thijssen DHJ (2018) Do acute effects of exercise on vascular function predict adaptation to training? Eur J Appl Physiol 118(3):523–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3724-8
Dulsky CC, Renzi CP, McLaurin NN, Wang T, Chen LS, Walters MR, Tanaka AH (2022) Effects of supra high-intensity interval training in police officers. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0022-4707.22.14396-3
Dutheil F, Chambres P, Hufnagel C, Auxiette C, Chausse P, Ghozi R, Paugam G, Boudet G, Khalfa N, Naughton G, Chamoux A, Mermillod M, Bertrand PR (2015) ‘Do well b.’: design of WELL being monitoring systems. A study protocol for the application in autism. BMJ Open 5(2):e007716. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-007716
Eicher JD, Maresh CM, Tsongalis GJ, Thompson PD, Pescatello LS (2010) The additive blood pressure lowering effects of exercise intensity on post-exercise hypotension. Am Heart J 160(3):513–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2010.06.005
Goto C, Higashi Y, Kimura M, Noma K, Hara K, Nakagawa K, Kawamura M, Chayama K, Yoshizumi M, Nara I (2003) Effect of different intensities of exercise on endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans: role of endothelium-dependent nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Circulation 108(5):530–535. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Cir.0000080893.55729.28
Green DJ, Maiorana A, O’Driscoll G, Taylor R (2004) Effect of exercise training on endothelium-derived nitric oxide function in humans. J Physiol 561(Pt 1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.068197
Gripp F, Nava RC, Cassilhas RC, Esteves EA, Magalhães COD, Dias-Peixoto MF, de Castro MF, Amorim FT (2021) HIIT is superior than MICT on cardiometabolic health during training and detraining. Eur J Appl Physiol 121(1):159–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04502-6
Halliwill JR (2001) Mechanisms and clinical implications of post-exercise hypotension in humans. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 29(2):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003677-200104000-00005
Kenney MJ, Seals DR (1993) Postexercise hypotension. Key features, mechanisms, and clinical significance. Hypertension 22(5):653–664. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.22.5.653
Kranen SH, Oliveira RS, Bond B, Williams CA, Barker AR (2023) The effect of 4 weeks of high-intensity interval training and 2 weeks of detraining on cardiovascular disease risk factors in male adolescents. Exp Physiol 108(4):595–606. https://doi.org/10.1113/ep090340
Lock M, Yousef I, McFadden B, Mansoor H, Townsend N (2023) Cardiorespiratory fitness and performance adaptations to high-intensity interval training: are there differences between men and women? A systematic review with meta-analyses. Sports Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-023-01914-0
MacInnis MJ, Gibala MJ (2017) Physiological adaptations to interval training and the role of exercise intensity. J Physiol 595(9):2915–2930. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp273196
Mäki-Petäjä KM, Barrett SM, Evans SV, Cheriyan J, McEniery CM, Wilkinson IB (2016) The role of the autonomic nervous system in the regulation of aortic stiffness. Hypertension 68(5):1290–1297. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.116.08035
Michael S, Graham KS, Davis GMO (2017) Cardiac autonomic responses during exercise and post-exercise recovery using heart rate variability and systolic time intervals-a review. Front Physiol 8:301. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00301
Montoye AHK, Clevenger KA, Pfeiffer KA, Nelson MB, Bock JM, Imboden MT, Kaminsky LA (2020) Development of cut-points for determining activity intensity from a wrist-worn ActiGraph accelerometer in free-living adults. J Sports Sci 38(22):2569–2578. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2020.1794244
Naylor LH, Davis EA, Kalic RJ, Paramalingam N, Abraham MB, Jones TW, Green DJ (2016) Exercise training improves vascular function in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Physiol Rep 4(4). https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12713
O’Brien MW, Johns JA, Robinson SA, Bungay A, Mekary S, Kimmerly DS (2020) Impact of High-Intensity Interval Training, Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training, and Resistance Training on Endothelial Function in Older Adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 52(5):1057–1067. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000002226
Pedralli ML, Marschner RA, Kollet DP, Neto SG, Eibel B, Tanaka H, Lehnen AM (2020) Different exercise training modalities produce similar endothelial function improvements in individuals with prehypertension or hypertension: a randomized clinical trial Exercise, endothelium and blood pressure. Sci Rep 10(1):7628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64365-x
Poon ET, Siu PM, Wongpipit W, Gibala M, Wong SH (2022) Alternating high-intensity interval training and continuous training is efficacious in improving cardiometabolic health in obese middle-aged men. J Exerc Sci Fit 20(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesf.2021.11.003
Qiu S, Cai X, Yin H, Sun Z, Zügel M, Steinacker JM, Schumann U (2018) Exercise training and endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(1):64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0711-2
Romero SA, Minson CT, Halliwill JR (2017) The cardiovascular system after exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 122(4):925–932. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00802.2016
Rosenblat MA, Perrotta AS, Thomas SG (2020) Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Sprint Interval Training on Time-Trial Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med 50(6):1145–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-020-01264-1
Ross LM, Porter RR, Durstine JL (2016) High-intensity interval training (HIIT) for patients with chronic diseases. J Sport Health Sci 5(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2016.04.005
Santana HA, Moreira SR, Asano RY, Sales MM, Córdova C, Campbell CS, Espindola FS, Sposito AC, Nóbrega OT, Simões HG (2013) Exercise intensity modulates nitric oxide and blood pressure responses in hypertensive older women. Aging Clin Exp Res 25(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0017-x
Saz-Lara A, Cavero-Redondo I, Álvarez-Bueno C, Notario-Pacheco B, Ruiz-Grao MC, Martínez-Vizcaíno V (2021) The Acute Effect of exercise on arterial stiffness in healthy subjects: a meta-analysis. J Clin Med 10(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020291
Seo MW, Lee JM, Jung HC, Jung SW, Song JK (2019) Effects of various work-to-rest ratios during high-intensity interval training on athletic performance in adolescents. Int J Sports Med 40(8):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0927-6884
Sessa F, Anna V, Messina G, Cibelli G, Monda V, Marsala G, Ruberto M, Biondi A, Cascio O, Bertozzi G, Pisanelli D, Maglietta F, Messina A, Mollica MP, Salerno M (2018) Heart rate variability as predictive factor for sudden cardiac death. Aging (Albany NY) 10(2):166–177. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101386
Tanaka LY, Bechara LR, dos Santos AM, Jordão CP, de Sousa LG, Bartholomeu T, Ventura LI, Laurindo FR, Ramires PR (2015) Exercise improves endothelial function: a local analysis of production of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species. Nitric Oxide 45:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2015.01.003
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 93(5):1043–1065
Thayer JF, Yamamoto SS, Brosschot JF (2010) The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Int J Cardiol 141(2):122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.09.543
Wewege MA, Ahn D, Yu J, Liou K, Keech A (2018) High-intensity interval training for patients with cardiovascular disease-is it safe? A systematic review. J Am Heart Assoc 7(21):e009305. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.118.009305
Acknowledgements
We would like to thanks all the participants in the research project.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020S1A5B5A17089215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M-WS, and HCJ conceived and designed the experiments. M-WS and HCJ performed the experiments. M-WS, and HCJ analyzed and interpreted the data. M-WS, SL, and HCJ contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data and wrote the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to declare for the present study.
Additional information
Communicated by Westerterp/Westerblad.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, MW., Lee, S. & Jung, H.C. Impact of supra-maximal interval training vs. high-intensity interval training on cardiac auto-regulation response in physically active adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 124, 1771–1780 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05402-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05402-1