Abstract
Aim
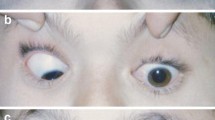
To compare the effectiveness of inferior oblique retroequatorial myopexy and inferior oblique myectomy in correction of inferior oblique overaction (IOOA).
Patients and methods
This was a pilot study study including forty patients with primary IOOA of all grades, with or without primary position horizontal deviations. Patients were randomized to have either IO retroequatorial myopexy, group A, or IO myectomy, group B. Success was defined as elimination of the IOOA at 6 months postoperatively. Secondary outcome measures included residual or recurrent elevation in adduction, development of postoperative hypotropia in adduction, postoperative contralateral IOOA, major intraoperative complications, and reversibility of the procedure.
Results
At 6 months postoperative, the success rate was higher in the myectomy group (76%) than in the myopexy group (58%); however, this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.1). The incidence of residual IOOA in myopexy group was significantly higher in patients with higher preoperative grades of IOOA (P ˂ 0.001). While this difference was not statistically significant among patients in myectomy group (P = 0.09). Collapse of V-pattern was acheived in nine (69%) patients in myopexy group compared with 8 (57%) in myectomy group with a statistically significant difference (P ≤ 0.001). No patients in myopexy group developed postoperative hypotropia in adduction or postoperative contralateral IOOA, compared with eight (22%) patients of myectomy group (P = 0.002) who developed postoperative hypotropia and two (66.6%) patients with unilateral IOOA who developed contralateral IOOA in myectomy group (P ˂ 0.001). No intraoperative complications were encountered in either group. postoperative.
Conclusions
Retroequatorial myopexy of the inferior oblique is as effective as inferior oblique myectomy in eliminating lower and moderate grades of primary IOOA; however, it is more effective in collapsing V-pattern associated with IOOA, and is not associated with postoperative hypotropia or contralateral IOOA after unilateral surgery. It can be used as a safe, reversible alternative to myectomy; however, it is not suitable for high grades of IOOA.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IOOA:
-
Inferior oblique overaction
- IOAT:
-
Inferior oblique anterior transposition
References
Choi DG, Chang BL (1992) Electron microscopic study on overacting inferior oblique muscles. Korean J Ophthalmol 6:69–75
Caldeira JA (2004) Some clinical characteristics of V-pattern exotropia and surgical outcome after bilateral recession of the inferior oblique muscle: a retrospective study of 22 consecutive patients and a comparison with V-pattern esotropia. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q 19:139–150
Modi NC, Jones DH (2008) Strabismus: background and surgical techniques. J Perioper Pract 18:532–535
Cho YA, Kim JH, Kim S (2006) Antielevation syndrome after unilateral anteriorization of the inferior oblique muscle. Korean J Ophthalmol 20:118–123
Duane A (1906) Tenotomy of inferior oblique and consideration of the conditions that may call for the operation. Br Med J 2:1867
Costenbader FD, Kertesz E (1946) Relaxing procedures of the inferior oblique; a comparative study. Am J Ophthalmol 57:276–280
Elliott RL, Nankin SJ (1981) Anterior transposition of the inferior oblique. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 18:35–38
Del Monte MA, Parks MM (1983) Denervation and extirpation of the inferior oblique: an improved weakening procedure for marked overaction. Ophthalmology 90:1178–1185
Parks MM (1985) Inferior oblique weakening procedures. Int Ophthalmol Clin 25(107):117
Cho YA (1987) Treatment of marked overaction of inferior oblique: denervation and extirpation of inferior oblique. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 28(381):386
Wright KW (2007) Inferior oblique muscle weakening procedures . In Color atlas of strabismus surgery ( strategies and techniques), edited by Wright KW . Springer Science and Business Media, LLC,USA.: 17:166 , 170-176
White LW (1943) Recession of the inferior oblique muscle. Arch Ophthalmol 29:1033
White JW (1943) Surgery of the inferior oblique at or near the insertion. Am J Ophthalmol 26:586
White JW (1933) Paralysis of the superior rectus muscle. Trans Am Ophthamol Soc 31:551
Dunnington JH (1943) A discussion. In White, J.W. : Recession of the inferior oblique muscle. Arch Ophth 29:1033
Brown, HW (1950) Surgery of the oblique muscles. In Allen, J. H. (ed.) : Strabismus Ophthalmic Symposium. St. Louis, C. V. Mosby 401
Fink WH (1951) Oblique muscle surgery from the anatomic viewpoint. Am J Ophthalmol 34:261
Berens C, Cole HG, Chamichian S, Enos MV (1852) Retroplacement of the inferior oblique at its sceleral insertion. Am J Ophthalmol 35:217
Traboulsi EI, Sachdeva R, Rychwalski P, Marcotty A (2012) Comparison of inferior oblique myectomy to recession for the treatment of superior oblique palsy. JAAPOS. 16(1):e9
Mims JL 3rd, Wood RC (1989) Bilateral anterior transposition of the inferior obliques. Arch Ophthalmol 107:41–44
Ghazawy S, Reddy AR, Kipioti A, McShane P, Arora S, Bradbury JA (2007) Myectomy versus anterior transposition for inferior oblique overaction. J AAPOS 11(6):601–605
Merino P, Blanco I, Liaño PG (2016) Fat adherence syndrome following inferior oblique surgery: treatment and outcomes. Aust J Optom 9(4):240–245
Ganesh SC, Rao SG, Narendran K, Dhage AR (2019) Adherence syndrome following inferior oblique anteropositioning - a case report. Strabismus. Mar 27(1):11–15
Farvardin M, Nazarpoor S (2002) Anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle for treatment of superior oblique palsy. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 39:100–104
Bremer DL, Rogers L, Quick LD (1986) Primary-position hypotropia after anterior transposition of the inferior oblique. Arch Ophthalmol 104:229–232
Kushner BJ (1997) Restriction of elevation in abduction after inferior oblique anteriorization. J AAPOS 1:55–62
Santiago AP, Isenberg SJ, Apt L, Roh YB (1997) The effect of anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle on ocular torsion. J AAPOS 1:191–196
Awadein A, Gawdat G (2008) Bilateral inferior oblique myectomy for asymmetric primary inferior oblique overaction. J AAPOS 12:560–564
Sanjari MS, Shahraki K, Nekoozadeh S, Tabatabaee SM, Shahraki K, Aghdam KA (2014) Surgical treatments in inferior oblique muscle overaction. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 9(3):291–295
Stager D Jr, Dao LM, Felius J (2015) Uses of the inferior oblique muscle in strabismus surgery. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 22(3):292–297
Lee JE, Yang HK, Hwang JM (2016) Surgical outcomes of inferior oblique myectomy in unilateral congenital superior oblique palsy with or without trochlear nerve. PLoS One 11(7):e0156872. Published 2016 Jul 8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156872
Kushner BJ (2007) The inferior oblique muscle adherence syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 125(11):1510–1514. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.125.11.1510
Oteyza J, García de Oteyza G (2016) The second European meeting of young ophthalmologists VIDEO — inferior oblique fadenoperation: a new weakening technique Available at:https://www.healio.com/ophthalmology/retina-vitreous/news/online/%7Bcbd83439-a4b8-4137-a505-22b76d505593%7D/video--inferior-oblique-fadenoperation-a-new-weakening-technique (Accessed: 18 June 2018)
Doughty DD, Lenarson LW, Scott WE (1978) A graphic portrayal of versions. Perspect Ophthalmol 2:55–59
Wright KW, Hong P (2006) Anatomy and physiology of eye movements In Handbook of pediatric strabismus and Amblyopia, edited by Wright KW , Spiegel PH and Thompson LS .Springer Science and Business Media, Inc, USA.:2:45
Cuppers C (1976) The so-called “fadenoperation” (surgical correction by well defined changes in the arc of contact). In Fells, P. (ed.): Proceedings of the Second Congress of the International Strabismological Association. Marseilles, Diffusion Generale de Librarie. 395-400
Tomarchio S, Sabetti L, Tomarchio M, Berarducci A (2015) New surgical intervention for the weakening of the inferior oblique muscle: equatorial scleral anchor. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 52(1):58–60
Sabetti L, Tomarchio S, Piozzi E, Magli A (2017) Equatorial scleral anchor for the weakening of the inferior oblique muscle. Int J Ophthalmic Pathol 6(2)
Apt L, Call NB (1978) Inferior oblique muscle recession. Am J Ophthalmol 85:95–100
Stager DR (2001) Anatomy and surgery of the inferior oblique muscle: recent findings. J AAPOS 5:203–208
Stager DR (1997) The neurofibrovascular bundle of the inferior oblique muscle as the ancillary origin of that muscle. J AAPOS 1(4):216–225
Mostafa AM, Kassem RR (2018) Comparative study of unilateral versus bilateral inferior oblique recession/anteriorization in unilateral inferior oblique overaction. Eur J Ophthalmol 28(3):272–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study idea and design was conceived by Heba Metwally. Literature screening and selection were performed by Ameera Abdelhameed. Patients selection and follow-up were performed by Heba metwally, Manal Kasem, and Ameera Abdelhameed. Data extraction and statistical synthesis were performed by Manal Kasem. Preparation of the first draft of the manuscript was done by Ameera Gamal and reviewed by Heba Metwally and Manal Kasem. Final review of the manuscript was performed by Heba metwally and Manal Kasem. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript that was submitted for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The manuscript was accepted in part as an oral presentation at 5th Magrabi International congress Abu-Dhabi 26th–28th January 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasem, M., Metwally, H., El-adawy, I.T. et al. Retro-equatorial inferior oblique myopexy for treatment of inferior oblique overaction. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 258, 1991–1997 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-020-04742-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-020-04742-4