Abstract
Background
Understanding the pathophysiology of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) and identifying its clinical symptoms and associated risk factors are crucial for doctors in order to create effective prevention and therapeutic methods for this prevalent otolaryngologic emergency.
Methods
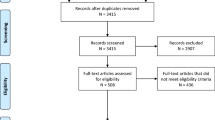
This study focuses on investigating the correlation between the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CAR) and SSNHL complicated by hypertension. In this study, 120 patients diagnosed with SSNHL were divided into groups with and without hypertension, and propensity score matching was used to compare and analyze the severity, type, prognosis, and CAR levels in SSNHL.
Results
The results showed that the SSNHL group with hypertension had significantly higher CAR levels, age, hearing curve abnormalities, and more severe hearing loss compared to the control group with isolated SSNHL. These differences were statistically significant (p < 0.001). Among different subtypes of SSNHL, CAR levels increased progressively with the advancement of the condition, and these differences were also statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In summary, in patients with SSNHL, those with hypertension had higher CAR levels than those without a history of hypertension, and they experienced more severe hearing loss. Moreover, there was a clear correlation between CAR levels and the extent of SSNHL, indicating that greater CAR levels in patients with SSNHL are connected to more severe hearing loss in various hearing patterns and perhaps indicative of a poorer prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current investigation are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Yamada S, Kita J, Shinmura D et al (2022) Update on findings about sudden sensorineural hearing loss and insight into its pathogenesis. J Clin Med 11(21):6387–6403
Plontke SK, Meisner C, Agrawal S et al (2022) Intratympanic corticosteroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7(7):CD008080
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai DB, Schwartz SR et al (2019) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 161(1_suppl):S1–S45
Alexander TH, Harris JP (2013) Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 34(9):1586–1589
Michel O (2011) The revised version of the german guidelines “sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss.” Laryngorhinootologie 90(5):290–293
Hung WC, Lin KY, Cheng PW et al (2021) Sudden deafness: a comparison between age groups. Int J Audiol 60(11):911–916
Lenkeit CP, Lofgren DH, Zappia J (2023) Cardiovascular risk factors and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case-control study. Otol Neurotol 44(2):121–125
Nagaoka J, Anjos MF, Takata TT et al (2010) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: evolution in the presence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemias. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 76(3):363–369
Quaranta N, De Ceglie V, D’Elia A (2016) Endothelial dysfunction in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review. Audiol Res 6(1):151–168
Shen Y, Zheng Z, **ao L et al (2021) Association of glycosylated hemoglobin A1c level with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective study. Front Endocrinol 763021(12):1–9
Marlow NM, Malaty J, Jo A et al (2017) Hearing impairment and undiagnosed disease: the potential role of clinical recommendations. J Speech Lang Hear Res 60(1):231–237
Karanfil M, Gayretli YK (2021) The association of aortic elasticity properties with novel inflammatory marker CRP/albumin ratio. Clin Exp Hypertens 43(8):780–787
Karabag Y, Cagdas M, Rencuzogullari I et al (2018) Relationship between C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and coronary artery disease severity in patients with stable angina pectoris. J Clin Lab Anal 32(7):e22457
Ocal R, Akin OF, Gulluev M et al (2020) Is the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio a prognostic and predictive factor in sudden hearing loss? Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 86(2):180–184
Ma X, Wang FY, Yu LS et al (2015) Guideline of diagnosis and treatment of sudden deafness (2015). Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 50(6):443–447
Kirbac A, Boke B (2021) Effects of primary arterial hypertension on cochlear function. Acta Otolaryngol 141(2):158–162
Wattamwar K, Qian ZJ, Otter J et al (2018) Association of cardiovascular comorbidities with hearing loss in the older old. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(7):623–629
Hara K, Okada M, Takagi D et al (2020) Association between hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes and prevalence of hearing impairment in Japan. Hypertens Res 43(9):963–968
Doyle AE (1991) Hypertension and vascular disease. Am J Hypertens 4(2 Pt 2):103S-106S
Matsunaga M, Yatsuya H, Iso H et al (2017) Similarities and differences between coronary heart disease and stroke in the associations with cardiovascular risk factors: the Japan collaborative cohort study. Atherosclerosis 261:124–130
Umesawa M, Sairenchi T, Haruyama Y et al (2019) Association between hypertension and hearing impairment in health check-ups among Japanese workers: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 9(4):e28392
Savoia C, Battistoni A, Calvez V et al (2017) Microvascular alterations in hypertension and vascular aging. Curr Hypertens Rev 13(1):16–23
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Pons H, Quiroz Y et al (2014) Autoimmunity in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol 10(1):56–62
Caillon A, Schiffrin EL (2016) Role of inflammation and immunity in hypertension: recent epidemiological, laboratory, and clinical evidence. Curr Hypertens Rep 18(3):21–30
Chen ZT, Guo Y, Zhang J et al (2023) The predictive utility of atherosclerosis-related risk factors as predictors of the prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in older adults. Acta Otolaryngol 143(4):296–300
Simoes J, Vlaminck S, Seica R et al (2023) Cardiovascular risk and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 133(1):15–24
Qin G, Tu J, Liu L et al (2016) Serum albumin and C-reactive protein/albumin ratio are useful biomarkers of Crohn’s disease activity. Med Sci Monit 22:4393–4400
Zhou T, Zhan J, Hong S et al (2015) Ratio of C-reactive protein/albumin is an inflammatory prognostic score for predicting overall survival of patients with small-cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 5:10481
Liu X, Sun X, Liu J et al (2015) Preoperative C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for gastric cancer. Transl Oncol 8(4):339–345
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N et al (2015) The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, a novel inflammation-based prognostic score, predicts outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 22(3):803–810
Reed NS, Huddle MG, Betz J et al (2019) Association of midlife hypertension with late-life hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 161(6):996–1003
Przewozny T, Gojska-Grymajlo A, Kwarciany M et al (2016) Hypertension is associated with dysfunction of both peripheral and central auditory system. J Hypertens 34(4):736–744
Bao M, Song Y, Cai J et al (2019) Blood pressure variability is associated with hearing and hearing loss: a population-based study in males. Int J Hypertens 2019:9891025
Agarwal S, Mishra A, Jagade M et al (2013) Effects of hypertension on hearing. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65(Suppl 3):614–618
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation (BK20201220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study’s concept and layout were proposed by Xu Zhang, Enze Wu and Yunlong Hu. The data collection and analysis were carried out by Xu Zhang, Aijuan Cao Qiuling Dang, Wentao Zhang and Yunlong Hu. The literature search was completed by Xu Zhang, Qiuling Dang, Yao Zhang, Maohua Wang and Bing Guan. The core manuscript was written by Xu Zhang, while editing and critical revision were carried out by Bing Guan, Enze Wu and Yunlong Hu. The study was managed by Bing Guan, Enze Wu and Yunlong Hu. The funding was obtained by Bing Guan and Yunlong Hu. The final draught of the paper has been approved by all authors once they have read it. The final manuscript was read and approved by all writers.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Ethics Review Committee of the Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital Affiliated to Yangzhou University (Approval No. 2023ky138) and conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Informed consent was taken before each procedure from the patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Cao, A., Dang, Q. et al. Study on the correlation of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio with sudden sensorineural hearing loss complicated by hypertension: a prospective study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08684-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08684-z