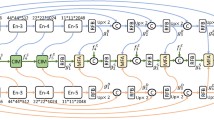
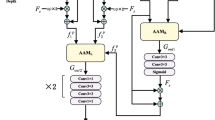
Abstract
Multi-modality images with complementary cues can significantly improve the performance of salient object detection (SOD) methods in challenging scenes. However, existing methods are specially designed for RGB-D or RGB-T SOD in general, thus it is necessary to bridge the gap to develop a unified SOD framework for processing various multi-modality images. To address this issue, we propose a unified multi-modality interaction fusion framework for RGB-D and RGB-T SOD, named UMINet. We deeply investigate the differences between appearance maps and complementary images and design an asymmetric backbone to extract appearance features and complementary cues. For the complementary cues branch, a complementary information aware module (CIAM) is proposed to perceive and enhance the weights of complementary modality features. We also propose a multi-modality difference fusion (MDF) block to fuse cross-modality features. This MDF block simultaneously considers the differences and consistency between the appearance features and complementary features. Furthermore, to promote the rich contextual dependencies and integrate cross-level multi-modality features, we design a mutual refinement decoder (MRD) to progressively predict salient results. The MRD consists of three reverse perception blocks (RPB) and five sub-decoders. Extensive experiments are provided to indicate the substantial improvement achieved by the proposed UMINet over the existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) models on six RGB-D SOD datasets and three RGB-T SOD datasets.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The data are available within this article. The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available at the following link: https://github.com/nffxgln/UMINet.
References
Borji, A., Cheng, M.-M., Jiang, H., Li, J.: Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(12), 5706–5722 (2015)
Min, X., Zhang, H.: Saliency detection with color contrast based on boundary information and neighbors. Vis. Comput. 31(3), 355–364 (2015)
Borji, A., Cheng, M.-M., Hou, Q., Jiang, H., Li, J.: Salient object detection: a survey. Comput. Visual Media 5(2), 117–150 (2019)
Xu, M., Liu, B., Fu, P., Li, J., Hu, Y.H.: Video saliency detection via graph clustering with motion energy and spatiotemporal objectness. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 21(11), 2790–2805 (2019)
Xu, M., Liu, B., Fu, P., Li, J., Hu, Y.H., Feng, S.: Video salient object detection via robust seeds extraction and multi-graphs manifold propagation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 30(7), 2191–2206 (2020)
Ye, L., Zhou, K., **yin, W., Gong, P.: A novel multi-graph framework for salient object detection. Vis. Comput. 35, 1683–1699 (2019)
Fan, D.P., Zhou, T., Ji, G. P., Zhou, Y., Chen, G., Fu, H., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Inf-net: automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2020)
Yu-Huan, W., Gao, S.-H., Mei, J., Jun, X., Fan, D.-P., Zhang, R.-G., Cheng, M.-M.: JCS: An explainable COVID-19 diagnosis system by joint classification and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 3113–3126 (2021)
Ma, C., Miao, Z., Zhang, X.P., Li, M.: A saliency prior context model for real-time object tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 19(11), 2415–2424 (2017)
Feng, W., Han, R., Guo, Q., Zhu, J., Wang, S.: Dynamic saliency-aware regularization for correlation filter-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(7), 3232–3245 (2019)
Gao, L., Liu, B., Fu, P., Xu, M., Li, J.: Visual tracking via dynamic saliency discriminative correlation filter. Appl. Intell., pp. 1–15 (2021)
Cong, R., Lei, J., Zhang, C., Huang, Q., Cao, X., Hou, C.: Saliency detection for stereoscopic images based on depth confidence analysis and multiple cues fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(6), 819–823 (2016)
Liang, Y., Liu, H., Ma, N.: A novel deep network and aggregation model for saliency detection. Vis. Comput. 36(9), 1883–1895 (2020)
Wang, X., Wang, W., Bi, H., Wang, K.: Reverse collaborative fusion model for co-saliency detection. Visual Comput. pp. 1–11 (2021)
Liu, Z., Duan, Q., Shi, S., Zhao, P.: Multi-level progressive parallel attention guided salient object detection for RGB-D images. Vis. Comput. 37, 529–540 (2021)
Shu, X., Xu, B. Zhang, L., Tang, J.: Multi-granularity anchor-contrastive representation learning for semi-supervised skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2022)
Shu, X., Yang, J., Yan, R., Song, Y.: Expansion-squeeze-excitation fusion network for elderly activity recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2022)
Xu, B., Shu, X., Song, Y.: X-invariant contrastive augmentation and representation learning for semi-supervised skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process (2022)
Zhang, J., Zou, X., Kuang, L.-D., Wang, J., Sherratt, R.S., **oafeng, Y., Cctsdb,: a more comprehensive traffic sign detection benchmark. Human-centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 12, 2022 (2021)
Li, P., Chen, Y.: Research into an image inpainting algorithm via multilevel attention progression mechanism. Math. Probl. Eng. 1–12, 2022 (2022)
Chen, Y., **a, R., Zou, K., Yang, K.: Ffti: Image inpainting algorithm via features fusion and two-steps inpainting. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 91, 103776 (2023)
**a, R., Chen, Y., Ren, B.: Improved anti-occlusion object tracking algorithm using unscented rauch-tung-striebel smoother and kernel correlation filter. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. (2022)
Zhang, J., Feng, W., Yuan, T., Wang, J., Sangaiah, A.K.: Scstcf: spatial-channel selection and temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. Appl. Soft Comput. 118, 108485 (2022)
Xu, M., Fu, P., Liu, B., Yin, H., Li, J.: A novel dynamic graph evolution network for salient object detection. Appl. Intell. (2021)
Li, T., Song, H., Zhang, K., Liu, Q.: Recurrent reverse attention guided residual learning for saliency object detection. Neurocomputing 389, 170–178 (2020)
Shuhan, Chen, **uli, Tan, Ben, Wang, and Xuelong, Hu: Reverse attention for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 234–250, 2018
Arridhana, Ciptadi, Tucker, Hermans, and James M, Rehg: An in depth view of saliency. Georgia Institute of Technology, 2013
David, Feng, Nick, Barnes, Shaodi, You, and Chris, McCarthy: Local background enclosure for rgb-d salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 2343–2350, 2016
Liangqiong, Q., He, S., Zhang, J., Tian, J., Tang, Y., Yang, Q.: Rgbd salient object detection via deep fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(5), 2274–2285 (2017)
Chen, H., Li, Y.: Three-stream attention-aware network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(6), 2825–2835 (2019)
Jie, Wang, Kechen, Song, Yanqi, Bao, Liming, Huang, and Yunhui, Yan: Cgfnet: Cross-guided fusion network for rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021
Zhengzheng, T., Ma, Y., Li, Z., Li, C., Jieming, X.: and Yongtao Liu. A large-scale dataset and benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, Rgbt salient object detection (2022)
Zhengzheng, Tu, Tian, **a, Chenglong, Li, Yijuan, Lu, and **, Tang: M3s-nir: Multi-modal multi-scale noise-insensitive ranking for rgb-t saliency detection. In 2019 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), pages 141–146. IEEE, 2019
Gao, L., Liu, B., **, F., Mingzhu, X.: Depth-aware inverted refinement network for rgb-d salient object detection. Neurocomputing 518, 507–522 (2023)
Houwen, Peng, Bing, Li, Weihua, **ong, Weiming, Hu, and Rongrong, Ji: Rgbd salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In European conference on computer vision, pages 92–109. Springer, 2014
Miao, Zhang, Yu Zhang, Yongri, Piao, Beiqi, Hu, and Huchuan, Lu: Feature reintegration over differential treatment: A top-down and adaptive fusion network for rgb-d salient object detection. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pages 4107–4115, 2020
Miao, Zhang, Weisong, Ren, Yongri, Piao, Zhengkun, Rong, and Huchuan, Lu: Select, supplement and focus for rgb-d saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 3472–3481, 2020
Yongri, Piao, Zhengkun, Rong, Miao, Zhang, Weisong, Ren, and Huchuan, Lu: A2dele: Adaptive and attentive depth distiller for efficient rgb-d salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 9060–9069, 2020
Shuhan, Chen and Yun, Fu: Progressively guided alternate refinement network for rgb-d salient object detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 520–538. Springer, 2020
Wang, J., Chen, S., Lv, X., **uqi, X., Xuelong, H.: Guided residual network for rgb-d salient object detection with efficient depth feature learning. Vis. Comput. 38(5), 1803–1814 (2022)
**g, Zhang, Deng-**, Fan, Yuchao, Dai, **n, Yu, Yiran, Zhong, Nick, Barnes, and Ling, Shao: Rgb-d saliency detection via cascaded mutual information minimization. In International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021
Zhang, Y., Zheng, J., Li, L., Liu, N., Jia, W., Fan, X., Chengpei, X., He, X.: Rethinking feature aggregation for deep rgb-d salient object detection. Neurocomputing 423, 463–473 (2021)
Peng, Sun, Wenhu, Zhang, Huanyu, Wang, Songyuan, Li, and ** Li: Deep rgb-d saliency detection with depth-sensitive attention and automatic multi-modal fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1407–1417, 2021
Wujie, Zhou, Qinling, Guo, **gsheng, Lei, Lu, Yu, and Jenq-Neng, Hwang: Ecffnet: Effective and consistent feature fusion network for rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021
Deng-**, Fan, Yingjie, Zhai, Ali, Borji, Jufeng, Yang, and Ling, Shao: Bbs-net: Rgb-d salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 275–292. Springer, 2020
Yuantao, Chen, Runlong, **a, Kai, Yang, and Ke, Zou: Mffn: image super-resolution via multi-level features fusion network. The Visual Computer, pages 1–16, 2023
Miao, Zhang, Sun **ao, Fei, Jie, Liu, Shuang, Xu, Yongri, Piao, and Huchuan, Lu: Asymmetric two-stream architecture for accurate rgb-d saliency detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 374–390. Springer, 2020
Riku, Shigematsu, David, Feng, Shaodi, You, and Nick, Barnes: Learning rgb-d salient object detection using background enclosure, depth contrast, and top-down features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pages 2749–2757, 2017
Chen, Q., Keren, F., Liu, Z., Chen, G., Hongwei, D., Qiu, B., Shao, L.: Ef-net: A novel enhancement and fusion network for rgb-d saliency detection. Pattern Recogn. 112, 107740 (2021)
Nian, Liu, Ni, Zhang, Ling, Shao, and Junwei, Han: Learning selective mutual attention and contrast for rgb-d saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021
**, W.-D., Jun, X., Han, Q., Zhang, Y., Cheng, M.-M.: Cdnet: Complementary depth network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 3376–3390 (2021)
Wei, Ji, Ge, Yan, **g**g, Li, Yongri, Piao, Shunyu, Yao, Miao, Zhang, Li, Cheng, and Huchuan, Lu: Dmra: Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for rgb-d saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022
Zhengyi, Liu, Yacheng, Tan, Qian, He, and Yun, **ao: Swinnet: Swin transformer drives edge-aware rgb-d and rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021
Wei, Gao, Guibiao, Liao, Siwei, Ma, Ge, Li, Yongsheng, Liang, and Weisi, Lin: Unified information fusion network for multi-modal rgb-d and rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021
Guo, Q., Zhou, W., Lei, J., Lu, Yu.: Tsfnet: Two-stage fusion network for rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1655–1659 (2021)
Lixin, An and Jikun, Chen: The research of salient object detection on rgb-t multi-source image. In 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), pages 1103–1107. IEEE, 2021
Huang, L., Song, K., Gong, A., Liu, C., Yan, Y.: Rgb-t saliency detection via low-rank tensor learning and unified collaborative ranking. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 27, 1585–1589 (2020)
Yanhua, Liang, Guihe, Qin, Minghui, Sun, Jun, Qin, Jie, Yan, and Zhonghan, Zhang: Multi-modal interactive attention and dual progressive decoding network for rgb-d/t salient object detection. Neurocomputing, 2022
Wei, Ji, **g**g, Li, Miao, Zhang, Yongri, Piao, and Huchuan, Lu: Accurate rgb-d salient object detection via collaborative learning. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVIII 16, pages 52–69. Springer, 2020
Zhu, X., Chen, C., Zheng, B., Yang, X., Gan, H., Zheng, C., Yang, A., Mao, L., Xue, Y.: Automatic recognition of lactating sow postures by refined two-stream rgb-d faster r-cnn. Biosys. Eng. 189, 116–132 (2020)
**aoqi, Zhao, Youwei, Pang, Lihe, Zhang, Huchuan, Lu, and **ang, Ruan: Self-supervised pretraining for rgb-d salient object detection. In AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 3, 2022
Zhengzheng, T., Li, Z., Li, C., Lang, Y., Tang, J.: Multi-interactive dual-decoder for rgb-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 5678–5691 (2021)
Zhang, Q., **ao, T., Huang, N., Zhang, D., Han, J.: Revisiting feature fusion for rgb-t salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 31(5), 1804–1818 (2020)
Kaiming, He, **angyu, Zhang, Shaoqing, Ren, and Jian, Sun: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 770–778, 2016
Ryoo, M., Piergiovanni, A.J., Arnab, A., Dehghani, M., Angelova, A.: Tokenlearner: adaptive space-time tokenization for videos. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 12786–12797 (2021)
Wu, Z., Su, L., Huang, Q.: Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3907–3916 (2019)
Wei, J., Wang, S., Huang, Q.: F\(^3\)net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artific. Intell. 34, 12321–12328 (2020)
Ju, R., Ge, L., Geng, W., Ren, T., Wu, G.: Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1115–1119. IEEE (2014)
Fan, D-P., Lin, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhu, M., Cheng, M-M.: Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: Models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2020)
Wang, G., Li, C., Ma, Y., Zheng, A., Tang, J., Luo, B.: RGB-T saliency detection benchmark: Dataset, baselines, analysis and a novel approach. In: Chinese Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies, pp. 359–369. Springer (2018)
Zhengzheng, T., **a, T., Li, C., Wang, X., Ma, Y., Tang, J.: RGB-T image saliency detection via collaborative graph learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(1), 160–173 (2019)
Chen, Q., Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Fu, K., Zhao, K.: 3-d convolutional neural networks for RGB-D salient object detection and beyond. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022)
Chen, T., **aoguang, H., **ao, J., Zhang, G., Wang, S.: Cfidnet: cascaded feature interaction decoder for RGB-D salient object detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 34(10), 7547–7563 (2022)
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., et al.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 32, 8026–8037 (2019)
Liu, L., Jiang, H., He, P., Chen, W., Liu, X., Gao, J., Han, J.: On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2019)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1597–1604. IEEE (2009)
Deng-**, F., Gong, C., Cao, Y., Ren, B., Cheng, M.-M., Borji, A: Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 698–704 (2018)
Deng-**, F., Cheng, M.-M., Liu, Y., Li, T., Borji, A: Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4548–4557 (2017)
Gao, W., Liao, G., Ma, S., Li, G., Liang, Y., Lin, W.: Unified information fusion network for multi-modal RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(4), 2091–2106 (2021)
Huo, F., Zhu, X., Zhang, L., Liu, Q., Shu, Yu.: Efficient context-guided stacked refinement network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(5), 3111–3124 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grants 62171156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Fu, P., Xu, M. et al. UMINet: a unified multi-modality interaction network for RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. Vis Comput 40, 1565–1582 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02870-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-02870-6