Abstract
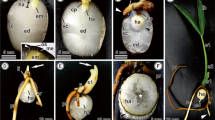
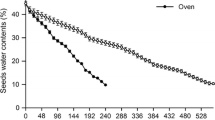
Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu, a member of the first new genus described and published by the Chinese botanist Hu, is an endangered plant endemic to China. We analysed mechanisms of seed dormancy in S. xylocarpa at the cytological level. Cell composition, structure, morphology, and hydration in fruit and seeds were observed using paraffin section detection, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and magnetic resonance imaging. The results indicate that mechanical constraints in the endosperm and endocarp are important causes of dormancy. Germination tests indicated that embryos are non-dormant; rather, the endosperm imposes significant mechanical constraints on germination, particularly around the radicle.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Baskin JM, Baskin CC, Li X (2000) Taxonomy, anatomy and evolution of physical dormancy in seeds. Plant Species Biol 15(2):139–152
Baskin JM, Baskin CC (2004) A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Sci Res 14(1):1–16
Fritsch PW, Morton CM, Chen T (2001) Phylogeny and biogeography of the Styracaceae. Int J Plant SCI 162(S6):S95–S116
Finch WE, Leubner G (2006) Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol 171(3):501–523
Guo C, Shen Y, Shi F (2018) Investigating seed dormancy in Pinus bungeana Zucc. ex Endl.: understanding the contributions of enclosing tissues and temperature on germination. Forests 9(401):1–13
Hu HH (1928) Sinojackia, a new genus of Styracaceae from southeastern China. J Arnold Arbor 9(2/3):130–131
Hill AW (1933) The method of germination of seeds enclosed in a stony endocarp. Ann Bot 47:873–887
Hill AW (1937) The method of germination of seeds enclosed in a stony endocarp II. Ann Bot 1(2):239–256
Holmes WS, Ooi MP, Kuang YC (2020) Signal-to-Noise Ratio contributors and effects in proximal near-Infrared spectral reflectance measurement on plant leaves: 2020 IEEE Inte Inst Meas Tech Conf (I2MTC).
ISTA (2013) International Rules for Seed Testing. International Seed Testing Association. Bass Swit, NW, 2013.
Jia SG, Shen YB (2007) Characteristics of embryo germination of Sinojackia xylocarpa. Com China horticult soc 2007(1):236–240.
Koopman R, Schaart G, Hesselink MK (2001) Optimisation of oil red O staining permits combination with immunofluorescence and automated quantification of lipids. Histochem cell biol 116(1):63–68.
Kucera B, Cohn MA, Leubner G (2005) Plant hormone interactions during seed dormancy release and germination. Seed Sci Res 15(4):281–307
Lin YT (2012) Analysis on superior strips oil content difference of Camellia oleifera around Luoyuan. Qinghai Agri Fore Sci Tech 000(002):16–20
Meng QF, Gao HL, Guo CC (2015) The raising seedling of endangered species Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu. Henan Sci 33(6):929–933
Penfield S (2017) Seed dormancy and germination. Curr Biol 27(17):R874–R878
Shi XH, Li NL, ** L (1999) Preliminary study on seed dormancy and germination of Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu seeds. J Zhejiang Fore Colle 16(3):228–233
Wang HC, He ZC, Li JQ (2003) Studies on karyotype of Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu and observations on its meiosis of pollen mother cell. J Wuhan Bota Res 021(003):198–202
Wang S, **e Y (2004) Red List of Chinese Species 2004(1):418
Xu BM, Sun YT, Guo C (2008) Propagation and Cultivation of Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu in Bei**g Area. Seed 07:19–23
Xu BM, Shi H (1999) Effect of acid treatment on Seed Germination of Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu seeds. Seed 000(005):45–47
Xu XG, Ding FF (2012) Preliminary study on seed dormancy and germination of Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hartw. Acta Bot Boreal 32(11):2270–2278
Xu XG, Guo XX (2019) Wu XP (2019) Seed characteristics and dormancy breaking methods of Styrax dasyanthus Perkins. Jiangsu Agri Sci 16:36
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the College of Forestry, Nan**g Forestry University, and Co-innovation Center for Sustainable Forestry in Southern China, Southern Tree Inspection Center National Forestry Administration.
Funding
This work was financed by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YBS conceived the original screening and research plans; YW performed the experiments using the MRI, SEM, and PSD methods; YW designed the experiments and analysed the data; YW conceived the project and wrote the article with contributions of all the authors. WQB proofreads the revised manuscript. HH proofreads the references. YW agrees to serve as the author responsible for contact and ensures communication. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
We strictly comply with the Convention on the Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, and also abide by Law of the People's Republic of China on Wildlife Protection. Research permission on Tilia miqueliana tree has been obtained from Jiangsu Wildlife Protection Station. The collection of experimental intact seeds was approved by Nan**g Forestry University in Jiangsu Province, China.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All the authors supported the publication of the article.
Additional information
Handling Author: Peter Hedden.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Bao, W.Q., Hu, H. et al. Mechanical Constraints in the Endosperm and Endocarp are Major Causes of Dormancy in Sinojackia xylocarpa Hu (Styracaceae) Seeds. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 644–657 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10572-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10572-3