Abstract
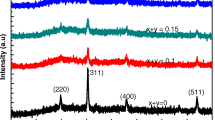
Dysprosium (Dy3+)-substituted Ni–Co nanoparticles were synthesized by sol–gel technique. Structural and morphological analyses were accomplished by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and field emission transmission electron microscopy (FE-TEM). The crystallite size and lattice parameter followed a decreasing trend up on increase in Dy3+ substitution for the concentration x ≤ 0.15, which is due to the hindrance in crystallite growth and deposition of Dy3+ on grain boundaries, respectively. The lattice strain was increased from 5.027 to 8.814 × \({10}^{-3}\) with enhancement in Dy3+ content. The morphological studies showed uniform distribution of particles with slight agglomeration and the average particle size was calculated to be 22.17 nm, which is in good agreement with XRD results. The magnetic studies were executed by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) over a wide range of applied magnetic field. The soft ferrimagnetic nature of these ferrites was revealed by narrow (M–H) curve. The magnetic parameters exhibited decreasing behavior upon increasing amount of substitution. The coercivity (Hc) was recorded to be 1097 Oe for x = 0.00 and saturation magnetization (Ms) was calculated in the range 27.04–40.86 emu/g. The anisotropy constant and magneton number were found to be in the range of 9887–46,703 erg/cm3 and 1.21–1.71 µB, respectively. These properties of prepared ferrites point towards their applicability in magnetic recording instruments, memory, and high-density data storage devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available with us corresponding author, [ZA Gilani] and can be presented upon reasonable request.
References
M.H. Ehsani, S. Esmaeili, M. Aghazadeh, P. Kameli, F.S. Tehrani, I. Karimzadeh, An investigation on the impact of Al do** on the structural and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2572-2
T. Dippong, I.G. Deac, O. Cadar, E.A. Levei, Effect of silica embedding on the structure, morphology and magnetic behavior of (Zn0.6Mn0.4Fe2O4)δ/(SiO2)(100−δ) nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 11, 2232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092232
T. Dippong, E.-A. Levei, D. Toloman, L. Barbu-Tudoran, O. Cadar, Investigation on the formation, structural and photocatalytic properties of mixed Mn-Zn ferrites nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 matrix. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 158, 105281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105281
A. Radoń, A. Włodarczyk, Ł Sieroń, M. Rost-Roszkowska, Ł Chajec, D. Łukowiec et al., Influence of the modifiers in polyol method on magnetically induced hyperthermia and biocompatibility of ultrafine magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 13, 7860 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-34738-z
A. Radoń, M. Kądziołka-Gaweł, D. Łukowiec, P. Gębara, K. Cesarz-Andraczke, A. Kolano-Burian et al., Influence of magnetite nanoparticles shape and spontaneous surface oxidation on the electron transport mechanism. Materials 14, 5241 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185241
A. Radoń, J. Kubacki, M. Kądziołka-Gaweł, P. Gębara, Ł Hawełek, S. Topolska et al., Structure and magnetic properties of ultrafine superparamagnetic Sn-doped magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by glycol assisted co-precipitation method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 145, 109530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109530
A. Radoń, S. Łoński, M. Kądziołka-Gaweł, P. Gębara, M. Lis, D. Łukowiec et al., Influence of magnetite nanoparticles surface dissolution, stabilization and functionalization by malonic acid on the catalytic activity, magnetic and electrical properties. Colloids Surf. A 607, 125446 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125446
M. Yehia, S. Ismail, A. Hashhash, Structural and magnetic studies of rare-earth substituted nickel ferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27, 771–774 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-013-2340-z
Y. Fang, S. Zhang, P.R. Ohodnicki, G. Wang, Relation between cation distribution and chemical bonds in spinel NiFe2O4. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104436 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104436
S. Chakrabarty, S. Bandyopadhyay, M. Pal, A. Dutta, Sol-gel derived cobalt containing Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles: dielectric relaxation and enhanced magnetic property study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 259, 124193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.124193
A.K. Nikumbh, R.A. Pawar, D.V. Nighot, G.S. Gugale, M.D. Sangale, M.B. Khanvilkar et al., Structural, electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of rare-earth substituted cobalt ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 201–209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.11.052
C. Murugesan, K. Ugendar, L. Okrasa, J. Shen, G. Chandrasekaran, Zinc substitution effect on the structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite. Ceram. Int. 47, 1672–1685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.284
Z. Zhang, Study on the influence of magnesium do** on the magnetic properties of spinel Zn-Mg ferrite. Mater. Today Commun. 26, 101734 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101734
A.V. Raut, R.S. Barkule, D.R. Shengule, K.M. Jadhav, Synthesis, structural investigation and magnetic properties of Zn2+ substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358–359, 87–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.01.039
R. Kambale, K. Song, Y. Koo, N. Hur, Low temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline Dy3+ doped cobalt ferrite: structural and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 053910 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3632987
S. Bhandare, R. Kumar, A. Anupama, M. Mishra, R.V. Kumar, V. Jali et al., Effect of Mg-substitution in Co–Ni-Ferrites: cation distribution and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 251, 123081 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123081
A.K. Vishwakarma, B. Sen Yadav, J. Singh, S. Sharma, N. Kumar, Antibacterial activity of PANI coated CoFe2O4 nanocomposite for gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Mater. Today Commun. 31, 103229 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103229
M. Stefanescu, M. Stoia, T. Dippong, O. Stefanescu, P. Barvinschi, Preparation of CoXFe3-XO4 oxydic system starting from metal nitrates and propanediol. Acta Chim. Slov. 56, 379–385 (2009)
M. Stefanescu, M. Stoia, C. Caizer, T. Dippong, P. Barvinschi, Preparation of Co x Fe 3–x O 4 nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of some organo-metallic precursors. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 97, 245–250 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0250-x
N. Gupta, A. Verma, S.C. Kashyap, D.C. Dube, Microstructural, dielectric and magnetic behavior of spin-deposited nanocrystalline nickel–zinc ferrite thin films for microwave applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308, 137–142 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.05.015
S. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, K. Lohar, S. Jadhav, N. Kulkarni, K. Jadhav, Electrical and switching properties of NiAlxFe2− xO4 ferrites synthesized by chemical method. Physica B 406, 663–668 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.11.081
M. Kokare, N.A. Jadhav, Y. Kumar, K. Jadhav, S. Rathod, Effect of Nd3+ do** on structural and magnetic properties of Ni0. 5Co0. 5Fe2O4 nanocrystalline ferrites synthesized by sol-gel auto combustion method. J. Alloy. Compd. 748, 1053–1061 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.168
C. Luadthong, V. Itthibenchapong, N. Viriya-empikul, K. Faungnawakij, P. Pavasant, W. Tanthapanichakoon, Synthesis, structural characterization, and magnetic property of nanostructured ferrite spinel oxides (AFe2O4, A= Co, Ni and Zn). Mater. Chem. Phys. 143, 203–208 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.08.052
R.S. Yadav, J. Havlica, J. Masilko, L. Kalina, J. Wasserbauer, M. Hajdúchová et al., Impact of Nd3+ in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles on cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 399, 109–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.09.055
S. Joshi, M. Kumar, S. Chhoker, G. Srivastava, M. Jewariya, V.N. Singh, Structural, magnetic, dielectric and optical properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1076, 55–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.07.048
M. Kokare, N.A. Jadhav, V. Singh, S. Rathod, Effect of Sm3+ substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Co nanoferrites. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 107–116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.10.045
Z. Karimi, Y. Mohammadifar, H. Shokrollahi, S.K. Asl, G. Yousefi, L. Karimi, Magnetic and structural properties of nano sized Dy-doped cobalt ferrite synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 361, 150–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.01.016
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (REåNd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.05.030
F.L. Deepak, M. Bañobre-López, E. Carbó-Argibay, M.F. Cerqueira, Y. Piñeiro-Redondo, J. Rivas et al., A systematic study of the structural and magnetic properties of Mn-, Co-, and Ni-doped colloidal magnetite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 11947–11957 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01575
V.L. Deringer, C. Goerens, M. Esters, R. Dronskowski, B.P. Fokwa, Chemical modeling of mixed occupations and site preferences in anisotropic crystal structures: case of complex intermetallic borides. Inorg. Chem. 51, 5677–5685 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic300023t
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, C. Leostean, O. Cadar, Impact of annealing temperature and ferrite content embedded in SiO2 matrix on the structure, morphology and magnetic characteristics of (Co0.4Mn0.6Fe2O4)δ (SiO2)100-δ nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compounds 868, 159203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159203
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, Investigation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Mn) obtained by thermal decomposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 8483 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158483
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, I.A. Auwal, S.E. Shirsath, A. Manikandan, A. Baykal et al., Impact of Tm3+ and Tb3+ rare earth cations substitution on the structure and magnetic parameters of Co-Ni nanospinel ferrite. Nanomaterials 10, 2384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122384
M.F. Warsi, A. Iftikhar, M.A. Yousuf, M.I. Sarwar, S. Yousaf, S. Haider et al., Erbium substituted nickel–cobalt spinel ferrite nanoparticles: tailoring the structural, magnetic and electrical parameters. Ceram. Int. 46, 24194–24203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.199
D. Phugate, R.B. Borade, S. Kadam, L. Dhale, R. Kadam, S.E. Shirsath et al., Effect of Ho3+ ion do** on thermal, structural, and morphological properties of Co–Ni ferrite synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 3545–3554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05616-w
A.B. Kadam, V.K. Mande, S.B. Kadam, R.H. Kadam, S.E. Shirsath, R.B. Borade, Influence of gadolinium (Gd3+) ion substitution on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 840, 155669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155669
A.D. Patil, S.M. Patange, P.M. Dighe, S.F. Shaikh, Au.H.S. Rana, B. Pandit et al., Tuning the structural, optical and magnetic properties of NiCuZn (Ni0.4Cu0.3Zn0.3Fe2O4) spinel ferrites by Nb2O5 additive. Ceram. Int. 48, 27039–27050 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.06.016
V. Bhanu, P.V. Prakash Madduri, M. Harsita, S. Soumya, T. Durga Rao, P.K. Raju et al., Enhanced magnetic anisotropy in Dy-doped nanocrystalline NiFe2O4. Mater. Today Commun. 35, 105859 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105859
A. Maqsood, K. Khan, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, M. Malik, Spectroscopic and magnetic investigation of NiCo nanoferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 7493–7497 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.04.092
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, I.G. Deac, I. Petean, G. Borodi, O. Cadar, Sol-gel synthesis, structure, morphology and magnetic properties of Ni0.6Mn0.4Fe2O4 nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 matrix. Nanomaterials 11, 3455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123455
T. Dippong, D. Toloman, M. Dan, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, Structural, morphological and photocatalytic properties of Ni-Mn ferrites: Influence of the Ni: Mn ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 913, 165129 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165129
A. Zubair, Z. Ahmad, A. Mahmood, W.-C. Cheong, I. Ali, M.A. Khan et al., Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Eu-doped CoFe2O4 nano-ferrites. Results Phys. 7, 3203–3208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.08.035
A. Kadam, S. Shinde, S. Yadav, P. Patil, K. Rajpure, Structural, morphological, electrical and magnetic properties of Dy doped Ni–Co substitutional spinel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 59–64 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.10.008
R. Zakir, S.S. Iqbal, A.U. Rehman, S. Nosheen, T.S. Ahmad, N. Ehsan et al., Spectral, electrical, and dielectric characterization of Ce-doped Co-Mg-Cd spinel nano-ferrites synthesized by the sol-gel auto combustion method. Ceram. Int. 47, 28575–28583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.016
K. Tanbir, M.P. Ghosh, R.K. Singh, M. Kar, S. Mukherjee, Effect of do** different rare earth ions on microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of nickel–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 435–443 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02546-9
R. Kumar, P.B. Barman, R.R. Singh, An innovative direct non-aqueous method for the development of Co doped Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Today Commun. 27, 102238 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102238
P. Gębara, M. Cesnek, J. Bednarcik, Anomalous behavior of thermal expansion of α-Fe impurities in the La (Fe Co, Si) 13-based alloys modified by Mn or selected lanthanides (Ce, Pr, Ho). Curr. Appl. Phys. 19, 188–192 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2018.12.001
M. Almessiere, B. Unal, Y. Slimani, H. Gungunes, M. Toprak, N. Tashkandi et al., Effects of Ce–Dy rare earths co-do** on various features of Ni–Co spinel ferrite microspheres prepared via hydrothermal approach. J. Market. Res. 14, 2534–2553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.142
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, O. Cadar, I.G. Deac, M. Lazar, G. Borodi et al., Effect of amorphous SiO2 matrix on structural and magnetic properties of Cu0. 6Co0. 4Fe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 849, 156695 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156695
K.M. Srinivasamurthy, K. Manjunatha, E.I. Sitalo, S.P. Kubrin, I.C. Sathish, S. Matteppanavar et al., Effect of Ce3+ substitution on the structural, morphological, dielectric, and impedance spectroscopic studies of Co–Ni ferrites for automotive applications. Indian J. Phys. 94, 593–604 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01495-7
M. Salgaonkar, R. Gad, Influence of B-site Gd+ 3 substitution on various properties of Co-ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 127, 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05026-2
M. Rahman, N. Hasan, M. Hoque, M. Hossen, M. Arifuzzaman, Structural, dielectric, and electrical transport properties of Al3+ substituted nanocrystalline Ni-Cu spinel ferrites prepared through the sol–gel route. Results Phys. 38, 105610 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105610
M. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A.D. Korkmaz, M. Sertkol, A. Baykal, I. Ercan et al., Sonochemical synthesis of CoFe2-xNdxO4 nanoparticles: structural, optical, and magnetic investigation. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 3837–3844 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05147-z
K. Lohar, A. Pachpinde, M. Langade, R. Kadam, S.E. Shirsath, Self-propagating high temperature synthesis, structural morphology and magnetic interactions in rare earth Ho3+ doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 604, 204–210 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.03.141
D. Pawar, P.P. Khirade, V. Vinayak, L. Ravangave, S. Rathod, Sol–gel auto-ignition fabrication of Gd3+ incorporated Ni0. 5Co0. 5Fe2O4 multifunctional spinel ferrite nanocrystals and its impact on structural, optical and magnetic properties. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03505-4
T. Dippong, D. Toloman, E.-A. Levei, O. Cadar, A. Mesaros, A possible formation mechanism and photocatalytic properties of CoFe2O4/PVA-SiO2 nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 666, 103–115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.05.021
T. Dippong, E.-A. Levei, I.G. Deac, F. Goga, O. Cadar, Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of NixZn1-xFe2O4/SiO2 (0≤ x≤ 1) spinel-based nanocomposites. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 144, 104713 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2019.104713
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, F. Goga, O. Cadar, Influence of Mn2+ substitution with Co2+ on structural, morphological and coloristic properties of MnFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. Mater Charact 172, 110835 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110835
L.B. Tahar, M. Artus, S. Ammar, L.S. Smiri, F. Herbst, M.J. Vaulay et al., Magnetic properties of CoFe1.9RE0.1O4 nanoparticles (RE=La, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Ho) prepared in polyol. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 3242–3250 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.06.031
P. Monisha, P. Priyadharshini, S. Gomathi, K. Pushpanathan, Influence of Mn dopant on the crystallite size, optical and magnetic behaviour of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109654 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109654
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamy, J.-M. Greneche, R. Murugaraj, Y. Lee, Electrical and magnetic behaviour of nanostructured MgFe2O4 spinel ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 504, 395–402 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.05.125
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal, Synthesis and characterization of Co1–2xNixMnxCeyFe2–yO4 nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 38, 188–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.07.005
A. Ditta, M.A. Khan, M. Junaid, R.A. Khalil, M.F. Warsi, Structural, magnetic and spectral properties of Gd and Dy co-doped dielectrically modified Co-Ni (Ni0. 4Co0. 6Fe2O4) ferrites. Physica B 507, 27–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2016.11.030
S. Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S. Behbahanian, J. Amighian, Synthesis and magnetic properties of NiFe2− xSmxO4 nanopowder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 410, 242–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.03.015
M.F. Sarac, Magnetic, structural, and optical properties of gadolinium-substituted Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 spinel ferrite nanostructures. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 397–406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05359-3
T. Dippong, E.A. Levei, I.G. Deac, I. Petean, O. Cadar, Dependence of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of manganese ferrite on Ni-Mn substitution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3097 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063097
A. Pachpinde, M. Langade, K. Lohar, S. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, Impact of larger rare earth Pr3+ ions on the physical properties of chemically derived PrxCoFe2− xO4 nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. 429, 20–26 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2013.11.018
M.A. Maksoud, A. El-Ghandour, A. Ashour, M. Atta, S. Abdelhaleem, A.H. El-Hanbaly et al., La3+ doped LiCo0. 25Zn0. 25Fe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystals: Insights on structural, optical and magnetic properties. J. Rare Earths 39, 75–82 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.12.017
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2024R699) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The role(s) of all the authors are listed as follows on the behalf of all the authors. FAS: conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection; preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. HMNHKA: development or design of methodology; creation of models. MK: provision of study materials, instrumentation, and computing resources analysis tools. ZAG: ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims; verification, experiments and other research outputs; oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution, including mentorship external to the core team. SMA: management and coordination responsibility for the research activity planning and execution. N-u-HK: maintain research data (including software code, where it is necessary for interpreting the data itself) for initial use and later reuse. MAS: preparation, creation, specifically critical review, commentary, or revision—including pre- or post-publication stages. MYK: application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikh, F.A., Asghar, H.M.N.u.H.K., Khalid, M. et al. Magnetically tuned Ni0.3Co0.7DyxFe2–xO4 ferrites for high-density data storage applications. Appl. Phys. A 130, 65 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07224-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07224-6