Abstract
Objectives
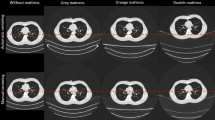
To assess the impact of patient off-centering on organ dose and image noise for head and thoracoabdominal CT in a pediatric phantom.
Methods
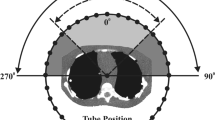
An anthropomorphic phantom simulating a 5-year-old child was used. Semiconductor dosimeters were placed in various cranial and thoracoabdominal organs. Head and thoracoabdominal CT were performed using automatic tube current modulation (ATCM) and default bowtie filters. The phantom was imaged repeatedly at vertical table positions ranging from − 6 to + 6 cm from the 0-position. Tube current time products (TCTP), organ doses, and image noise were recorded. Scatter radiation was measured in the thyroid for head CT. The effect of ATCM and bowtie filters was assessed.
Results
Depending on patient position, organ doses differed up to 22% for the supratentorial brain, 34% for the infratentorial brain, 19% for the eyes, 28% for the lungs, 25% for the stomach, and 22% for the liver compared with those in the 0-position. The relation between position and dose was linear and mainly affected by the bowtie filter in head CT, while it was quadratic and affected by ATCM and bowtie filter in thoracoabdominal CT. It further depended on the relative position of each organ to the isocenter. An inverse relation was found between position and image noise. Scatter radiation was not significantly related to patient positioning (p = 0.21).
Conclusions
In pediatric CT, vertical patient positioning had a substantial impact on radiation dose with differences of up to 34%, depending on the body region and location of each individual organ.
Key Points
• Patient off-centering has a substantial impact on organ radiation dose and image noise in pediatric CT.
• Impact of patient off-centering on radiation dose and noise differs between head and thoracoabdominal CT.
• Differences are caused by both ATCM and bowtie filter in thoracoabdominal CT, but mainly by bowtie filter in head CT.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATCM:
-
Automatic tube current modulation
- TCTP:
-
Tube current time product
References
Li J, Udayasankar UK, Toth TL, Seamans J, Small WC, Kalra MK (2007) Automatic patient centering for MDCT: effect on radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:547–552
Habibzadeh MA, Ay MR, Asl AR, Ghadiri H, Zaidi H (2012) Impact of miscentering on patient dose and image noise in x-ray CT imaging: phantom and clinical studies. Phys Med 28:191–199
Akin-Akintayo OO, Alexander LF, Neill R et al (2019) Prevalence and severity of off-centering during diagnostic CT: observations from 57,621 CT scans of the chest, abdomen, and/or pelvis. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 48:229–234
Saltybaeva N, Alkadhi H (2017) Vertical off-centering affects organ dose in chest CT: evidence from Monte Carlo simulations in anthropomorphic phantoms. Med Phys 44:5697–5704
Marsh RM, Silosky MS (2017) The effects of patient positioning when interpreting CT dose metrics: a phantom study. Med Phys 44:1514–1524
Kaasalainen T, Palmu K, Reijonen V, Kortesniemi M (2014) Effect of patient centering on patient dose and image noise in chest CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:123–130
Lambert JW, Kumar S, Chen JS, Wang ZJ, Gould RG, Yeh BM (2015) Investigating the CT localizer radiograph: acquisition parameters, patient centring and their combined influence on radiation dose. Br J Radiol 88:20140730
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is André Euler.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Not needed because of the design as a phantom study.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was not required because of the design as a phantom study.
Methodology
• prospective
• experimental
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 669 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Euler, A., Saltybaeva, N. & Alkadhi, H. How patient off-centering impacts organ dose and image noise in pediatric head and thoracoabdominal CT. Eur Radiol 29, 6790–6793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06330-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06330-5