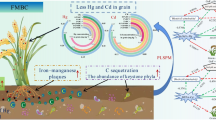
Abstract
The plastic film is extensively applied with limited recycling, leading to the long-run residue accumulation in soil, which offers a distinctive habitat for microorganisms, and creates a plastisphere. In this study, traditional low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic film and biodegradable polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) plastic film materials were selected to test their effects on soil microbial ecology. Based on high-throughput sequencing, compared to the soil environment, the alpha-diversity of bacterial communities in plastisphere was lower, and the abundance of Actinobacteria increased. Plastic film residues, as bacterial habitats, exhibited greater heterogeneity and harbor unique bacterial communities. The communities were distinguished between plastisphere and soil environment by means of a random-forest (RF) machine-learning model. Prominent distinctions emerged among bacterial functions between soil environment and plastisphere, especially regarding organics degradation. The neutral model and null model indicated that the constitution of bacterial communities was dominated by random processes except in LDPE plastisphere. The bacterial co-occurrence network of the plastisphere exhibited higher complexity and modularity. This study contributes to our comprehending of characteristics of plastisphere bacterial communities in soil environment and the associated ecological risks of plastic film residues accumulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data Availability FASTQ files are deposited in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information, accession numbers PRJNA1083493.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Zhang Q-Q, Ma Z-R, Cai Y-Y, Li H-R et al (2021) agricultural plastic pollution in china: generation of plastic debris and emission of phthalic acid esters from agricultural films. Environ Sci Technol 55(18):12459–12470. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c04369
Li S (2020) CHINA RURAL STATISTICAL YEARBOOK. China Statistics Press,
Zhang D, Ng EL, Hu W, Wang H et al (2020) Plastic pollution in croplands threatens long-term food security. Global Change Biol 26(6):3356–3367. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15043
Steinmetz Z, Wollmann C, Schaefer M, Buchmann C et al (2016) Plastic mulching in agriculture. Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation? Sci Total Environ 550:690–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.153
Duis K, Coors A (2016) Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ Sci Eur 28(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-015-0069-y
Tribedi P, Dey S (2017) Pre-oxidation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by ultraviolet light (UV) promotes enhanced degradation of LDPE in soil. Environ Monit Assess 189(12):624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6351-2
Campanale C, Galafassi S, Di Pippo F, Pojar I et al (2024) A critical review of biodegradable plastic mulch films in agriculture: Definitions, scientific background and potential impacts. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 170:117391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2023.117391
Qi R, Jones DL, Li Z, Liu Q et al (2020) Behavior of microplastics and plastic film residues in the soil environment: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 703:134722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134722
Huang Y, Liu Q, Jia W, Yan C et al (2020) Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ Pollut 260:114096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114096
Sintim HY, Flury M (2017) Is biodegradable plastic mulch the solution to agriculture’s plastic problem? Environ Sci Technol 51(3):1068–1069. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b06042
Bandopadhyay S, Martin-Closas L, Pelacho AM, DeBruyn JM (2018) biodegradable plastic mulch films: impacts on soil microbial communities and ecosystem functions. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00819
Costerton JW, Cheng KJ, Geesey GG, Ladd TI et al (1987) Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:435–464. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251
Ferreira FV, Cividanes LS, Gouveia RF, Lona LMF (2019) An overview on properties and applications of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)–PBAT based composites. Polym Eng Sci 59(s2):E7–E15. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24770
Ma J, Cao Y, Fan L, **e Y et al (2023) Degradation characteristics of polybutylene adipate terephthalic acid (PBAT) and its effect on soil physicochemical properties: a comparative study with several polyethylene (PE) mulch films. J Hazard Mater 456:131661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131661
Zettler ER, Mincer TJ, Amaral-Zettler LA (2013) Life in the “Plastisphere”: microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7137–7146. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401288x
Amaral-Zettler LA, Zettler ER, Mincer TJ (2020) Ecology of the plastisphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(3):139–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0308-0
Mughini-Gras L, van der Plaats RQJ, van der Wielen PWJJ, Bauerlein PS et al (2021) Riverine microplastic and microbial community compositions: a field study in the Netherlands. Water Res 192:116852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116852
Miao L, Wang P, Hou J, Yao Y et al (2019) Distinct community structure and microbial functions of biofilms colonizing microplastics. Sci Total Environ 650:2395–2402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.378
Wen-qing H (2011) Degradation of Biodegradable Plastic Mulch Film and Its Effect on the Yield of Cotton in **njiang Region,China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO et al (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12(9):635–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3330
Wu C, Ma Y, Wang D, Shan Y et al (2022) Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal plastic mulch film residue affects soil microorganisms and their metabolic functions. J Hazard Mater 423:127258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127258
Wang J, Huang M, Wang Q, Sun Y et al (2020) LDPE microplastics significantly alter the temporal turnover of soil microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 726:138682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138682
Liu L, Zou G, Zuo Q, Li C et al (2022) Soil bacterial community and metabolism showed a more sensitive response to PBAT biodegradable mulch residues than that of LDPE mulch residues. J Hazard Mater 438:129507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129507
Liu Y, Huang Q, Hu W, Qin J et al (2021) Effects of plastic mulch film residues on soil-microbe-plant systems under different soil pH conditions. Chemosphere 267:128901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128901
Khandare SD, Agrawal D, Mehru N, Chaudhary DR (2022) Marine bacterial based enzymatic degradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic. J Environ Chem Eng 10(3):107437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107437
Wang J, Qin X, Guo J, Jia W et al (2020) Evidence of selective enrichment of bacterial assemblages and antibiotic resistant genes by microplastics in urban rivers. Water Res 183:116113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116113
Wang T, Yu C, Chu Q, Wang F et al (2020) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of five pesticides on microplastics from agricultural polyethylene films. Chemosphere 244:125491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125491
Wang J, Wang L, Zhu L, Wang J et al (2022) Antibiotic resistance in agricultural soils: Source, fate, mechanism and attenuation strategy. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52(6):847–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835438
Sharma MD, Elanjickal AI, Mankar JS, Krupadam RJ (2020) Assessment of cancer risk of microplastics enriched with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mater 398:122994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122994
Frère L, Maignien L, Chalopin M, Huvet A et al (2018) Microplastic bacterial communities in the Bay of Brest: Influence of polymer type and size. Environ Pollut 242:614–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.023
Kooi M, Nes EHV, Scheffer M, Koelmans AA (2017) Ups and downs in the ocean: effects of biofouling on vertical transport of microplastics. Environ Sci Technol 51(14):7963–7971. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04702
Ortega-González DK, Martínez-González G, Flores CM, Zaragoza D et al (2015) Amycolatopsis sp. Poz14 isolated from oil-contaminated soil degrades polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 99:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.01.008
Hara A, Syutsubo K, Harayama S (2003) Alcanivorax which prevails in oil-contaminated seawater exhibits broad substrate specificity for alkane degradation. Environ Microbiol 5(9):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-2920.2003.00468.x
Sangeetha Devi R, Rajesh Kannan V, Nivas D, Kannan K et al (2015) Biodegradation of HDPE by Aspergillus spp from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar India. Mar Pollut Bull. 96(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.050
Yu T, Li Y (2014) Influence of poly(butylenes adipate-co-terephthalate) on the properties of the biodegradable composites based on ramie/poly(lactic acid). Composites, Part A 58:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.11.013
Moreno MM, Moreno A (2008) Effect of different biodegradable and polyethylene mulches on soil properties and production in a tomato crop. Sci Hortic 116(3):256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2008.01.007
Xue N, Wang L, Li W, Wang S et al (2020) Increased inheritance of structure and function of bacterial communities and pathogen propagation in plastisphere along a river with increasing antibiotics pollution gradient. Environ Pollut 265:114641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114641
Brodhagen M, Peyron M, Miles C, Inglis DA (2015) Biodegradable plastic agricultural mulches and key features of microbial degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(3):1039–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6267-5
Zhang J, Zhang B, Liu Y, Guo Y et al (2018) Distinct large-scale biogeographic patterns of fungal communities in bulk soil and soybean rhizosphere in China. Sci Total Environ 644:791–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.016
Jiao S, Yang Y, Xu Y, Zhang J et al (2020) Balance between community assembly processes mediates species coexistence in agricultural soil microbiomes across eastern China. ISME J 14(1):202–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0522-9
Wu W, Lu H-P, Sastri A, Yeh Y-C et al (2017) Contrasting the relative importance of species sorting and dispersal limitation in sha** marine bacterial versus protist communities. ISME J 12(2):485–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.183
Li C, Gan Y, Zhang C, He H et al (2021) “Microplastic communities” in different environments: Differences, links, and role of diversity index in source analysis. Water Res 188:116574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116574
Amir M, Bano N, Baker A, Zia Q et al (2022) Isolation and optimization of extracellular PHB depolymerase producer Aeromonas caviae Kuk1-(34) for sustainable solid waste management of biodegradable polymers. PLoS ONE 17(4):e0264207. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264207
Amir M, Bano N, Gupta A, Zaheer MR et al (2024) Purification and characterization of extracellular PHB depolymerase enzyme from Aeromonas caviae Kuk1-(34) and their biodegradation studies with polymer films. Biodegradation 35(2):137–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10051-4
Li K, Xu L, Bai X, Zhang G et al (2024) Differential fungal assemblages and functions between the plastisphere of biodegradable and conventional microplastics in farmland. Sci Total Environ 906:167478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167478
Wan X, Gao Q, Zhao J, Feng J et al (2020) Biogeographic patterns of microbial association networks in paddy soil within Eastern China. Soil Biol Biochem 142:107696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107696
Carstensen DW, Sabatino M, Morellato LPC (2016) Modularity, pollination systems, and interaction turnover in plant-pollinator networks across space. Ecology 97(5):1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1890/15-0830.1
Li Y, Gao W, Wang C, Gao M (2023) Distinct distribution patterns and functional potentials of rare and abundant microorganisms between plastisphere and soils. Sci Total Environ 873:162413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162413
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52200109) and the State Scholarship Fund and the Key R&D and Promotion Project of Henan Province (No.202102310278). The authors would also like to thank the support of the School of Water Conservancy Science and Engineering in Zhengzhou University.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52200109), the State Scholarship Fund and the Key R&D and Promotion Project of Henan Province (No.202102310278).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yuanyuan Jiao contributed toward investigation, data curation, visualization, and writing – original draft. Guangyi Zhang contributed toward writing – review & editing, methodology, resources, and supervision. **aoyang Ai contributed toward formal analysis, investigation and data curation. **ao**g Wang contributed toward investigation, data curation and conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
The submitted work is original and has not been submitted to other journals.
Consent to Participate
The authors have agreed to be listed and approved the submitted version of the manuscript.
Consent for Publication
The authors hereby consent for the article publication in Current Microbiology journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, Y., Zhang, G., Ai, X. et al. Comparison of the Effects of LDPE and PBAT Film Residues on Soil Microbial Ecology. Curr Microbiol 81, 185 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-024-03722-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-024-03722-9