Abstract
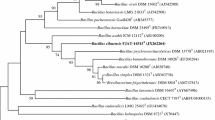
A Gram-positive bacterium, designated strain XY18T, was isolated from a cured vanilla bean in Hainan province, China. Cells were rod-shaped, endospore producing, and peritrichous flagella. Strain XY18T grew at salinities of 0–8 % (w/v) NaCl (optimally 1–4 %), pH 4.0–8.0 (optimally 5.0–7.0 %) and temperature range 20–45 °C (optimally 28–35 °C). The predominant menaquinone was MK-7. The major cellular fatty acids were anteiso-C15:0, iso-C15:0, anteiso-C17:0, and iso-C17:0. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that strain XY18T was a member of the genus Bacillus, and closely related to B. amyloliquefaciens NBRC 15535T and B. siamensis PD-A10T, with 99.1 and 99.2 % sequence similarity, respectively. However, the DNA–DNA hybridization value between strain XY18T and B. amyloliquefaciens NBRC 15535T was 35.7 %. The genomic DNA G+C content of strain XY18T was 46.4 mol%, significantly differed from B. siamensis PD-A10T (41.4 %), which was higher than the range of 4 % indicative of species. On the basis of polyphasic taxonomic study, including phenotypic features, chemotaxonomy, and phylogenetic analyses, strain XY18T represents a novel species within the genus Bacillus, for which the name Bacillus vanillea sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is XY18T (=CGMCC 8629 = NCCB 100507).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandna P, Mayilraj S, Kuhad RC (2013) Bacillus paraflexus sp. nov., isolated from compost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:4735–4743
Chen YG, Zhang YQ, He JW, Klenk HP, **ao JQ, Zhu HY, Tang SK, Li WJ (2011) Bacillus hemicentroti sp. nov., a moderate halophile isolated from a sea urchin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2950–2955
Dastager SG, Mawlankar R, Tang SK, Srinivasan K, Ramana VV, Shouche YS (2014) Bacillus enclensis sp. nov., isolated from sediment sample. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 105(1):199–206
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
General T, Mamatha V, Divya KA, Appaiah KAA (2009) Diversity of yeast with β-glycosidase activity in vanilla (Vanilla planifolia) plant. Curr Sci 96(11):1501–1505
Hu HY, Lim BR, Naohiro G, Koich FJ (2001) Analytical precision and repeatability of respiratory quinones for quantitative study of microbial community structure in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 47:17–24
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Kämpfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Microbiol 42:989–1005
Kang H, Weerawongwiwat V, Kim JH, Sukhoom A, Kim W (2013) Bacillus songklensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4189–4195
Krulwich TA, Hicks DB, Swartz TH, Ito M (2007) Bioenergetic adaptations that support alkaliphily. In: Gerday C, Glansdorff N (eds) Physiology and biochemistry of extremophiles. ASM, Washington, pp 311–329
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Kwon SW, Sa TM (2010) Bacillus methylotrophicus sp. nov., a methanol-utilizing, plant-growth-promoting bacterium isolated from rice rhizosphere soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2490–2495
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Patterton HG, Graves S (2000) DNAssist: the integrated editing and analysis of molecular biology sequences in windows. Bioinformatics 16:652–653
Peng LL, Wang LM, Che CC, Yang G, Yu B, Ma YH (2013) Bacillus sp. strain P38: an efficient producer of l-lactate from cellulosic hydrolysate, with high tolerance for 2-furfural. Bioresour Technol 149:169–176
Priefert H, Rabenhorst J, Steinbuchel A (2001) Biotechnological production of vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:296–314
Priest FG, Goodfellow M, Shute LA, Berkeley RCW (1987) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens sp. nov. norn. rev. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 37:69–71
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1994) Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 44:256–264
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1996) Bacillus vallismortis sp. nov., a close relative of Bacillus subtilis, isolated from soil in death valley, California. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 46(2):470–475
RÖling WFM, Josef K, Martin B, Anton A, Stam H, Verseveld HWV (2001) Microorganisms with a taste for vanilla: microbial ecology of traditional Indonesian vanilla curing. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(5):1995–2003
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl 20:1–6
Sharp MD, Kocaoglu-Vurma NA, Langford V, Rodriguez-Saona LE, Harper WJ (2012) Rapid discrimination and characterization of vanilla bean extracts by attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy and selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry. J Food Sci 77:284–292
Shi R, Yin M, Tang S, Lee JC, Park DJ, Zhang YJ, Kim CJ, Li WJ (2011) Bacillus luteolus sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from a salt field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1344–1349
Stackebrandt E, Fredericksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PA, Kämpfer P, Maiden MC, Nesme X, Rosselló-Mora R, Swings J, Trüper HG, Vauterin L, Ward AC, Whitman WB (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Sumpavapol P, Tongyonk L, Tanasupawat S, Chokesajjawatee N, Luxananil P, Visessanguan W (2010) Bacillus siamensis sp. nov., isolated from salted crab (poo-khem) in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2364–2370
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Higgins T, Gibson J (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wang YQ, Yuan Y, Yu Z, Yang GQ, Zhou SG (2014) Bacillus borbori sp. nov., isolated from an electrochemically active biofilm. Curr Microbiol 67:718–724
Yang GQ, Zhou XM, Zhou SG, Wang YQ, Wang DM (2013) Bacillus thermotolerans sp. nov., a thermophilic bacterium capable of reducing humus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3672–3678
Yu Z, Wang YQ, Qin DX, Yang GQ, Zhou SG (2014) Bacillus sediminis sp. nov., isolated from an electroactive biofilm. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104(6):1109–1116
Zhai L, Ma YW, Xue YF, Ma YH (2014) Bacillus alkalicola sp. nov., an alkaliphilic, gram-positive bacterium isolated from Zhabuye lake in Tibet, China. Curr Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s00284-014-0576-x
Zhang JJ, Kang Z, Ling ZM, Cao WL, Liu L, Wang M, Du GC, Chen J (2013) High-level extracellular production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase in Bacillus subtilis with optimized regulatory elements. Bioresource Technol 146:543–548
Zhou Y, Wei W, Che QL, Xu YX, Wang X, Huang X, Lai R (2008) Bacillus pallidus sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2850–2854
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Q. Wang for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by funds from the National Science and technology support program (2012BAD36B03) and Chinese Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1630052012017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yg., Gu, Fl., Li, Jh. et al. Bacillus vanillea sp. nov., Isolated from the Cured Vanilla Bean. Curr Microbiol 70, 235–239 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0707-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0707-4