Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between changes in IL-1β expression and intestinal apoptosis after chemotherapy. And we further determine whether interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) reduces apoptosis in vivo after 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) chemotherapy in the small intestine.
Methods
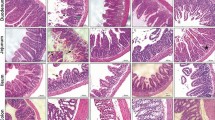
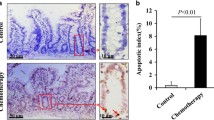
Intestinal mucositis was induced in mice by intraperitoneal injection of a single dose of 5-FU (200 mg/kg). IL-1Ra (1 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously twice daily after 5-FU injection. 5-FU-induced intestinal apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay. The expression of IL-1β induced by 5-FU in local intestinal tissue was examined by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Assessment of 5-FU-induced mucositis (histology, diarrhea scores, bowel weight) was performed. The apoptosis-related proteins were investigated by western blotting analysis. The proliferation of intestine was examined by immunohistological staining of PCNA. Viability of IEC-6 cells was determined using the CCK-8 assay. The apoptosis of IEC-6 cells was examined by Hoechst 33342 staining.
Results
The variation of IL-1β expression induced by 5-FU was in accordance with the changes in intestinal apoptosis. Administration of IL-1Ra could block the destructive effect of IL-1β and reduce apoptosis in the small intestinal crypt after chemotherapy. The protection against apoptosis was in accordance with the reduction of the up-regulation of Bax and caspase 3 and the elimination of the down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Moreover, IL-1Ra attenuated the severity of intestinal mucositis induced by 5-FU and enhanced intestinal crypt proliferation. In vitro experiments showed that IL-1Ra suppressed apoptosis and increased cell viability in enterocyte IEC-6 cells treated with 5-FU. Additionally, IL-1Ra did not affect the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-FU in tumor CT-26 xenograft mice.
Conclusions
Our studies elucidate that IL-1β is quite possibly involved in and mediated the course of intestinal apoptosis after 5-FU chemotherapy. Administered with IL-1Ra protects mice against intestinal apoptosis induced by 5-FU, relieves mucosal impairment of the small intestine, and facilitates the recovery of the intestinal mucosa. IL-1Ra treatment offers a novel promising strategy for the prevention and cure of chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis in clinical practice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen JM, Gibson RJ, Cummins AG et al (2006) Intestinal mucositis: the role of the Bcl-2 family, p53 and caspases in chemotherapy-induced damage. Support Care Cancer 14:713–731
Benson AB 3rd, Ajani JA, Catalano RB et al (2004) Recommended guidelines for the treatment of cancer treatment-induced diarrhea. J Clin Oncol 22:2918–2926
Symonds RP (1998) Treatment-induced mucositis: an old problem with new remedies. Br J Cancer 77:1689–1695
Watson AJ (1995) Necrosis and apoptosis in the gastrointestinal tract. Gut 37:165–167
Inomata A, Horii I, Suzuki K (2002) 5-Fluorouracil-induced intestinal toxicity: what determines the severity of damage to murine intestinal crypt epithelia? Toxicol Lett 133:231–240
Pritchard DM, Potten CS, Hickman JA et al (1998) The relationships between p53-dependent apoptosis, inhibition of proliferation, and 5-fluorouracil-induced histopathology in murine intestinal epithelia. Cancer Res 58:5453–5465
Anilkumar TV, Sarraf CE, Hunt T et al (1992) The nature of cytotoxic drug-induced cell death in murine intestinal crypts. Br J Cancer 65:552–558
Keefea DM, Brealey J, Goland GJ et al (2000) Chemotherapy for cancer causes apoptosis that precedes hypoplasia in crypts of the small intestine in humans. Gut 47:632–637
Logan RM, Gibson RJ, Bowen JM et al (2008) Characterisation of mucosal changes in the alimentary tract following administration of irinotecan: implications for the pathobiology of mucositis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:33–41
Logan RM, Stringer AM, Bowen JM et al (2008) Serum levels of NF-kappaB and pro-inflammatory cytokines following administration of mucotoxic drugs. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1139–1145
Giannoukakis N, Rudert WA, Ghivizzani SC et al (1999) Adenoviral gene transfer of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein to human islets prevents IL-1beta-induced beta-cell impairment and activation of islet cell apoptosis in vitro. Diabetes 48:1730–1736
Holmin S, Mathiesen T (2000) Intracerebral administration of interleukin-1beta and induction of inflammation, apoptosis, and vasogenic edema. J Neurosurg 92:108–120
Nesic O, Xu GY, McAdoo D et al (2001) IL-1 receptor antagonist prevents apoptosis and caspase-3 activation after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 18:947–956
Fortunato SJ, Menon R (2003) IL-1 beta is a better inducer of apoptosis in human fetal membranes than IL-6. Placenta 24:922–928
Ing DJ, Zang J, Dzau VJ et al (1999) Modulation of cytokine-induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis by nitric oxide, Bak, and Bcl-x. Circ Res 84:21–33
Mahr S, Neumayer N, Gerhard M et al (2000) IL-1beta-induced apoptosis in rat gastric enterochromaffin-like cells is mediated by iNOS, NF-kappaB, and Bax protein. Gastroenterology 118:515–524
Bowen JM, Gibson RJ, Keefe DM et al (2005) Cytotoxic chemotherapy upregulates pro-apoptotic Bax and Bak in the small intestine of rats and humans. Pathology 37:56–62
Kitada S, Krajewski S, Miyashita T et al (1996) Gamma-radiation induces upregulation of Bax protein and apoptosis in radiosensitive cells in vivo. Oncogene 12:187–192
Nita ME, Nagawa H, Tominaga O et al (1998) 5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines with modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. Br J Cancer 78:986–992
Dinarello CA (1997) Interleukin-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:253–265
Dewberry RM, King A, Crossman D et al (2008) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) modulates endothelial cell proliferation. FEBS Lett 582:886–890
Abbate A, Salloum FN, Vecile E et al (2008) Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits apoptosis in experimental acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 117:2670–2683
Sun CC, Pang JH, Cheng CY et al (2006) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) prevents apoptosis in ex vivo expansion of human limbal epithelial cells cultivated on human amniotic membrane. Stem Cells 24:2130–2139
Gibson RJ, Bowen JM, Inglis MR et al (2003) Irinotecan causes severe small intestinal damage, as well as colonic damage, in the rat with implanted breast cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:1095–1100
Potten CS, Grant HK (1998) The relationship between ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis and stem cells in the small and large intestine. Br J Cancer 78:993–1003
Rusai K, Huang H, Sayed N et al (2008) Administration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transpl Int 21:572–580
Chirivi RG, Garofalo A, Padura IM et al (1993) Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist inhibits the augmentation of metastasis induced by interleukin 1 or lipopolysaccharide in a human melanoma/nude mouse system. Cancer Res 53:5051–5054
McKenzieR C, Oran A, Dinarello CA et al (1996) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits subcutaneous B16 melanoma growth in vivo. Anticancer Res 16:437–441
Estrov Z, Kurzrock R, Estey E et al (1992) Inhibition of acute myelogenous leukemia blast proliferation by interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist and soluble IL-1 receptors. Blood 79:1938–1945
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z.-Q. Wu, X.-D. Han contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ZQ., Han, XD., Wang, Y. et al. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduced apoptosis and attenuated intestinal mucositis in a 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy model in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68, 87–96 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1451-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1451-5