Abstract
Background
Detailed investigation of the vasculature of the lateral aspect of the foot has rarely been presented. However, harvesting the flap in this area to cover defects of the foot and hand is highly important. Repair of soft-tissue defects at the forefoot remains a challenge in reconstructive surgery. This study explores the characteristics of the distal-based lateral dorsal cutaneous neuro-lateral plantar venofasciocutaneous flap pedicled with the lateral plantar artery perforator of the fifth metatarsal bone to establish a repair procedure for ulcers or defects in the forefoot region.
Methods
This study is divided into two parts: anatomical study and simulated operation. Thirty cadavers were utilized in the anatomical study after arterial injection. The tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal bone was used as the anatomical landmark. The lateral plantar artery perforator of the fifth metatarsal bone was identified through dissection. The perforators were dissected under a microscope. The details of the lateral plantar artery perforators, the distribution of the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve and lateral plantar vein, the anastomosis in the lateral plantar artery perforator of the fifth metatarsal bone, the nutrient vessels of the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve and lateral plantar vein, and other arteries of the lateral foot were recorded. The flap-raising procedure was performed on three fresh cadavers.
Results
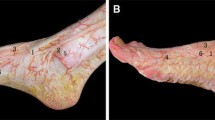
The lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve originated from sural nerve, traveled obliquely downward along the anterior lateral margin of the foot, and accompanied by the lateral plantar vein after bifurcation, and was eventually distributed on the lateral aspect of the foot. The nutrifying arteries to the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve and lateral plantar vein were present segmentally and mainly originated from the lateral plantar artery perforator of the fifth metatarsal bone. These nitrifying arteries constantly originated from the lateral plantar artery in the area of tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal, ran along the medial side of the fifth metatarsal, traveled between the fifth metatarsal bone and the lateral muscle group (the flexor digitorum brevis and the abductor digiti minimi muscles), pierced the aponeurosis, vascularized the skin of the anterior lateral plantar region, and resulted in many minute branches, which anastomosed with the lateral tarsal artery and fourth dorsal metatarsal artery. The anatomical study showed that (1) the vasculature pattern can roughly be classified into three types and (2) constant anastomoses occurred between the above-mentioned arteries in the lateral-dorsum region of the foot.
Conclusion
A reliable large- or medium-sized neuro-venocutaneous flap with lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve, lateral plantar vein, and nutrient vessels can be raised using only the perforator of the lateral plantar artery of the fifth metatarsal bone, which is thin, is in the immediate vicinity of the forefoot, and has a reliable retrograde blood supply. This flap can be considered an alternative means to reconstruct soft-tissue defects of the forefoot.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarante J, Martins A, Reis J (1988) A distally based median plantar flap. Ann Plast Surg 20:468–470
Bach AD, Leffler M, Kneser U, Kopp J, Horch RE (2007) The versatility of the distally based peroneus brevis muscle flap in reconstructive surgery of the foot and lower leg. Ann Plast Surg 58:397–404
Bhandari PS, Sobti C (1999) Reverse flow instep island flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1986–1989
Cavadas PC (2003) Reversed saphenous neurocutaneous island flap: clinical experience and evolution to the posterior tibial perforator-saphenous subcutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:837–839
Gabrielli C, Olave E, Mandiola E, Rodrigues CF, Prates JC (2001) The deep plantar arch in humans: constitution and topography. Surg Radiol Anat 23:253–258
Ishikura N, Heshiki T, Tsukada S (1995) The use of a free medialis pedis flap for resurfacing skin defects of the hand and digits: results in five cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:100–107
Karacaoglan N (1996) Distal foot coverage with a reverse dorsalis pedis flap. Ann Plast Surg 36:224
Kneser U, Bach AD, Polykandriotis E, Kopp J, Horch RE (2005) Delayed reverse sural flap for staged reconstruction of the foot and lower leg. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:1910–1917
Koshima I, Urushibara K, Inagawa K, Hamasaki T, Moriguchi T (2001) Free medial plantar perforator flaps for the resurfacing of finger and foot defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:1753–1758
Kurata S, Hashimoto H, Terashi H, Honda T, Takayasu S (1992) Reconstruction of the distal foot dorsum with a distally based extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap. Ann Plast Surg 29:76–79
Li L, Song D, Zheng H, Hou C, Lin J, **e Z, Zhuang Y (2015) Anatomical basis of the reverse lateral plantar artery perforator flap design. Surg Radiol Anat 37:983–988
Masquelet AC, Romana MC (1990) The medialis pedis flap: a new fasciocutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 85:765–772
Masquelet AC, Romana MC, Wolf G (1992) Skin island flaps supplied by the vascular axis of the sensitive superficial nerves: anatomic study and clinical experience in the leg. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:1115–1121
Morrison WA, Crabb DM, O’Brien BM, Jenkins A (1983) The instep of the foot as a fasciocutaneous island and as a free flap for heel defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 72:56–65
Nakajima H, Imanishi N, Fukuzumi S, Minabe T, Fukui Y, Miyasaka T, Kodama T, Aiso S, Fu**o T (1999) Accompanying arteries of the lesser saphenous vein and sural nerve: anatomic study and its clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:104–120
Noever G, Bruser P, Kohler L (1986) Reconstruction of heel and sole defects by free flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 78:345–352
Reiffel RS, McCarthy JG (1980) Coverage of heel and sole defects: a new subfascial arterialized flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 66:250–260
Roll C, Prantl L, Nerlich M, Kinner B (2008) Osteo-fasciocutaneous parascapular flap transfer for reconstruction of the first ray of the foot. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128:857–863
Ruan HJ, Cai PH, Schleich AR, Fan CY, Chai YM (2010) The extended peroneal artery perforator flap for lower extremity reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 64:451–457
Sakai S, Soeda S, Kanou T (1988) Distally based lateral plantar artery island flap. Ann Plast Surg 21:165–169
Shanahan RE, Gingrass RP (1979) Medial plantar sensory flap for coverage of heel defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 64:295–298
Song D, Yang X, Wu Z, Li L, Wang T, Zheng H, Hou C (2016) Anatomic basis and clinical application of the distally based medialis pedis flaps. Surg Radiol Anat 38:213–221
Taylor GI (2003) The angiosomes of the body and their supply to perforator flaps. Clin Plast Surg 30:331–342 (v)
Trevisan C, Mattavelli M, Monteleone M, Marinoni EC (2008) Pulp thumb defect reconstruction using a twin neurovascular island flaps: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128:195–198
Wu Z, Song D, Lin J, Zheng H, Hou C, Li L, Wang T (2015) Anatomic basis of the distally based venocutaneous flap on the medial plantar artery of the hallux with medial plantar vein and nutrient vessels: a cadaveric dissection. Surg Radiol Anat 37:975–981
Xu YQ, Zhu YL, Wu NX, Li J, Yang J, He XQ (2010) Distal foot coverage with reverse dorsal pedal neurocutaneous flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:164–169
Yoshimura Y, Nakajima T, Kami T (1985) Distally based abductor digiti minimi muscle flap. Ann Plast Surg 14:375–377
Zhuang YH, Zheng HP, Lin SQ, Xu DC (2011) Vasculature at the medial aspect of the foot and clinical application of flaps based on it for forefoot reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:1967–1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
T. Wang and J. Lin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Lin, J., Song, D. et al. Anatomical basis and design of the distally based lateral dorsal cutaneous neuro-lateral plantar venofasciocutaneous flap pedicled with the lateral plantar artery perforator of the fifth metatarsal bone: a cadaveric dissection. Surg Radiol Anat 39, 141–147 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1712-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1712-z