Abstract
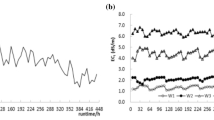
This study investigated the characteristics of emitter clogging substance in 16 kinds of drip irrigation emitters using 3 kinds of water sources that could typically induce composite clogging in the Yellow River irrigation area. The research results indicate that there was remarkable randomness in the behavior of composite clogging substances in a single emitter, and peak randomness (\(\Delta F_{Q}^{t}\)) values were 19.5–20.8%, 20.5–22.4% and 25.9–28.2% higher than that with physical, chemical and biological clogging, respectively. Clogging in a single emitter also exhibited recoverability (\(R_{Q}^{{{\text{CD}}}}\)) which would be lost when the clogging degree reached 60–75%, and recoverability (\(R_{Q}^{{{\text{CD}}}}\)) showed the opposite variation rule to randomness (\(\Delta F_{Q}^{t}\)). Though clogging in a single emitter was associated with certain randomness and recoverability, the overall variation of the micro-irrigation system's average discharge variation ratio (Dra) and Christiansen’s uniformity (CU) was not affected. Instead, the two showed relatively consistent dynamic variation of mild fluctuation followed by acute descending. The fluctuation trend during the earlier stage lasted from 128 to 660 h, and descending branch slopes of Dra and CU during the later stage were 0.09–0.12 and 0.13–0.21, respectively. In terms of various types of emitters, \(\Delta F_{Q}^{t}\) generally demonstrated dynamic variation for a tape emitter (highest), a single-side labyrinth emitter (slightly lower), a cylindrical emitter (even lower) and a flat emitter (lowest). However, the dynamic variation of \(R_{Q}^{{{\text{CD}}}}\), Dra and CU were inverse. As far as various water sources were concerned, mixing water had the highest \(\Delta F_{Q}^{t}\), followed by Yellow River water, and surface lake water had the lowest \(\Delta F_{Q}^{t}\), while variation characteristics of \(R_{Q}^{{{\text{CD}}}}\), Dra and CU among the three water sources were inverse. The present study could provide reference for revealing the characteristics of composite clogging in emitters, thus constructing effective clogging control methods.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benham B, Ross B (2002) Filtration, treatment and maintenance considerations for micro-irrigation system. Va Coop Ext 442–757
Cappa A, Scicolone B (2005) Assessing dripper clogging and filtering performance using municipal wastewater. Irrig Drain 54(S1):71–79
Capra A, Scicolone B (2004) Emitter and filter tests for wastewater reuse by drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 68(2):135–149
EP405 1 (2003) Design and installation of micro-irrigation systems. ASABE Standards
GB/T 50485 (2009) Technical specifications of micro-irrigation engineering
Li JM (2008) The appearance and treatment measures of surface quality difference of single side labyrinth drip irrigation tape. Mod Agric 10:60–61 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li WS (2016) Suitability evaluation and selection method for emitters products under drip irrigation with Yellow River water. Thesis. China Agricultural University, China
Li GY, Wang JD, Alam M et al (2006a) Influence of geometrical parameters of labyrinth flow path of drip emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance. Trans ASABE 49(3):637–643
Li YK, Yang PL, Ren SM et al (2006b) Hydraulic characterizations of tortuous flow path drip irrigation emitter. J Hydrodyn 18(4):449–457
Li JS, Chen L, Li Y (2009) Comparison of clogging in drip emitters during application of sewage effluent and groundwater. Trans ASABE 52(4):1203–1211
Li YK, Liu YZ, Li GB et al (2010) The surface topographic characteristics of suspending sediment in two reclaimed wastewater and its effects on the clogging in labyrinth drip irrigation emitters. Irrig Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-010-0257-x
Liu HJ, Huang GH (2009) Laboratory experiment on drip emitter clogging with fresh water and treated sewage effluent. Agric Water Manag 96:745–756
Ma JX (2010) Causes of edge cracking with heat indentation of single side labyrinth. Water Sav Irrig 6:53–53 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma N, Qi XP (2015) Analysis on product quality on singe side labyrinth drip irrigation tape in **njiang region. Guangzhou Chem Ind Technol 43(13):52–54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Niu WQ, Yu LM, Wu PT et al (2009) Influence of angle of labyrinth channels on anti-clogging performance of emitter. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 40(9):51–67 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Pei YT, Li YK, Liu YZ et al (2014) Eight emitters clogging characteristics and its suitability evaluation under on-site reclaimed water drip irrigation. Irrig Sci 32(2):141–157
Puig-Bargués J, Barragán J, De Cartagena FR (2005) Filtration of effluents for microirrigation systems. Trans ASAE 48(3):969–978
Ravina EP, Sofer ZA, Marcu AS et al (1992) Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig Sci 13(3):129–139
Ravina E, Sofer Z, Marcu A et al (1997) Control of clogging in drip irrigation with stored treated municipal sewage effluent. Agric Water Manag 33(2):127–137
Wu XB (2006) Experimental study of drip irrigation system anti-clogging performance under reclaimed water irrigation. China Agricultural University, Bei**g (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HW, Yang LL, Han QW et al (2015) Research on the salt block of different types of emitters. Water Sav Irrig 7:36–39 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhangzhong LL, Yang PL, Ren SM et al (2016) Chemical-clogging of emitters and evaluation of their suitability for saline water drip irrigation. Irrig Drain. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.1972
Zhou B, Li YK, Song P et al (2014) Dynamic characteristics and inducing mechanism of emitter clogging in the drip irrigation system using Yellow River water. J Irrig Drain 33(4/5):123–128
Zhou B, Li YK, Liu YZ et al (2015) Effect of drip irrigation frequency on emitter clogging using reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 33(3):221–234
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Fund of China (51479197, 51321001) and the Special Scientific Research Fund of Public Welfare Profession of China (201401078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by J. L. Chávez.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Li, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Composite clogging characteristics of emitters in drip irrigation systems. Irrig Sci 37, 105–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-018-0605-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-018-0605-9