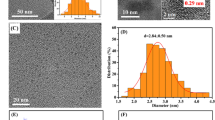
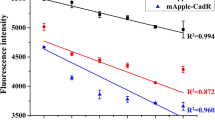
Abstract
Heavy metal(loid)s such as Cd and Hg adversely affect human health and are therefore strictly regulated and monitored; however, their quantitation in the environment is usually performed by expensive and time-consuming instrumental analysis techniques, which necessitates the search for more practical alternatives. Herein, we prepare enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)–based biomolecules for metal(loid) sensing by insertion of metal-binding loops (MBLs) into a loop region of eGFP to render this protein inactive and show that the binding of metal ions to MBLs induces a conformational change and restores the original activity. Specifically, eGFP with an MBL sequenced as CTTCGCG regains fluorescence upon exposure to Cd and Hg, which allows the above metals to be quantified in the concentration range of 0–5 μM. For practical applicability verification, the developed sensing platform is used to quantify Cd in artificially amended soil and water samples. Although the obtained results imply that sensor performance needs to be significantly improved, the presented design concept is believed to be of high value to researchers in the field of heavy metal sensing and facilitate the development of new biosensors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann AA (2002) Speciation of heavy metals in environmental water by ion chromatography coupled to ICP–MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 372(3):448–452
Baumann B, van der Meer JR (2007) Analysis of bioavailable arsenic in rice with whole cell living bioreporter bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 55(6):2115–2120
Belkin S (2003) Microbial whole-cell sensing systems of environmental pollutants. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(3):206–212
Brocklehurst KR, Hobman JL, Lawley B, Blank L, Marshall SJ, Brown NL, Morby AP (1999) ZntR is a Zn (II)-responsive MerR-like transcriptional regulator of zntA in Escherichia coli. Mol Micribiol 31(3):893–902
Cabantous S, Terwilliger TC, Waldo GS (2005) Protein tagging and detection with engineered self-assembling fragments of green fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 23(1):102–107
Cabantous S, Nguyen HB, Pedelacq J-D, Koraïchi F, Chaudhary A, Ganguly K, Lockard MA, Favre G, Terwilliger TC, Waldo GS (2013) A new protein-protein interaction sensor based on tripartite split-GFP association. Sci Rep 3:2854
Harms H, Wells MC, van der Meer JR (2006) Whole-cell living biosensors—are they ready for environmental application? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(3):273–280
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68(1):167–182
Kang Y, Lee W, Jang G, Kim B-G, Yoon Y (2018a) Modulating the sensing properties of Escherichia coli-based bioreporters for cadmium and mercury. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(11):4863–4872
Kang Y, Lee W, Kim S, Jang G, Kim B-G, Yoon Y (2018b) Enhancing the copper-sensing capability of Escherichia coli-based whole-cell bioreporters by genetic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(3):1513–1521
Küpper H, Küpper F, Spiller M (1998) In situ detection of heavy metal substituted chlorophylls in water plants. Photosynth Res 58(2):123–133
Kuswandi B (2003) Simple optical fibre biosensor based on immobilised enzyme for monitoring of trace heavy metal ions. Anal Bioanal Chem 376(7):1104–1110
Lee W, Kim H, Kang Y, Lee Y, Yoon Y (2019) A biosensor platform for metal detection based on enhanced green fluorescent protein. Sensors 19(8):1846
Peralta-Videa JR, Lopez ML, Narayan M, Saupe G, Gardea-Torresdey J (2009) The biochemistry of environmental heavy metal uptake by plants: implications for the food chain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41(8–9):1665–1677
Rawson DM, Willmer AJ, Turner AP (1989) Whole-cell biosensors for environmental monitoring. Biosensors 4(5):299–311
Robbens J, Dardenne F, Devriese L, De Coen W, Blust R (2010) Escherichia coli as a bioreporter in ecotoxicology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(5):1007–1025
Schalk IJ, Hannauer M, Braud A (2011) New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ Microbiol 13(11):2844–2854
Shekhawat SS, Ghosh I (2011) Split-protein systems: beyond binary protein–protein interactions. Curr Opin Chem Biol 15(6):789–797
Singh A, Prasad SM (2011) Reduction of heavy metal load in food chain: technology assessment. Rev Environ Sci Bio 10(3):199–214
Stynen B, Tournu H, Tavernier J, Van Dijck P (2012) Diversity in genetic in vivo methods for protein-protein interaction studies: from the yeast two-hybrid system to the mammalian split-luciferase system. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76(2):331–382
Turpeinen R, Virta M, Häggblom MM (2003) Analysis of arsenic bioavailability in contaminated soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(1):1–6
Yoon Y, Kang Y, Chae Y, Kim S, Lee Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016a) Arsenic bioavailability in soils before and after soil washing: the use of Escherichia coli whole-cell bioreporters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(3):2353–2361
Yoon Y, Kim S, Chae Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016b) Evaluation of bioavailable arsenic and remediation performance using a whole-cell bioreporter. Sci Total Environ 547:125–131
Yoon Y, Kim S, Chae Y, Kang Y, Lee Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016c) Use of tunable whole-cell bioreporters to assess bioavailable cadmium and remediation performance in soils. PLoS One 11(5):e0154506
Yoon Y, Kang Y, Lee W, Oh K-C, Jang G, Kim B-G (2018) Modulating the properties of metal-sensing whole-cell bioreporters by interfering with Escherichia coli metal homeostasis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 28(2):323–329
Yuan C-g, Shi J-b, He B, Liu J-f, Liang L-n, Jiang G-b (2004) Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environ Int 30(6):769–783
Zhylyak G, Dzyadevich S, Korpan Y, Soldatkin A, El’Skaya A (1995) Application of urease conductometric biosensor for heavy-metal ion determination. Sens and Actuators B Chem 24(1–3):145–148
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (NRF-2017R1E1A1A01073894 to Y. Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 206 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Lee, W. & Yoon, Y. Heavy metal(loid) biosensor based on split-enhanced green fluorescent protein: development and characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 6345–6352 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09908-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09908-7