Abstract
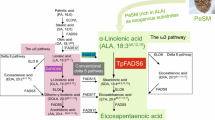
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid for human beings. At present, the production of commercially available long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, mainly from wild-caught ocean fish, is struggling to meet the increasing demand for EPA. Production of EPA by microorganisms may be an alternative, effective and economical method. The oleaginous fungus Pythium splendens RBB-5 is a potential source of EPA, and thanks to the simple culture conditions required, high yields can be achieved in a facile manner. In the study, lipid metabolomics was performed in an attempt to enhance EPA biosynthesis in Pythium splendens. Synthetic, metabolic regulation and gene expression analyses were conducted to clarify the mechanism of EPA biosynthesis, and guide optimization of EPA production. The results showed that the Δ6 desaturase pathway is the main EPA biosynthetic route in this organism, and ∆6, ∆12 and Δ17 desaturases are the rate-limiting enzymes. All the three desaturase genes were separately introduced into the parent strain to increase the flow of fatty acids into the Δ6 desaturase pathway. Enhanced expression of these key enzymes, in combination with improved regulation of metabolism, resulted in a maximum yield of 1.43 g/L in the D12 transgenic strain, which represents a tenfold increase over the parent strain before optimization. This is the higher EPA production yield yet reported for a microbial system. Our findings may allow the production of EPA at an industrial scale, and the strategy employed could be used to increase the production of EPA or other lipids in oleaginous microorganisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert DH, Rhamy RK, Coniglio JG (1979) Desaturation of eicosa-11, 14-dienoic acid in human testes. Lipids 14(5):498–500. doi:10.1007/BF02533468
Bardon S, Le MT, Alessandri JM (1996) Metabolic conversion and growth effects of n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the T47D breast cancer cell line. Cancer Lett 99(1):51–58. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(95)04037-4
Cheng MH, Walker TH, Hulbert GJ, Raman DR (1999) Fungal production of eicosapentaenoic and arachidonic acids from industrial waste streams and crude soybean oil. Bioresour Technol 67(2):101–110
Dedyukhina EG, Chistyakova TI, Vainshtein MB (2011) Biosynthesis of arachidonic acid by micromycetes (review). Appl Biochem Micro 47(2):109–117. doi:10.1134/S0003683811020037
Domingo JL (2007) Omega-3 fatty acids and the benefits of fish consumption: is all that glitters gold? Environ Int 33(7):993–998. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.05.001
Farag MA, Huhman DV, Dixon RA, Sumner LW (2008) Metabolomics reveals novel pathways and differential mechanistic and elicitor-specific responses in phenylpropanoid and isoflavonoid biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula cell cultures. Plant Physiol 146(2):387–402. doi:10.1104/pp.107.108431
Higashiyama K, Fujikawa S, Park EY, Shimizu S (2002) Production of arachidonic acid by Mortierella fungi. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 7(5):252–262. doi:10.1007/BF02932833
Hu JR (2011) Mutation breeding of high yielding strain of eicosapentaenoic acid and effect of citric acid on the lipid synthesis. Food and Fermentation Industries 37(2):46–49
Hu JR, Zhou PP, Zhu YM, Ren L, Yu LJ (2011) Isolation of eicosapentaenoic acid-producing fungi from soil based on PCR amplification. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung C 66(7):429–433. doi:10.5560/ZNC.2011.66c0429
Jacobson TA (2008) Role of n-3 fatty acids in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr 87(6):1981–1990
** MJ, Huang H, **ao AH, Gao Z, Liu X, Peng C (2009) Enhancing arachidonic acid production by Mortierella alpina ME-1 using improved mycelium aging technology. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 32(1):117–122. doi:10.1007/s00449-008-0229-1
Li Q, Bai Z, O'Donnell A, Harvey LM, Hoskisson PA, McNeil B (2011) Oxidative stress in fungal fermentation processes: the roles of alternative respiration. Biotechnol Lett 33(3):457–467. doi:10.1007/s10529-010-0471-x
Liu JM, Li DR, Yin YT, Wang H, Li MT, LJ Y (2011) ∆6-Desaturase from Mortierella alpina: cDNA cloning, expression, and phylogenetic analysis. Biotechnol Lett 33(10):1985–1991. doi:10.1007/s10529-011-0650-4
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△CT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Manger MS, Strand E, Ebbing M, Seifert R, Refsum H, Nordrehaug JE, Nilsen DW, Drevon CA, Tell GS, Bleie O, Vollset SE, Pedersen ER, Nygard O (2010) Dietary intake of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and coronary events in Norwegian patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Clin Nutr 92(1):244–251. doi:10.3945/ ajcn.2010.29175
Mullen A, Loscher CE, Roche HM (2010) Anti-inflammatory effects of EPA and DHA are dependent upon time and dose-response elements associated with LPS stimulation in THP-1-derived macrophages. J Nutr Biochem 21:444–450. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.02.008
Napier JA, Michaelson LV, Sayanova O (2003) The role of cytochrome b5 fusion desaturases in the synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prostag Leukotr Ess 68(2):135–143. doi:10.1016/S0952-3278(02)00263-6
Pardini RS (2006) Nutritional intervention with omega-3 fatty acids enhances tumor response to anti-neoplastic agents. Chem Biol Interact 162(2):89–105. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2006.05.012
Park WJ, Kothapalli KSD, Lawrence P, Tyburczy C, Brenna JT (2009) An alternate pathway to long-chain polyunsaturates: the FADS2 gene product ∆8-desaturases 20:2 n-6 and 20:3 n-3. J Lipid Res 50(6):1195–1202. doi:10.1194/jlr.M800630-JLR200
Qu L, Ji XJ, Ren LJ, Nie ZK, Feng Y, WJ W, Ouyang PK, Huang H (2011) Enhancement of docosahexaenoic acid production by Schizochytrium sp. using a two-stage oxygen supply control strategy based on oxygen transfer coefficient. Lett Appl Microbiol 52(1):22–27. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02960.x
Sayanova OV, Napier JA (2004) Eicosapentaenoic acid: biosynthetic routes and the potential for synthesis in transgenic plants. Phytochem 65:147–158. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2003.10.017
Su JY (2006) Nutrition and development tendency of soybean products. China Oils and Fats 31(8):40–41. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1003-7969.2006.08.012
Wang L, Chen W, Feng Y, Ren Y, ZN G, Chen HQ, Wang HC, Thomas MJ, Zhang BX, Berquin IM, Li Y, JS W, Zhang HX, Song YD, Liu X, Norris JS, Wang S, Du P, Shen JG, Wang N, Yang YL, Wang W, Feng L, Ratledge C, Zhang H, Chen YQ (2011) Genome characterization of the oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina. PLoS One 6(12):e28319. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028319
Warude D, Joshi K, Harsulkar A (2006) Polyunsaturated fatty acids: biotechnology. Crit Rev Biotechnol 26(2):83–93. doi:10.1080/07388550600697479
Wen ZY, Chen F (2003) Heterotrophic production of eicosapentaenoic acid by microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 21:273–294. doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(03)00051-X
Wu JL, Li XZ, Zhang HS, Wang J, Zhang XX (2012) Nutrition ingredient of soybean and its products. Farm Products Processing 8:53–56,77. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9646(C).2012.08.001
Wynn JP, Hamid AA, Ratledge C (1999) The role of malic enzyme in the regulation of lipid accumulation in filamentous fungi. Microbiology 145(8):1911–1917. doi:10.1099/13500872-145-8-1911
Xue ZX, Sharpe PL (2013) Production of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. Nature Bio 31(8):734–740. doi:10.1038/nbt.2622
Yazawa K (1996) Production of eicosapentaenoic acid from marine bacteria. Lipids 31(1):297–300. doi:10.1007/BF02637095
Yu LJ, Li W, Mei XG, Wu YN (1999) Study on improving the effect of metabolic pathway regulation on taxol biosynthesis. J Hua zhong Univ of Sci & Tech 27(4):100–103
Zhang Y, Ratledge C (2008) Multiple isoforms of malic enzyme in the oleaginous fungus, Mortierella alpina. Mycol Res 112(6):725–730. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2008.01.003
Zhang RJ, Zhu YM, Ren L, Zhou PP, JR H, LJ Y (2013) Identification of a fatty acid D6-desaturase gene from the eicosapentaenoic acid-producing fungus Pythium splendens RBB-5. Biotechnol Lett 35(3):431–438. doi:10.1007/s10529-012-1101-6
Zhu M, Zhou PP, LJ Y (2002) Extraction of lipids from Mortierella alpina and enrichment of arachidonic acid from the fungal lipids. Bioresour Technol 84(1):93–95. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00028-7
Zhu YM, Zhou PP, JR H, Zhang RJ, Ren L, Li MT, Ning F, Chen W, LJ Y (2013) Characterization of Pythium transcriptome and gene expression analysis for different fermentation stage. PLoS One 8(6):e65552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065552
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20976065). We thank Mrs. Hong Cheng and Mrs. **aoman Gu of the Analysis and Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for GC–MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Zhou, P., Zhu, Y. et al. Improved eicosapentaenoic acid production in Pythium splendens RBB-5 based on metabolic regulation analysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 3769–3780 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8044-0