Abstract
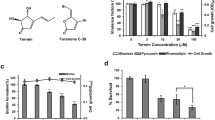
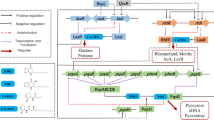
Quorum sensing (QS) has been recognized to play an important role in many pathogenic bacteria and has become a novel target for the treatment of infectious disease. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is highly resistant to antibiotic treatment, largely due to its ability to form biofilms, and QS was found to be essential for the creation of mature, differentiated biofilms in this organism. A novel QS inhibitor, C2 (N-decanoyl-l-homoserine benzyl ester), can attenuate not only total protease and elastase activity, but also swarming motility and biofilm formation in the P. aeruginosa strain PAO1. We demonstrated that C2 showed a significant inhibitory effect on biofilm formation in a dose-dependent manner. Data from cDNA microarray showed that expression of 382 genes (∼6.4 %) was significantly different with C2 treatment, including downregulation of 215 genes (∼3.6 %) and upregulation of 167 genes (∼2.8 %). Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed that the gene qscR, which encodes the LuxR-type receptor QscR (quorum sensing control repressor), was significantly upregulated by 375.4 % during C2 treatment. The mechanism by which C2 inhibits biofilm formation may be through repression of Las and Rhl systems by QscR. C2 was shown to reduce biofilm formation; in combination with antibiotics, it abolishes biofilm formation completely. This result may pave the way for new treatments for biofilm-related infections and may be exploited for the general prevention of biofilm formation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes LM, Ferreira RR, Buckner MC, Finlay BB (2010) Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology-(UK) 156:2271–2282
Bernard CS, Bordi C, Termine E, Filloux A, de Bentzmann S (2009) Organization and pprb-dependent control of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa tad locus, involved in flp pilus biology. J Bacteriol 191:1961–1973
Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M (2007) The role of quorum sensing in the pathogenicity of the cunning aggressor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:409–414
Choi SH, Greenberg EP (1991) The C-terminal region of the Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein contains an inducer-independent lux gene activating domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88, 11115–11119
Chugani S, Greenberg EP (2010) LuxR homolog-independent gene regulation by acyl-homoserine lactones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(23):10673–10678
Darzins A (1994) Characterization of a Pseudomonas-aeruginosa gene-cluster involved in pilus biosynthesis and twitching motility—sequence similarity to the chemotaxis proteins of enterics and the gliding bacterium myxococcus-xanthus. Mol Microbiol 11:137–153
Fuqua C (2006) The QscR quorum-sensing regulon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an orphan claims its identity. J Bacteriol 188:3169–3171
Geller DE, Pitlick WH, Nardella PA, Tracewell WG, Ramsey BW (2002) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of aerosolized tobramycin in cystic fibrosis. Chest 122(1):219–226
Ha CW, Park SJ, Im SJ, Park SJ, Lee JH (2012) Interspecies signaling through QscR, a quorum receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Cells 33:53–59
Harmsen M, Yang L, Pamp SJ, Tolker-Nielsen T (2010) An update on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation, tolerance, and dispersal. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 59(3):253–268
Hentzer M, Wu H, Andersen JB, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Bagge N, Kumar N, Schembri MA, Song ZJ, Kristoffersen P, Manefield M, Costerton JW, Molin S, Eberl L, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2003) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. Embo J 22:3803–3815
Holloway BW, Krishnapillai V, Morgan AF (1979) Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev 43:73–102
Ishida T, Ikeda T, Takiguchi N, Kuroda A, Ohtake H, Kato J (2007) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by n-acyl cyclopentylamides. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3183–3188
Kohler T, Curty LK, Barja F, van Delden C, Pechere JC (2000) Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J Bacteriol 182:5990–5996
Landini P, Antoniani D, Burgess J, Grant NR (2010) Molecular mechanisms of compounds affecting bacterial biofilm formation and dispersal. Appl Microbiol Biotech 86(3):813–823
Laskowski MA, Kazmierczak BI (2006) Mutational analysis of rets, an unusual sensor kinase-response regulator hybrid required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Infect Immun 74:4462–4473
Laskowski MA, Osborn E, Kazmierczak BI (2004) A novel sensor kinase-response regulator hybrid regulates type III secretion and is required for virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 54:1090–1103
Ledgham F, Ventre I, Soscia C, Foglino M, Sturgis JN, Lazdunski A (2003) Interactions of the quorum sensing regulator qscr: interaction with itself and the other regulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasr and rhlr. Mol Microbiol 48:199–210
Lee JH, Lequette Y, Greenberg EP (2006) Activity of purified qscr, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum-sensing transcription factor. Mol Microbiol 59:602–609
Lequette Y, Lee JH, Ledgham F, Lazdunski A, Greenberg EP (2006) A distinct qscr regulon in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing circuit. J Bacteriol 188:3365–3370
Liang HH, Deng X, Ji QJ, Sun F, Shen T, He C (2012) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa global regulator VqsR directly inhibits QscR to control quorum-sensing and virulence gene expression. J Bacteriol 194(12):3098–3108
Lintz MJ, Oinuma K, Wysoczynski CL, Greenberg EP, Churchill ME (2011) Crystal structure of QscR, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing signal receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:15763e15768
Liu HB, Lee JH, Kim JS, Park S (2010) Inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing regulator, qscr. Biotechnol Bioeng 106:119–126
Mattmann ME, Shipway PM, Heth NJ, Blackwell HE (2011) Potent and selective synthetic modulators of a quorum sensing repressor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa identified from second-generation libraries of n-acylated l-homoserine lactones. ChemBioChem 12:942–949
Oinuma KI, Greenberg EP (2011) Acyl-homoserine lactone binding to and stability of the orphan Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing signal receptor qscR. J Bacteriol 193(2):421–428
Park SJ, Liu HB, Park SH, Lee JH (2013) Modulation of QscR, a quorum sensing receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, by truncation of a signal binding domain. Res Microbiol 164:375–381
Pesci EC, Milbank JB, Pearson JP, McKnight S, Kende AS, Greenberg EP, Iglewski BH. (1999) Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 11229–11234
Rudrappa T, Bais HP (2008) Curcumin, a known phenolic from curcuma longa, attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1 in whole plant and animal pathogenicity models. J Agric Food Chem 56:1955–1962
Schuster M, Lostroh CP, Ogi T, Greenberg EP (2003) Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: a transcriptome analysis. J Bacteriol 185:2066–2079
Schweizer HP (2003) Efflux as a mechanism of resistance to antimicrobials in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related bacteria: unanswered questions. Genet Mol Res 2:48–62
Smith KM, Bu YG, Suga H (2003) Induction and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by synthetic autoinducer analogs. Chem Biol 10:81–89
Sobke A, Klinger M, Hermann B, Sachse S, Nietzsche S, Makarewicz O, Keller PM, Pfister W, Straube E (2012) The urinary antibiotic 5-nitro-8-hydroxyquinoline (nitroxoline) reduces the formation and induces the dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by chelation of iron and zinc. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(11):6021–6025
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman F, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GKS, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964
Ueda A, Wood TK (2009) Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase tpbA (PA3885). Plos Pathogens 5(6):e1000483
Venturi V, Friscina A, Bertani I, Devescovi G, Aguilar C (2004) Quorum sensing in the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Res Microbiol 155:238–244
Wagner-Dobler I, Thiel V, Eberl L, Allgaier M, Bodor A, Meyer S, Ebner S, Hennig A, Pukall R, Schulz S (2005) Discovery of complex mixtures of novel long-chain quorum sensing signals in free-living and host-associated marine alphaproteo bacteria. Chembiochem 6:2195–2206
Whitchurch CB, Hobbs M, Livingston SP, Krishnapillai V, Mattick JS (1991) Characterization of a Pseudomonas-aeruginosa twitching motility gene and evidence for a specialized protein export system widespread in eubacteria. Gene 101:33–44
Yang YX, Xu ZH, Zhang YQ, Tian J, Weng LX, Wang LH (2012) A new quorum-sensing inhibitor attenuates virulence and decreases antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Microbiol 50(6):987–993
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB933301), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81273409, 90813010), and the Ministry of Education of China (IRT1148). We also acknowledge the Pseudomonas Genome Database publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, LX., Yang, YX., Zhang, YQ. et al. A new synthetic ligand that activates QscR and blocks antibiotic-tolerant biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 2565–2572 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5420-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5420-x