Abstract
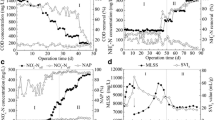
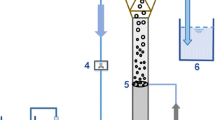
This study studied the cultivation of granules from an expanded granular sludge bed reactor that simultaneously transforms sulfates, nitrates, and oxygen to elementary sulfur, nitrogen gas, and carbon dioxides, respectively. The living cells accumulate at the granule outer layers, as revealed by the multicolor staining and confocal laser scanning microscope technique. The microbial community comprises sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB, Desulfomicrobium sp.), heterotrophic (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Sulfurospirillum sp.), and autotrophic denitrifiers (Sulfurovum sp. and Paracoccus denitrificans) whose population dynamics at different sulfate and nitrate loading rates are monitored with the single-strand conformation polymorphism and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis technique. The Desulfomicrobium sp. presents one of the dominating strains following reactor startup. At high sulfate and nitrate loading rates, the heterotrophic denitrifiers overcompete autotrophic denitrifiers to reduce SRB activities. Conversely, suddenly reducing nitrate loading rates completely removes the heterotrophic denitrifier Sulfurospirillum sp. from the granules and activates the autotrophic denitrifiers. The physical fixation of different groups of functional strains in granules fine-tunes the strains’ activities, and hence the reactor performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Physiological characterization and interactions of isolates in phenol-degrading aerobic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:899–905
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Chen C, Ren NQ, Wang AJ, Yu ZG, Lee DJ (2008) Simultaneous biological removal of sulfur, nitrogen and carbon using EGSB reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:1057–1063
Chen MY, Lee DJ, Tay JH, Show KY (2007) Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:467–474
Chuang SH, Pai TY, Horng RY (2005) Biotreatment of sulfate-rich wastewater in an anaerobic/micro-aerobic bioreactor system. Environ Technol 26:993–1001
De Smul A, Geothals L, Verstraete W (1999) Effect of COD to sulphate ratio and temperature in expanded-granular-sludge-blanket reactors for sulphate reduction. Process Biochem 34:407–416
De Smul A, Verstraete W (1999) Retention of sulfate-reducing bacteria in expanded granular-sludge-blanket reactors. Water Environ Res 71:427–431
Dries J, De Smul A, Goethals L, Grootaerd H, Verstraete W (1998) High rate biological treatment of sulfate-rich wastewater in an acetate-fed EGSB reactor. Biodegradation 9:103–111
Hubert C, Voordouw G (2007) Oil field souring control by nitrate-reducing Sulfurospirillum spp. that outcompete sulfate-reducing bacteria for organic electron donors. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2644–2652
Inagaki F, Takai K, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K (2004) Sulfurovum lithotrophicm gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoauthtroph within the epsilon-Protebacteria isolated from Okinawa Torugh hydrothermal sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1477–1482
Kim S, Jung H, Kim KS, Kim IS (2004) Treatment of high nitrate-containing wastewaters by sequential heterotrophic and autotrophic denitrification. J Environ Eng ASCE 130:1475–1480
Kodama Y, Ha LT, Watanabe K (2007) Sulfurospirillum cavolei sp nov, a facultatively anaerobic sulfur-reducing bacterium isolated from an underground crude oil storage cavity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:827–831
Maidak BL, Cole JR, Parker CT, Garrity GM, Larsen N, Li B, Lilburn TG, McCaughey MJ, Olsen GJ, Overbeek R, Pramanik S, Schmidt TM, Tiedje JM, Woese CR (1999) A new version of the RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 27:171–173
Reyes-Avila J, Razo-Flores, Gomez J (2004) Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen, carbon and sulfur by denitrification. Water Res 38:3313–3321
Rozanova EP, Nazina TN, Galushko AS (1988) Isolation of a new genus of sulfate-reducing bacteria and description of a new species of this genus, Desulfomicrobium apsheronum gen. nov., sp. nov. Mikrobiologiya 57:634–641
Vallero MVG, Lens PNL, Bakker C, Lettinga G (2003) Sulfidogenic volatile fatty acid degradation in a baffled reactor. Water Sci Technol 48:81–88
Weijma J, Bots EAA, Tandlinger G, Stams AJM, Pol LWH, Lettinga G (2002) Optilisation of sulphate reduction in a methanol-fed thermophilic bioreactor. Water Res 36:1825–1833
Weijma J, Pol LWH, Stams AJM, Lettinga G (2000) Performance of a thermophilic sulfate and sulfite reducing high rate anaerobic reactor fed with methanol. Biodegradation 11:429–439
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 50638020) and Ministry of Education of China (Development of simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification process and the control strategy for high strength wastewater, New Century Distinguished Young Scientist Supporting Plan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Ren, N., Wang, A. et al. Microbial community of granules in expanded granular sludge bed reactor for simultaneous biological removal of sulfate, nitrate and lactate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 1071–1077 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1503-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1503-5