Abstract
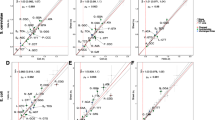
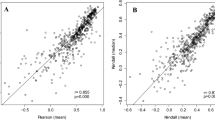
In free-living microorganisms, such as Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, both synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution frequencies correlate with expression levels. Here, we have tested the hypothesis that the correlation between amino acid substitution rates and expression is a by-product of selection for codon bias and translational efficiency in highly expressed genes. To this end, we have examined the correlation between protein evolutionary rates and expression in the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori, where the absence of selection on synonymous sites enables the two types of substitutions to be uncoupled. The results revealed a statistically significant negative correlation between expression levels and nonsynonymous substitutions in both H. pylori and E. coli. We also found that neighboring genes located on the same, but not on opposite strands, evolve at significantly more similar rates than random gene pairs, as expected by co-expression of genes located in the same operon. However, the two species differ in that synonymous substitutions show a strand-specific pattern in E. coli, whereas the weak similarity in synonymous substitutions for neighbors in H. pylori is independent of gene orientation. These results suggest a direct influence of expression levels on nonsynonymous substitution frequencies independent of codon bias and selective constraints on synonymous sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi H (1994) Synonymous codon usage in Drosophila melanogaster: natural selection and translational accuracy. Genetics 136:927–936
Akashi H (2003) Translational selection and yeast proteome evolution. Genetics 164:1291–1303
Akashi H, Gojobori T (2002) Metabolic efficiency and amino acid composition in the proteomes of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:3695–3700
Alm RA, Ling LS, Moir DT, King BL, Brown ED, Doig PC, Smith DR, Noonan B, Guild BC, deJonge BL, Carmel G, Tummino PJ, Caruso A, Uria-Nickelsen M, Mills DM, Ives C, Gibson R, Merberg D, Mills SD, Jiang Q, Taylor DE, Vovis GF, Trust TJ (1999) Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397:176–180
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Andersson SG, Kurland CG (1990) Codon preferences in free-living microorganisms. Microbiol Rev 54:198–210
Andersson SGE, Sharp PM (1996) Codon usage and base composition in Rickettsia prowazekii. J Mol Evol 42:525–536
Ball CA, Awad IA, Demeter J, Gollub J, Hebert JM, Hernandez-Boussard T, ** H, Matese JC, Nitzberg M, Wymore F, Zachariah ZK, Brown PO, Sherlock G (2005) The Stanford Microarray Database accommodates additional microarray platforms and data formats. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D580–582
Banerjee T, Basak S, Gupta SK, Ghosh TC (2004) Evolutionary forces in sha** the codon and amino acid usages in Blochmannia floridanus. J Biomol Struct Dyn 22:13–23
Bernstein JA, Khodursky AB, Lin PH, Lin-Chao S, Cohen SN (2002) Global analysis of mRNA decay and abundance in Escherichia coli at single-gene resolution using two-color fluorescent DNA microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9697–9702
Bhardwaj N, Lu H (2005) Correlation between gene expression profiles and protein-protein interactions within and across genomes. Bioinformatics 21:2730–2738
Bjellqvist B, Hughes GJ, Pasquali C, Paquet N, Ravier F, Sanchez J-C, Frutiger S, Hochstrasser DF (1993) The focusing positions of polypeptides in immobilized pH gradients can be predicted from their amino acid sequences. Electrophoresis 14:1023–1031
Blattner FR, Plunkett III G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Viodes J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF et al. (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453–1462
Bloom JD, Adami C (2003) Apparent dependence of protein evolutionary rate on number of interactions is linked to biases in protein-protein interactions data sets. BMC Evol Biol 3:21
Bloom JD, Adami C (2004) Evolutionary rate depends on number of protein-protein interactions independently of gene expression level: response. BMC Evol Biol 4:14
Butland G, Peregrin-Alvarez JM, Li J, Yang W, Yang X, Canadien V, Starostine A, Richards D, Beattie B, Krogan N, Davey M, Parkinson J, Greenblatt J, Emili A (2005) Interaction network containing conserved and essential protein complexes in Escherichia coli. Nature 433:531–537
Coghlan A, Wolfe KH (2000) Relationship of codon bias to mRNA concentration and protein length in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 16:1131–1145
Dong H, Nilsson L, Kurland CG (1996) Co-variation of tRNA abundance and codon usage in Escherichia coli at different growth rates. J Mol Biol 260:649–663
Dos Reis, Wernisch L, Saava R (2003) Unexpected correlations between gene expression and codon usage bias from microarray data for the whole Escherichia coli K-12 genome. Nucleic Acids Res 31:6976–6985
Duret L, Mouchiroud D (1999) Expression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4482–4487
Duret L, Mouchiroud D (2000) Determinants of substitution rates in mammalian genes: expression patterns affect selection intensity but not mutation rate. Mol Biol Evol 17:68–74
Drummond DA, Bloom JD, Adami C, Wilke CO, Arnold FH (2005) Why highly expressed proteins evolve slowly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14338–14343
Finlay BB, Falkow S (1997) Common themes in microbial pathogenicity revisited. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:136–169
Fraser HB, Hirsh AE, Steinmetz LM, Scharfe C, Feldman MW (2002) Evolutionary rate in the protein interaction network. Science 296:750–752
Fraser HB, Wall DP, Hirsh AE (2003) A simple dependence between protein evolution rate and the number of protein-protein interactions. BMC Evol Biol 3:11
Fraser HB, Hirsh AE (2004) Evolutionary rate depends on number of protein-protein interactions independently of gene expression level. BMC Evol Biol 4:13
Goetz RM, Fuglsang A (2005) Correlation of codon bias measures with mRNA levels: analysis of transcriptome data from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Acta 327:4–7
Goto S, Nishioka T, Kanehisa M (1998) LIGAND: chemical database for enzyme reactions. Bioinformatics 14:591–599
Herbeck JT, Wall DP, Wernegreen JJ (2003) Gene expression level influences amino acid usage, but not codon usage, in the tsetse fly endosymbiont Wigglesworthia. Microbiology 149:2585–2598
Herbeck JT, Wall DP (2005) Converging on a general model of protein evolution. Trends Biotechnol 23:485–487
Hirsh AE, Fraser HB (2001) Protein dispensability and rate of evolution. Nature 411:1046–1049
Hirsh AE (2003) Rate of evolution and gene dispensability—reply. Nature 421:497–498
Ikemura T (1981) Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol 146:1–21
Ikemura T (1982) Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. J Mol Biol 158:573–597
Ikemura T (1985) Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol 2:13–34
Jeong H, Tombor B, Albert R, Oltvai ZN, Barabasi AL (2000) The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 407:651–654
Jordan IK, Rogozin IB, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2002) Essential genes are more evolutionarily conserved than are nonessential genes in bacteria. Genome Res 12:962–968
Jordan IK, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2003) No simple dependence between protein evolution rate and the number of protein-protein interactions: only the most prolific interactors tend to evolve slowly. BMC Evol Biol 3:1
Jordan IK, Marino-Ramirez L, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2004) Conservation and coevolution in the scale-free human gene coexpression network. Mol Biol Evol 21:2058–2070
Kanaya S, Yamada Y, Kudo Y, Ikemura T (1999) Studies of codon usage and tRNA genes of 18 unicellular organisms and quantification of Bacillus subtilis tRNAs: gene expression level and species-specific diversity of codon usage based on multivariate analysis. Gene 238:143–155
Kavermann H, Burns BP, Angermuller K, Odenbreit S, Fischer W, Haas R (2003) Identification and characterization of Helicobacter pylori genes essential for gastric colonization. J Exp Med 197:813–822
Klasson L, Andersson SGE (2004) Evolution of minimal-gene-sets in host-dependent bacteria. Trends Microbiol 12:37–43
Koonin EV (2000) How many genes can make a cell: the minimal-gene-set concept. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 1:99–116
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580
Krylov DM, Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV (2003) Gene loss, protein sequence divergence, gene dispensability, expression level, and interactivity are correlated in eukaryotic evolution. Genome Res 13:2229–22235
Kurland CG (1987) Strategies for efficiency and accuracy in gene expression. 1. The major codon preference: a growth optimization strategy. Trends Biochem Sci 12:126–128
Lafay B, Atherton JC, Sharp PM (2000) Absence of translationally selected synonymous codon usage bias in Helicobacter pylori. Microbiology 146:851–860
Li W-H, Wu CI, Luo CC (1985) A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitutions considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide codon change. Mol Biol Evol 2:150–174
Lobry JR, Gautier C (1994) Hydrophobicity, expressivity and aromaticity are the major trends of amino-acid usage in 999 Escherichia coli chromosome-encoded genes. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3174–3180
Lu H, Zhao WM, Zheng Y, Wang H, Qi M, Yu XP (2005) Analysis of synonymous codon usage bias in Chlamydia. Acta Biochem Biophys Sin 37:1–10
Maniloff J (1996) The minimal cell genome: on being the right size. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10004–10006
Marais G, Domazet-Loso T, Tautz D, Charlesworth B (2004) Correlated evolution of synonymous and nonsynonymous sites in Drosophila. J Mol Evol 59:771–779
Marshall B, Warren R (1984) Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 8390:1311–1315
Moran NA, Dunbar HE, Wilcox JL (2005) Regulation of transcription in a reduced bacterial genome: Nutrient-provisioning genes of obligate symbiont Buchnera aphidicola. J Bacteriol 187:4229–4237
Mouchiroud D, Gautier C, Bernardi G (1995) Frequencies of synonymous substitutions in mammals are gene-specific and correlated with frequencies of nonsynonymous substitutions. J Mol Evol 40:107–113
Mushegian AR, Kooonin EV (1996) A minimal gene set for cellular life derived by comparison of complete bacterial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10268–10273
Mushegian AR (1999) The minimal genome concept. Curr Opin Genet Dev 9:709–714
Newman MEJ (2001) Scientific collaboration networks. II. Shortest paths, weighted networks, and centrality. Phys Rev E 64:016132
Nuzhdin SV, Wayne ML, Harmon KL, McIntyre LM (2004) Common pattern of evolution of gene expression level and protein sequence in Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 21:1308–1317
Pal C, Papp B, Hurst LD (2001) Highly expressed genes in yeast evolve slowly. Genetics 158:927–931
Pal C, Papp B, Hurst LD (2003) Genomic function: Rate of evolution and gene dispensability. Nature 421:496–497
Papp B, Pal C, Hurst LD (2004) Metabolic network analysis of the causes and evolution of enzyme dispensability in yeast. Nature 429:661–664
Peek RM, Blaser MJ (2002) Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Camcer 2:28–37
Pleissner K-P, Eifert T, Buettner S, Schmidt F, Boehme M, Meyer TF, Kaufmann SHE, Jungblut PR (2004) Web-accessible proteome databases for microbial research. Proteomics 4:1305–1313
Rain JC, Selig L, De Reuse H, Battaglia V, Reverdy C, Simon S, Lenzen G, Petel F, Wojcik J, Schachter V, Chemama Y, Labigne A, Legrain P (2001) The protein–protein interaction map of Helicobacter pylori. Nature 409:211–215
Rison SCG, Teichmann SA, Thorton JM (2002) Homology, pathway distance and chromosomal localization of the small molecule metabolism enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 318:911–932
Rispe C, Delmotte F, van Ham RCHJ, Moya A (2004) Mutational and selective pressures on codon and amino acid usage in Buchnera, endosymbiotic bacteria of aphids. Genome Res 14:44–53
Rocha EP, Danchin A (2004) An analysis of determinants of amino acids substitution rates in bacterial proteins. Mol Biol Evol 21:108–116
Salama NR, Shepherd B, Falkow S (2004) Global transposon mutagenesis and essential gene analysis of Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol 186:7926–7935
Schaber J, Rispe C, Wernegree J, Burness A, Delmotte F, Silva FJ, Moya A (2005) Gene expression levels influence amino acid usage and evolutionary rates in endosymbiotic bacteria. Gene 352:109–117
Sharp PM (1991) Determinants of DNA sequence divergence between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: codon usage, map position and concerted evolution. J Mol Evol 33:23–33
Sharp PM, Bailes E, Grocook RJ, Peden JF, Sockett RE (2005) Variation in the strength of selected codon usage bias among genes. Nucl Acids Res 33:1141–1153
Sharp PM, Li W-H (1987) The codon adaptation index—a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res 15:1281–1295
Smith MJ, Smith NH, O’Rourke M, Spratt BG (1993) How clonal are bacteria? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4384–4388
Suerbaum S, Michetti P (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med 347:1175–1186
Suerbaum S, Smith JM, Bapumia K, Morelli G, Smith NH, Kunstmann E, Dyrek I, Achtman M (1998) Free recombination within Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12619–12624
Teichmann S (2002) The constraints protein-protein interactions place on sequence divergence. J Mol Biol 324:399–407
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tomb JF, White O, Kerlavage AR, Clayton RA, Sutton GG, Fleischmann RD, Ketchum KA, Klenk HP, Gill S, Dougherty BA, Nelson K, Quackenbush J, Zhou L, Kirkness EF, Peterson S, Loftus B, Richardson D, Dodson R, Khalak HG, Glodek A, McKenney K, Fitzegerald LM, Lee N, Adams MD, Hickey EK, Berg DE, Gocayne JD, Utterback TR, Peterson JD, Kelley JM, Cotton MD, Weidman JM, Fujii C, Bowman C, Watthey L, Wallin E, Hayes WS, Borodovsky M, Karp PD, Smith HO, Fraser CM, Venter JC (1997) The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 388:539–547
Wall DP, Hirsh AE, Fraser HB, Kumm J, Giaever G, Eisen MB, Feldman MW. (2005) Functional genomic analysis of the rates of protein evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5483–5488
Wei Y, Lee JM, Richmond C, Blattner FR, Rafalski JA, LaRossa RA (2001) High-density microarray-mediated gene expression profiling of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183:545–556
Wilcox JL, Dunbar HE, Wolfinger RD, Moran NA (2003) Consequences of reductive evolution for gene expression in an obligate endosymbiont. Mol Microbiol 48:1491–1500
Williams EJB, Hurst LC (2000) The proteins of linked genes evolve at similar rates. Nature 407:900–903
Yang J, Gu Z, Li WH (2003) Rate of protein evolution versus fitness effect of gene deletion. Mol Biol Evol 20:772–774
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2000) Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 17:32–43
Zhang J, He X (2005) Significant impact of protein dispensability on the instantaneous rate of protein evolution. Mol Biol Evol 22:1147–1155
Zhang L, Li WH (2004) Mammalian house-kee** genes evolve more slowly than tissue-specific genes. Mol Biol Evol 21:236–239
Acknowledgments
We thank Eduardo P. Rocha for kindly providing data on E. coli/S. typhimarium/Y. pestis orthologs. This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR), the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (KAW), and the European Union (EU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Nicolas Galtier]
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sällström, B., Arnaout, R.A., Davids, W. et al. Protein Evolutionary Rates Correlate with Expression Independently of Synonymous Substitutions in Helicobacter pylori . J Mol Evol 62, 600–614 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0104-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0104-5