Abstract
Objective: A new formulation of propofol 6% in Lipofundin MCT/LCT 10% (propofol 6% SAZN) has been developed in order to reduce the fat, emulsifier and volume load that is given during prolonged infusions of propofol. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety characteristics of propofol 6% SAZN were investigated during a short-term infusion and compared with the commercially available product propofol 1% in Intralipid 10% (Diprivan-10) and propofol 1% in Lipofundin MCT/LCT 10% (propofol 1% SAZN).
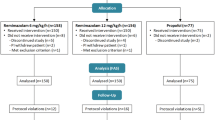
Methods: In a randomised double-blind study, 24 male patients received a 5-h infusion of propofol at the rate of 1 mg/kg/h for sedation in the immediate postoperative period following coronary artery bypass surgery.
Results: The average pharmacokinetic parameter estimates of clearance (Cl), volume of distribution at steady state (Vd,ss), elimination half-life (t 1/2,β) and distribution half-life (t 1/2,α) observed in the three groups were 28 ± 1.1 ml/kg/min, 1.8 ± 0.12 l/kg, 94 ± 4.1 min and 3.1 ± 0.26 min, respectively (mean ± SEM, n=24) and no significant differences were noted between the three formulations (P > 0.05). In one patient receiving propofol 6% SAZN, in two patients receiving propofol 1% SAZN and in three patients receiving Diprivan-10, the level of sedation was inadequate and additional sedative medication had to be given. In all other 18 patients, the level of sedation was adequate. The mean propofol concentration in these six inadequately sedated patients was lower than the adequately sedated patients (P=0.015). The serum triglyceride concentrations were not significantly different between the groups studied. No adverse events occurred in any of the patients.
Conclusions: The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety characteristics of propofol 6% SAZN are in good agreement with those of the 1% formulations. Propofol 6% SAZN therefore provides a useful alternative to the commercially available 1% formulation for short-term sedation in the intensive care unit. Expected advantages in long-term sedation of the 6% over 1% formulation are the subject of an ongoing study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 June 1999 / Accepted in revised form: 23 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knibbe, C., Aarts, L., Kuks, P. et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol 6% SAZN versus propofol 1% SAZN and Diprivan-10 for short-term sedation following coronary artery bypass surgery. E J Clin Pharmacol 56, 89–95 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050726
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050726